The chip giant introduced Thunderbolt 5, an important renewal of its well-known cable connectivity standard, which takes us directly to a new generation and which, as we will see in this article, represents a big improvement over Thunderbolt 4, which is the current standard.
In case someone gets lost, I think it’s a good place to start by remembering what exactly is Intel Thunderboltbecause it will give us the foundation we need for everyone to understand how it differs and what improvements the new standard will bring compared to Thunderbolt 4.
It goes o.a high-speed connector that appears as an all-in-one solution. high performance. This all-in-one connector concept is due to the fact that we can use the Thunderbolt connector as a traditional USB Type-C to transfer data at high speed, as well as to power accessories and charge devices, and even as a connector for outputting images from monitors. high definition.
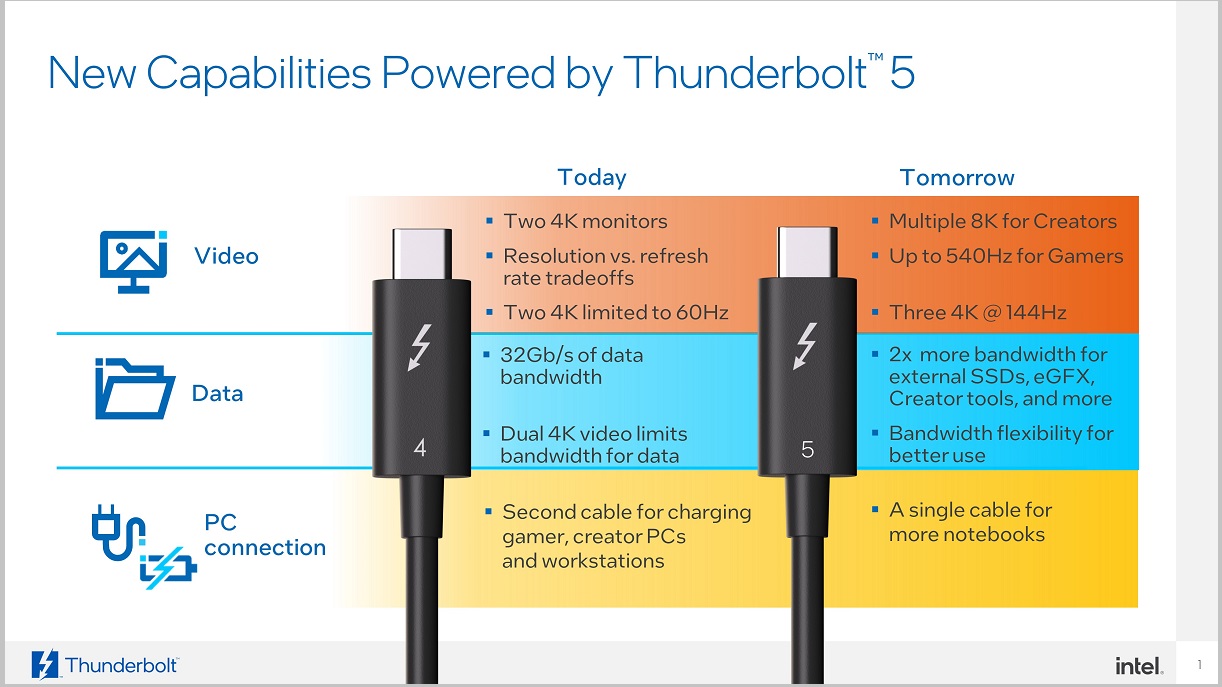
Take a look at the attached image to see what we can do with a single Thunderbolt 4 connector. Compared to the USB 4 connector that takes the base of the Intel standard, we see that many valuable features and characteristics of Thunderboltincluding the necessary tests and certifications to guarantee overall stability, They are optional on USB 4with all that it can mean for the end user.
In its early days, Thunderbolt came to the market as an elitist solution far from the average user, but that has completely changed. This standard is compatible with a wide range of operating systems, including everything from Linux to Windows, Chrome OS and macOS, and its realization has increased immensely thanks to its democratization and inclusion in equipment with a price below 400 euros.
