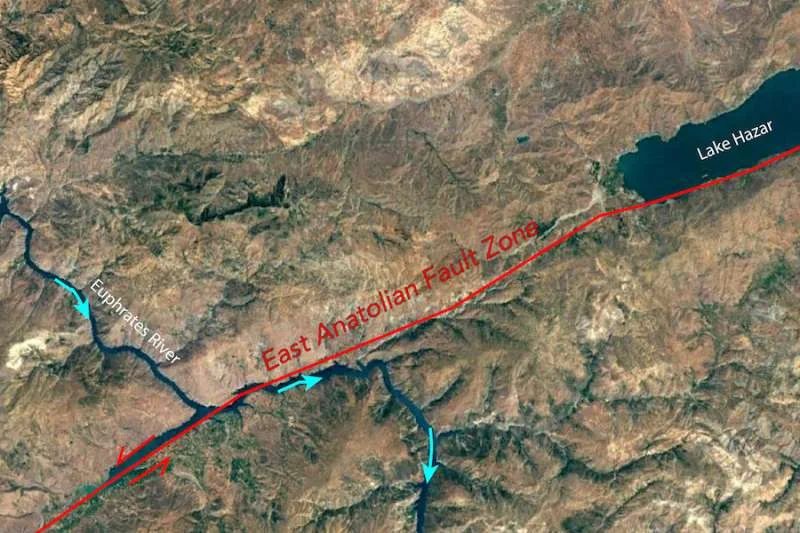
An international team led by the University of Minnesota Twin Cities has, for the first time, accurately determined the age and formation process of the East Anatolian Fault, which stretches from east to south of Turkey and is involved in the formation of the Anatolian tectonic structure. number plate.
The fault zone was the site of two devastating earthquakes that hit Turkey and Syria in February 2023. While the researchers’ findings don’t help predict the timing or size of earthquakes, they may help geologists make decisions about infrastructure, allowing them to learn more about how long the area has been seismically active and how powerful earthquakes have shaped the landscape over time. and building layout. Their article was published geology, A peer-reviewed academic journal covering the earth sciences, published by the Geological Society of America.
The faults we see on the Earth’s surface are cracks caused by the movement of the planet’s massive tectonic plates. These movements cause stress to build up, and the release of this stress causes earthquakes felt by people at the surface.
“There are many tectonic plates on Earth,” said Donna Whitney, lead author of the paper, and Donna Whitney, McKnight University Emeritus Professor in the NG Winchell School of Earth and Environmental Sciences at the University of Minnesota. “They changed shape, size and position over time, but we rarely see the same shape. The Anatolian plate was formed relatively recently in geological terms, so it is easier for us to study the geology and draw conclusions about the processes that formed it. About the age of the Anatolian Plate and the East Anatolian Fault. There’s been a lot of discussion, but we’ve been able to show with our data that they probably formed five million years ago.”
The researchers’ findings stemmed from a project called Continental Dynamics-Central Anatolian Tectonics (CD-CAT) initiated by Whitney.
Whitney and his team began studying the Anatolian Plate in 2011 because they found evidence that the center of the plate has been bent for tens of millions of years, a process that usually only occurs at the edges of tectonic plates. Then, five million years ago, radical changes occurred. Since then, nearly all tectonic movements have concentrated along two major earthquake-producing faults: the North Anatolian Fault and the East Anatolian Fault.
By dating the cooling times of rocks in the Eastern Anatolian Rift and examining seismic data collected during the project, CD-CAT researchers determined the structure of the continents and the mantle in the region, confirming that this five-million-year-old point is prominent. Formation of the Anatolian Plate.
“Knowing the seismic history of this area is really important for predicting disasters related to how people interact with the landscape,” Whitney said. Said. “We can’t predict that there will be an X-magnitude earthquake on that fault at any given time, but we can get an idea of the fault’s past activity, how large events were, and how large the fault movement affected the landscape. We need to understand these structures because people live next to them and have infrastructure. ” Source