Did you know that the file ‘/ etc / hosts‘is also present in Windows? This file, which many people associate with Linux and Unix and Unix-like operating systems, is actually an old travel companion that allows you to map hostnames to IP addresses.
The hosts file or ‘/ etc / hosts’ (although this is not the only location that can be found because it depends on the operating system) was originally named HOSTS.TXT and was originally made available through the Stanford Research file share. ARPANET Members Institute, the first computer network created on behalf of the United States Department of Defense. Basically, what it contained and still contains are host names with their domain name IP addresses.
Due to its constant growth, the network became too large for manual maintenance, so between 1983 and 1984, the Domain Name System (DNS) seemed to provide a framework for immediate and dynamic hostname resolution.
Although DNS has greatly reduced the use of the hosts file, it is still useful for tasks such as redirect local domains to test sites, block internet content and prevent contact with activation servers in certain application hacking processes.
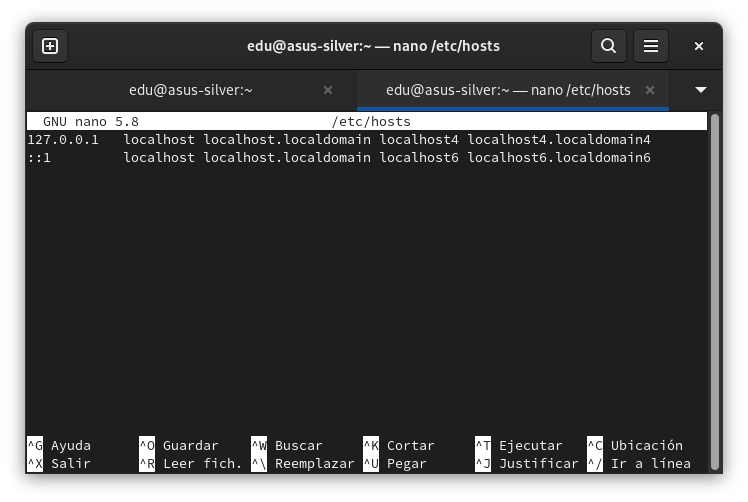
The ‘/ etc / hosts’ file on Linux
However, the hosts file also can be a vector of attack for malware. Under these circumstances, malware could modify the hosts file to redirect traffic to servers that host malicious or unwanted content. For example, it is possible that an infected user will eventually see strange ads or mine some cryptocurrency through their web browser, and these scenarios are probably more likely than seeing their computer unusable (although this can never be ruled out). Malicious actors often prefer to keep their malware unnoticed to avoid detection.
Despite its inconvenience, the hosts file can be used for configuration in addition to what has already been mentioned small test environment within a local area network (LAN). This is a scenario that we will cover in this post to learn how to configure a hosts file in Windows in a basic way.
Where is the ‘/ etc / hosts’ file located in Windows?
Without further delay, the path to follow in Windows Explorer is as follows: “My Computer”> C:> Windows> System32> Drivers> etc.> Hosts (the last element of the path is the file).