Thunderbolt 5 vs Thunderbolt 4

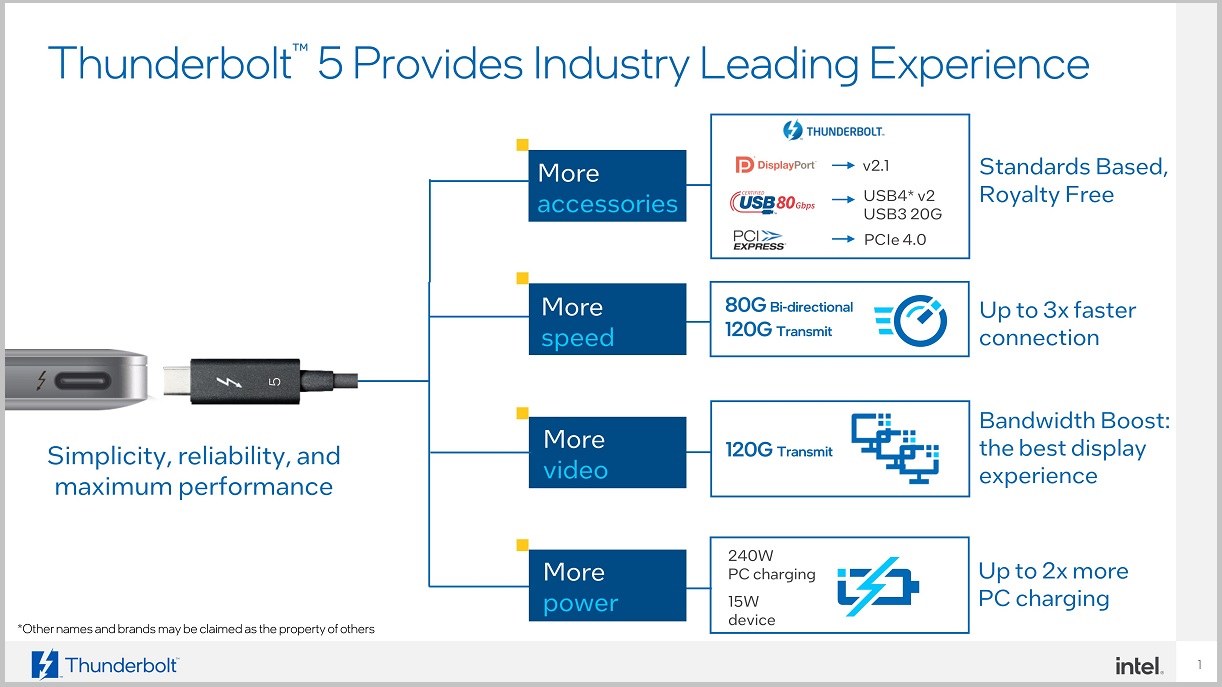
With the new standard, Intel managed to multiply the maximum bandwidth in one direction by three, going from 40 Gbps to 120 Gbps in transit or 80 Gbps in two directions. To give you a more realistic idea of the numbers we’re dealing with, this is the equivalent of bandwidth 15 GB/s, a figure that is the chip giant’s response to the growing demands and needs of professionals, gamers and content creators.
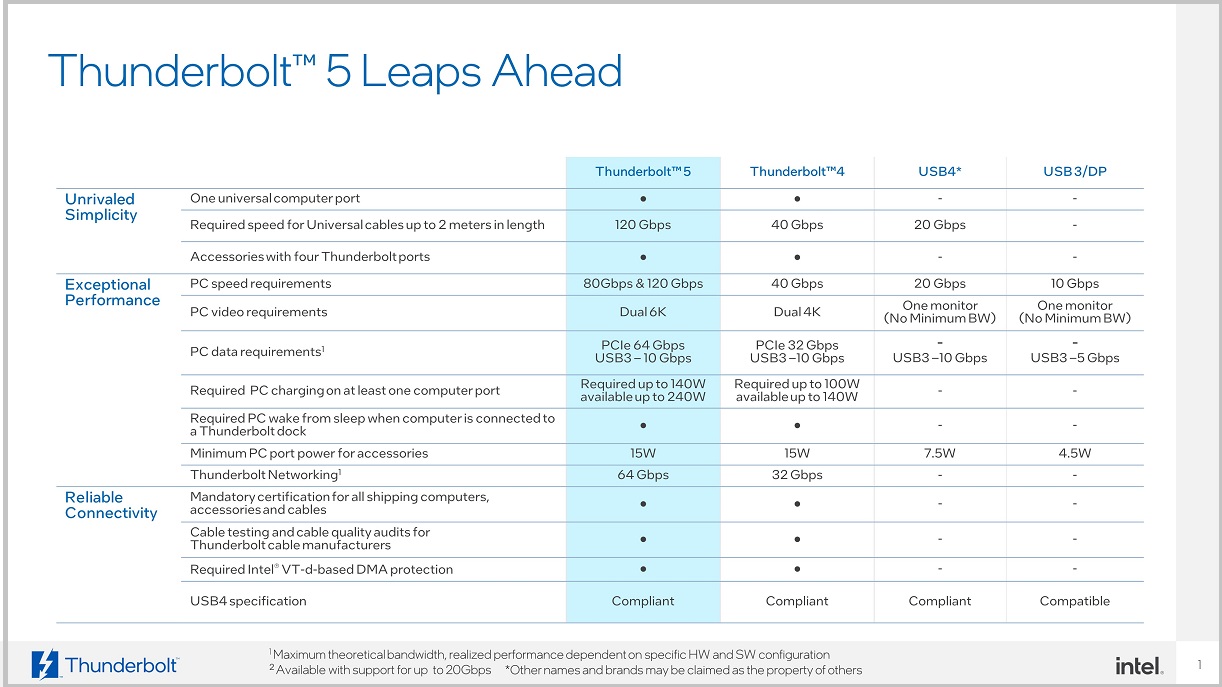
The possibilities offered by a connector like Thunderbolt 5 are truly impressive. You can see in the second picture direct comparison between this new standard and Thunderbolt 4, the differences are very significant. For example, with the new Intel connector we can:
- Use multiple 8K monitors.
- Supports monitors with a refresh rate of up to 540 Hz.
- It supports up to three 4K monitors with a refresh rate of 144 Hz.
