Google has announced plans to roll out advanced cellular security features, positioning Android as a leading mobile operating system to implement these measures. Advanced security features will be available to both consumers and businesses.
Key features introduced in Android 14
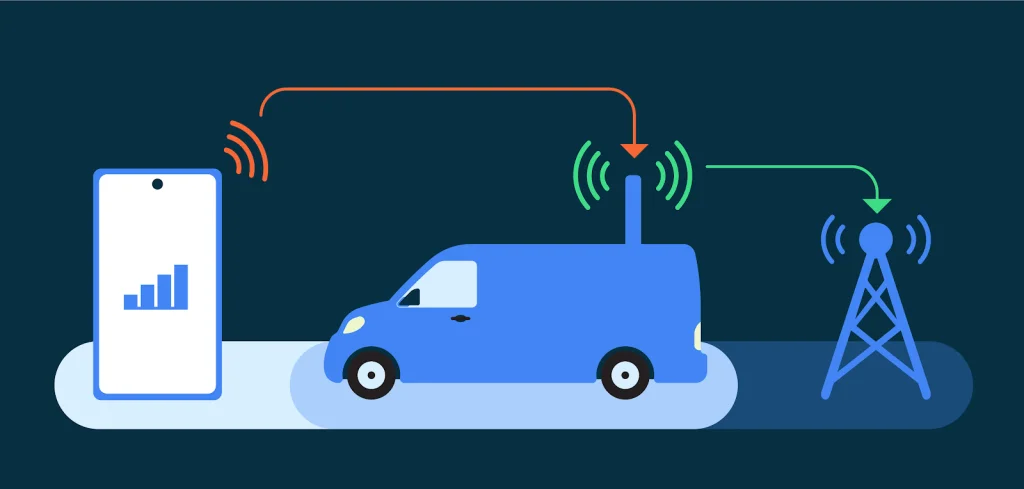
- Disable 2G support: Android 14 introduces an important feature that allows IT administrators to disable 2G support on managed devices. This measure is important because of the inherent vulnerability associated with 2G networks. Disabling 2G support reduces the risk of potential attacks and migration to less secure networks.
- Disable cellular with zero encryption: Android 14 also fixes a vulnerability caused by cellular connection with zero encryption. IP-based user traffic is encrypted end-to-end, while circuit-switched voice data and SMS remain exposed. Android 14 offers the user the ability to disable connections, increase the privacy of communication and protect confidential information with zero modem-level encryption.
Improve Android network security
Android’s security model assumes a hostile network environment to protect users from network threats. This approach relies on end-to-end encryption (E2EE) for all network traffic to resist packet injection, spoofing, and eavesdropping.
Mobile phone security issues
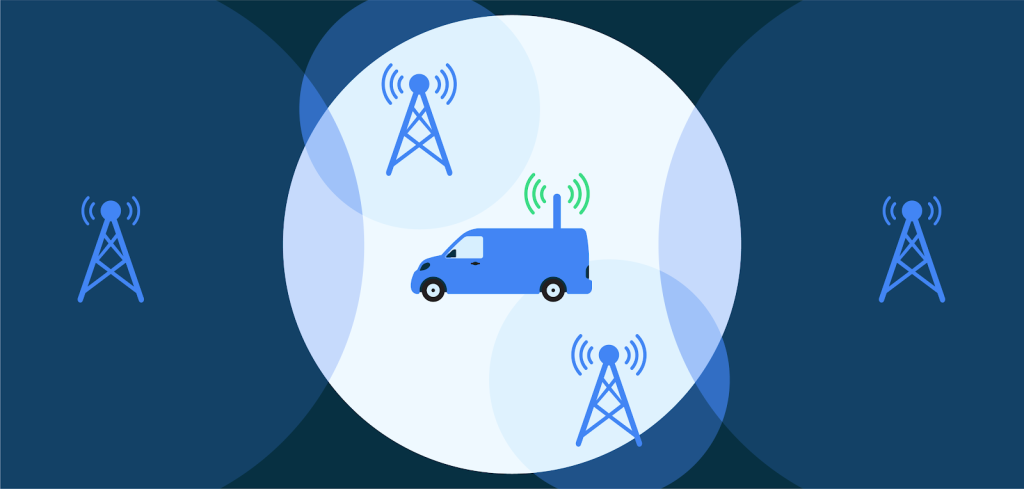
Cellular networks present unique security issues due to possible exploitation by rogue base stations (FBSs) and Stingrays. Android is aware of these risks and is actively involved in improving cellular security.
Addressing internal 2G security risks
2G networks created in 1991 lack the advanced security measures seen in later generations. The lack of mutual authentication in the Global Mobile Communications System (GSM) standard makes 2G vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks.
Legacy 2G network security, combined with the ability to force downgrades, leaves users significantly exposed to threats like FBS, IMSI interceptors, and Stingrays.
Enterprise-grade protection
Businesses using smartphones and tablets need reliable protection for sensitive data.
- Android Enterprise offers comprehensive connectivity security controls, including turning off Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and USB data transfer.
- Android 14 improves corporate security by allowing IT administrators to prevent devices from switching to 2G connections.
The fight against zero passwords
Android 14 removes the security risks associated with zero encryption connections on cellular networks. While IP traffic is E2EE, voice and SMS data can be accessed thanks to cellular level encryption.
Android 14 allows users to turn off support for zero-encryption connections, which provides privacy for devices with the latest radio hardware abstraction layer.
Collaboration for cellular security
Google is actively involved in the development of mobile security standards through partnerships with industry organizations such as the GSMA Fraud and Security Group and the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). Efforts are underway to modernize identity, trust and access control techniques to strengthen the security of telecommunications networks.
In future Android versions, Google plans to introduce additional security features to combat cellular threats. They invite cooperation with partners and standards organizations to jointly improve the security of telecommunications networks and overcome FBS threats. Source