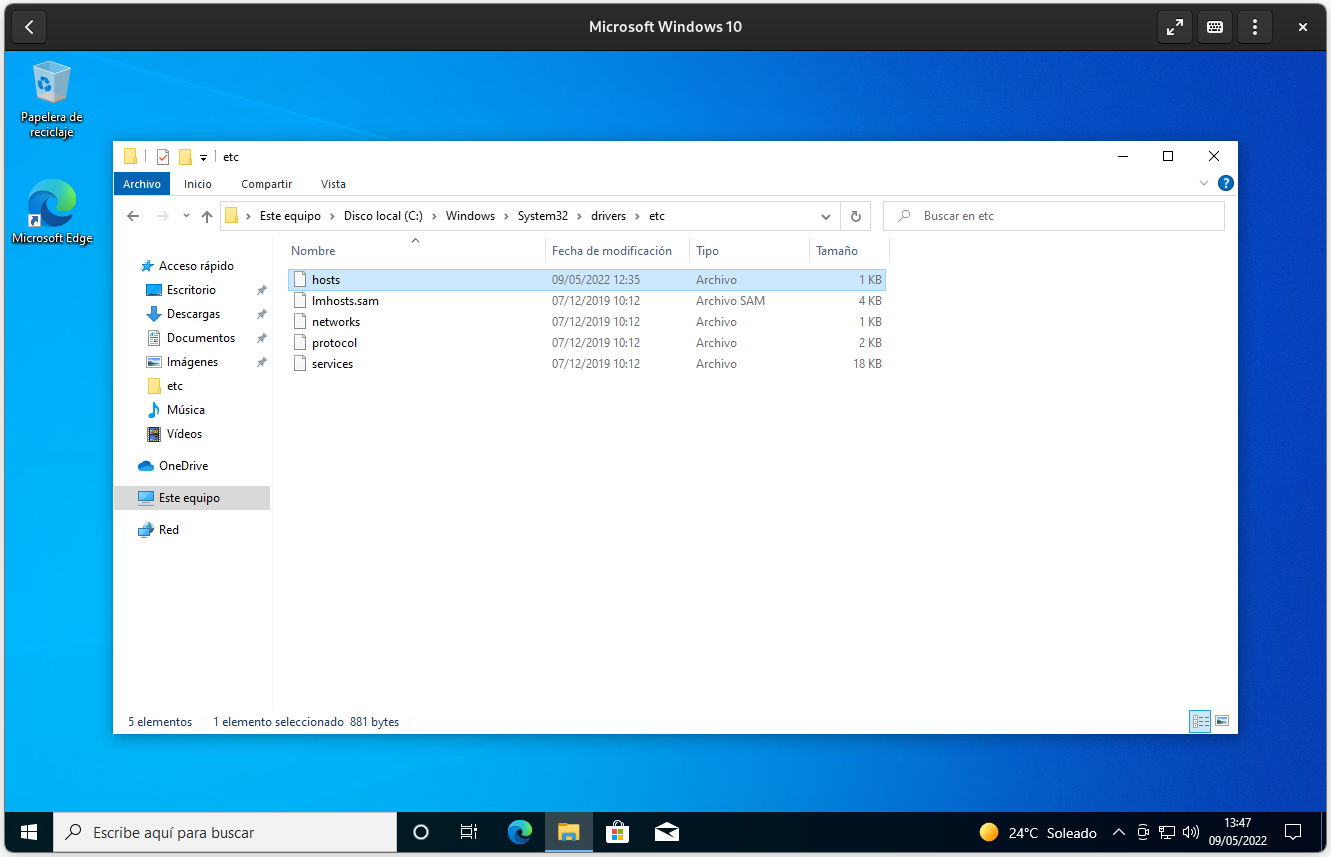
If you want, the path without the file is as follows copy and paste your location in the file explorer (you must first press’Ctrl + L‘):
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
And this is it the specific location of the ‘/ etc / hosts’ file in Windows (note that Microsoft does not care about the slashes ‘/’ and ‘\’):
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
How to edit a hosts file in Windows
Successive versions of Windows have introduced restrictions on critical system directories to prevent the user from modifying or deleting them (at least with the default operating system configuration). If you want to modify any content in System32, you must use a system administrator account because the normal one, although defined as an administrator by default, does not have write permission.
To edit a hosts file in Windows, you must first open Notepad as an administrator. To do this, open the System Start menu, type “Notepad” into the search engine, right-click on the application item you want to open and select “Run as administrator”. The system asks the user if he wants the application to make changes to the device, to which he must, of course, answer yes.