- Double your bandwidth when using external storage drives and graphics cards.
- Its greater bandwidth makes it a more versatile connector.
- We can charge devices with a power of 15 watts and computers with a maximum of 240 watts, which means up to twice the charging power.
- A single cable allows us to do more things.
If we compare it with DisplayPort 2.1next-generation standard for image output, we see that Thunderbolt 5 offers double the bandwidthwhich is also important because it allows us to have a much more complete picture of the true potential that this new Intel standard offers.
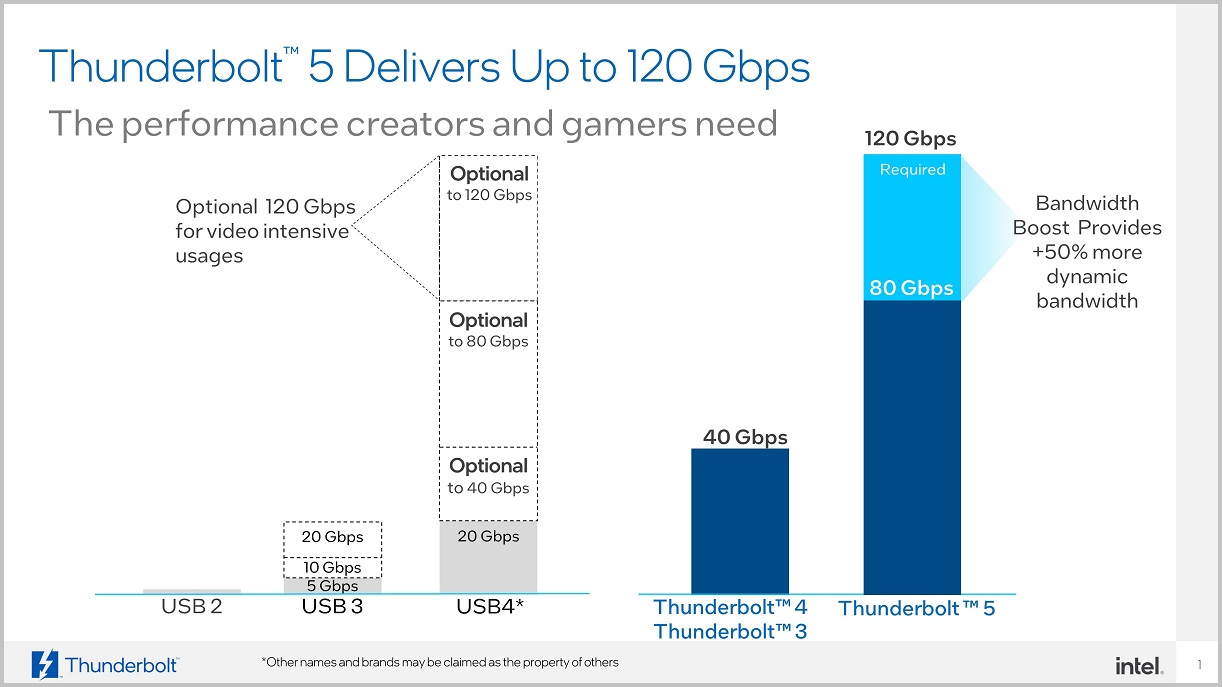
All those features They are mandatory in the Thunderbolt 5 standard, and this is exactly what sets this connector apart from USB 4 v2, as we can see in the second image. We must also remember everything I told you about stability tests and certifications, which are an important guarantee for this type of connector and which are always present in Intel solutions.
We said the Thunderbolt 5 connector could offer up to 120Gbps streaming bandwidth and up to 80Gbps bi-directional bandwidth, but many of our readers are probably wondering. What exactly does that mean.
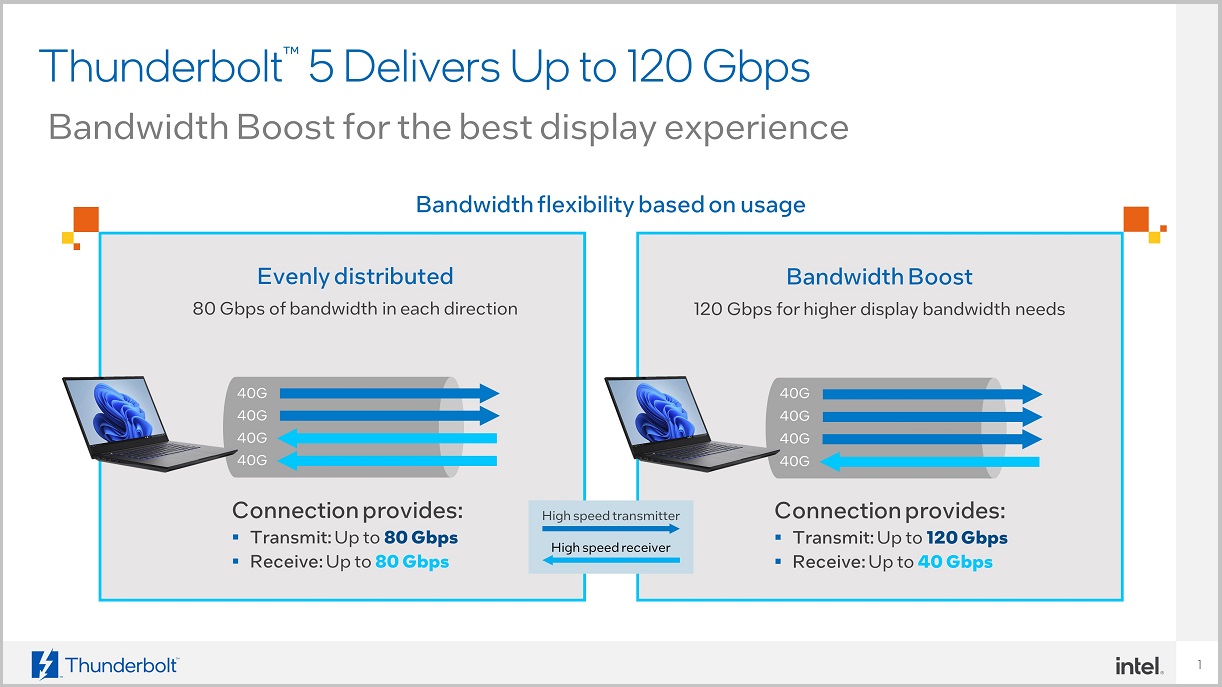
It is very easy to explain, look at the attached picture as you can see when this connector works bi-directionally, it is able to transmit and receive data at max. 80 Gbps in both directions, while with extended transmission bandwidth mode, it is able to transmit at 120 Gbps and receive data at 40 Gbps. In both cases, the total is the same, 160 Gbps, but it is managed and used differently.