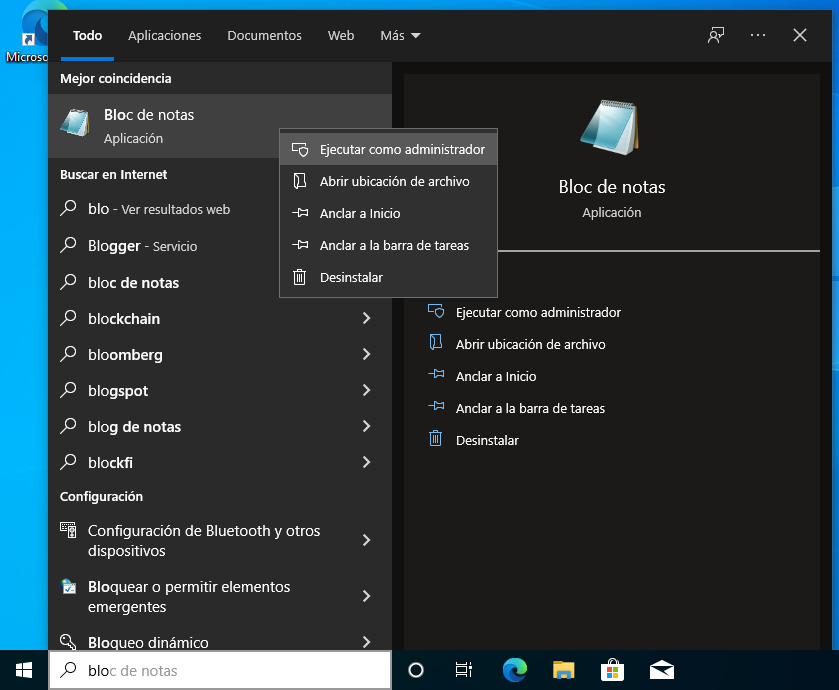
Once you open Notepad as an administrator, go to the menu File> Open To continue opening, it is worth redundancy, Windows hosts the files.
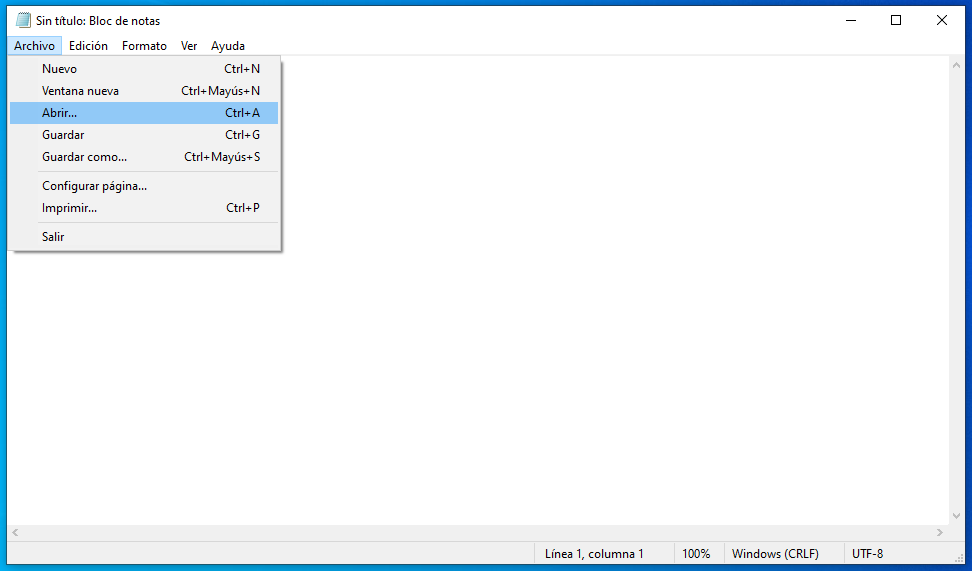
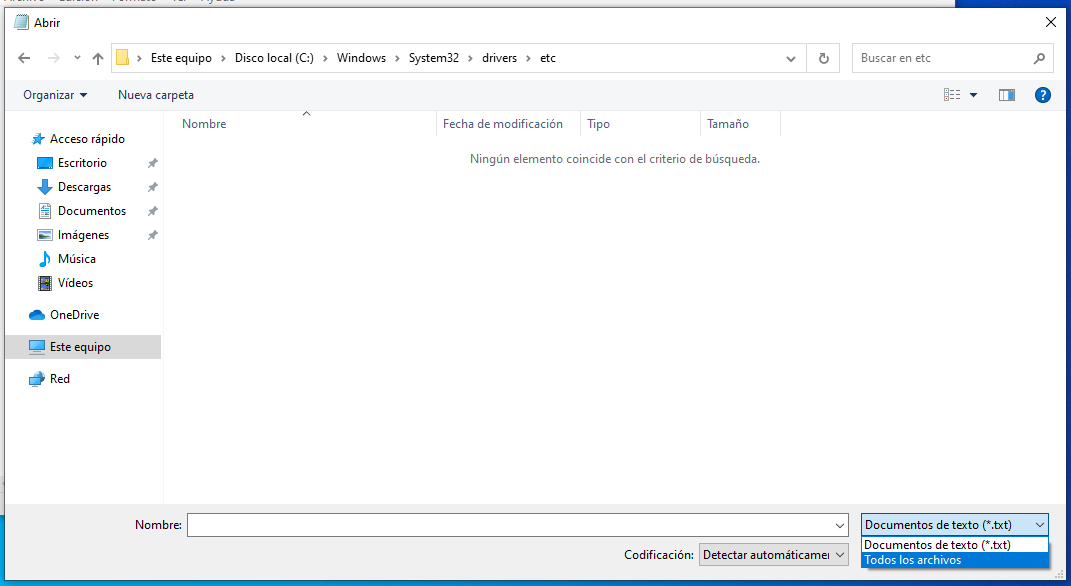
Remember that the way to find the hosts file in Windows is “My Computer”> C:> Windows> System32> drivers> etc.. However, when you get there, you will find that the folder is obviously empty, because Notepad cannot find any files with the extension ‘.txt’. This is solved by selecting “All files”In the drop-down list in the lower right corner of the dialog.
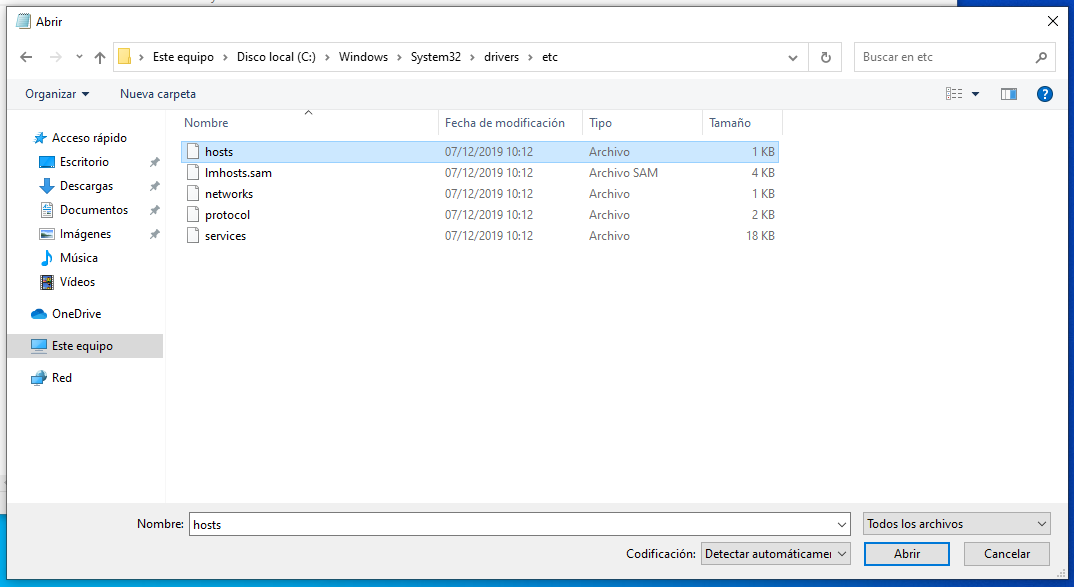
Alternatively, once the “Open” dialog opens in Notepad, you can press “ctrl + L” and then copy and paste the following into the address path. This will open the file directly:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
Once the file is opened hosts in WindowsIn the application it looks like this:
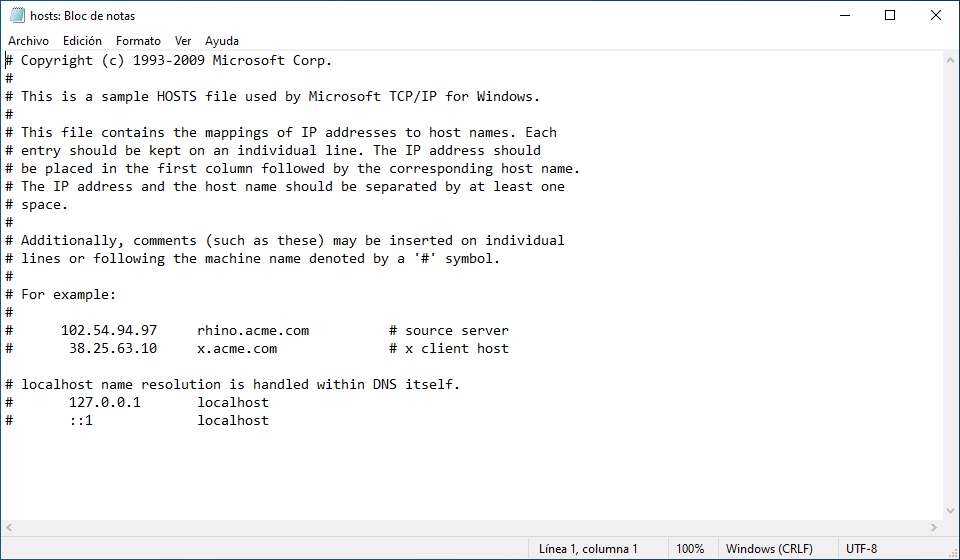
In this case, we have an instance of Windows 10 running on the GNOME Boxes virtual machine, so we introduced Host IP next to hostname (asus-silver). All lines that have a hash (#) in front of them are comments and are therefore ignored at the configuration level, but can be useful for describing what a given file or line does.
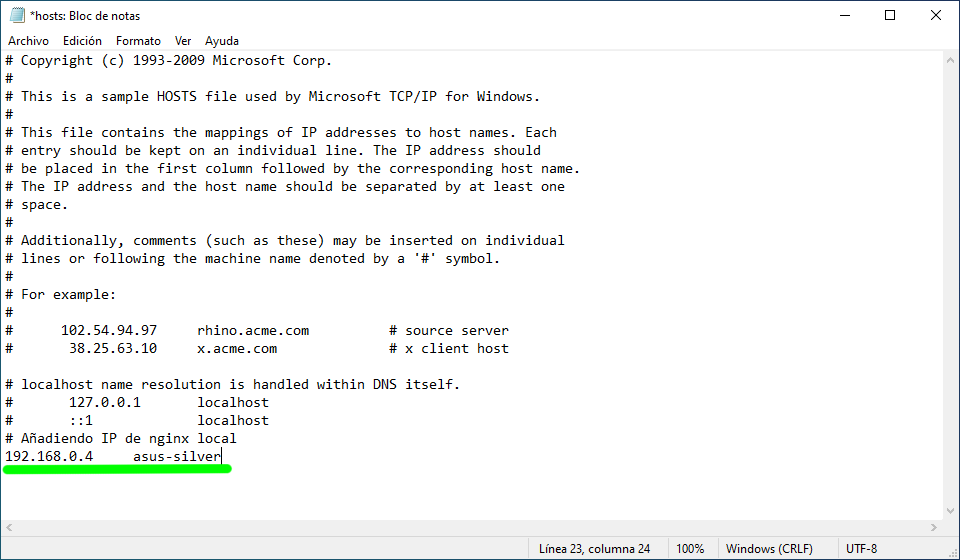
After making the appropriate edits to the file, the file is saved as usual, go to the File menu, and click Save.