To ensure this high level of performance and good signal stability Intel used PAM-3 (“Three-level Pulse Amplitude Modulation”), an advanced signaling technology that allows working with a larger amount of data per clock, and which uses current technologies at the level of printed circuit boards, connectors and passive cables up to one meter in length. The chip giant also confirmed the use of a new driver, known as Barlow Ridge.
Thunderbolt 5 is a step forward, but it doesn’t forget the past
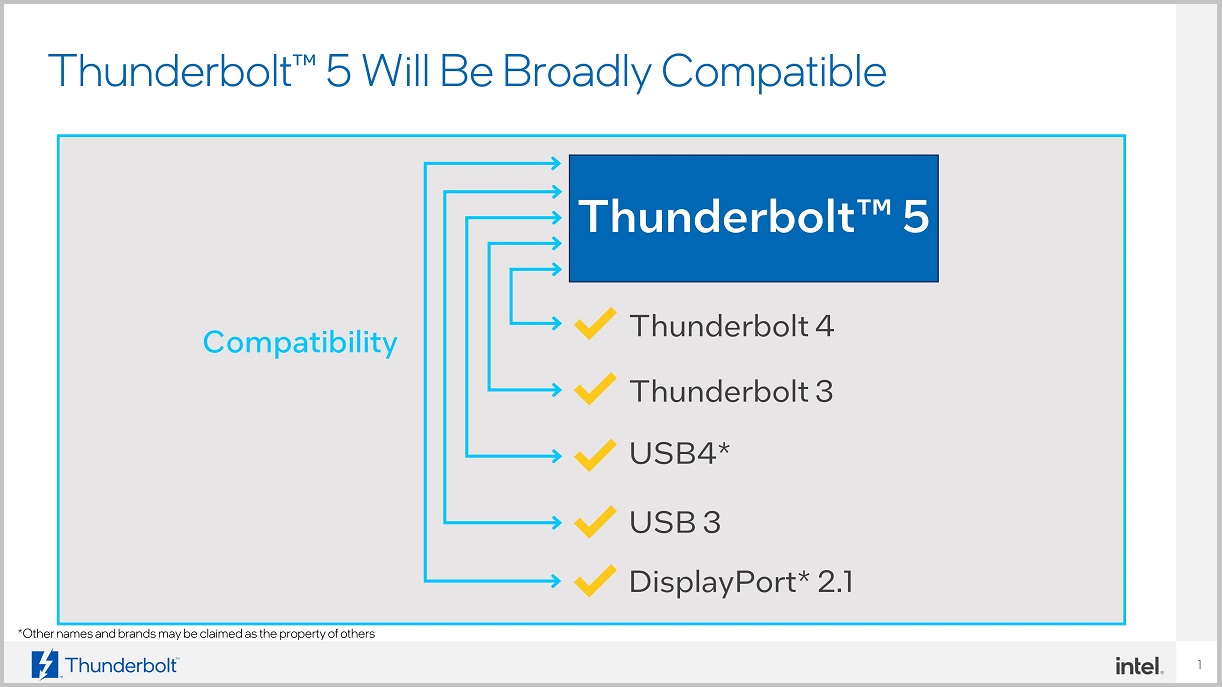
As you might expect, Thunderbolt 5 will be fully backwards compatible with USB 3, USB 4, Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 standards and will also be compatible with DisplayPort 2.1. This represents a very important value, no doubt about it.
It is also compatible with a wide range of devices and solutions, including docks, external graphics cards and accelerators, storage drives and more, and will offer Fully plug and play operationThis means plug and play without the need for complex configurations.
In terms of Intel’s identification and branding kept the focus of the current generation so as not to complicate things for the consumer. The logo remains the same, the lightning bolt arrow, and the design of both the port and cable remain unchanged, as you can see in the attached image.
When will Thunderbolt 5 be available?
Intel has confirmed that all technical assets will be released globally In the fourth quarter of this year and that they will be available to developers from that date. That means we’re only a few months away.
The first device with a Thunderbolt 5 connector and accessories compatible with this standard They will start arriving in 2024, although Intel has confirmed that it has already done first demonstrations with prototypes (both notebooks and docks).






