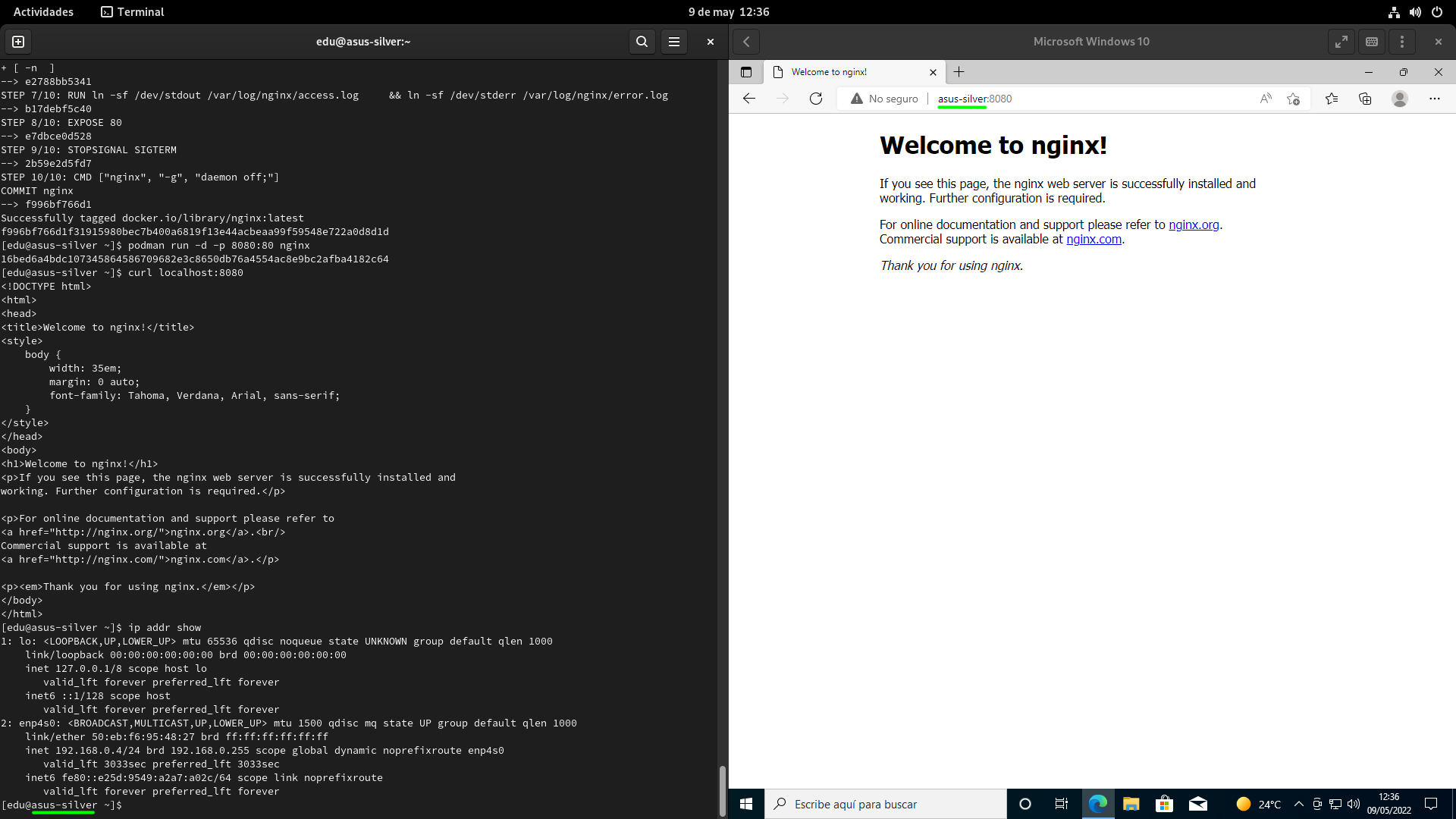
With the changes made to the file, we tried to access the HTTP server (nginx) running on the host computer via the Docker container with Podman. Instead of an IP address, which is a number that can be difficult to remember, we entered the device nameand from what you can see in the following figure, the Windows hosts file performs its role properly in displaying the content served by the host computer through the HTTP server.
Location of the hosts file on other operating systems
The hosts file performs essentially the same function on all operating systems, so we will mention its location in various examples, in which we will mention various operating systems that may or may not be popular. Please note that we have not taken into account if the user has permission, albeit indirectly, to modify it.
location in Android:
/etc/hosts # Que es un enlace simbólico hacia /system/etc/hosts
location in iOS Y Mac operating system:
/etc/hosts # Que es un enlace simbólico hacia /private/etc/hosts
location in haikus:
/system/settings/network/hosts
location in Linux, UnixUnix and POSIX:
/etc/hosts
conclusion
Although its use has declined over the decades, the hosts file is still useful for certain contexts, and as we have seen throughout this article, not only for creating a small test environment over a local area network, but also for defense purposes or limited access to certain resources.
Of course, we remember that he must be handled very carefully. As a basic advice, we recommend that you do not enter any public IPs unless you are completely clear about what you are doing. If you want to play with it, it is best to enter IP addresses from the local network.
