Sand dunes reveal atmospheric wind patterns on Mars
- September 26, 2023
- 0
Mars is one of the most studied components of the solar system, but there are always new discoveries in Earth’s neighbor. On Earth, we can make direct measurements
Mars is one of the most studied components of the solar system, but there are always new discoveries in Earth’s neighbor. On Earth, we can make direct measurements

Mars is one of the most studied components of the solar system, but there are always new discoveries in Earth’s neighbor. On Earth, we can make direct measurements to understand our planet’s meteorological activity, but on Mars, scientists must use field evidence to discern this information.
One such feature of the Red Planet’s landscape is sand dunes in deserts; They are crescent-shaped sand dunes formed by wind blowing predominantly in one direction in regions where sand supply is limited. Such eolian dunes are significantly affected by atmospheric circulation on the planet’s surface. A new study has been published Geophysical Research LettersHe found that local terrains at scales smaller than 100 km (for example, rocky or deep impact craters from icy meteorites) can deflect winds and cause changes in dune formation.
Dr. is an associate professor at the Technion Institute of Technology in Israel. Lior Rubanenko and colleagues used machine learning to characterize Martian wind patterns based on the morphology of more than 700,000 dunes. These data were obtained from images taken with a special camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, a spacecraft that has been orbiting the planet since 2006 to collect information about the planet’s geology and climate.
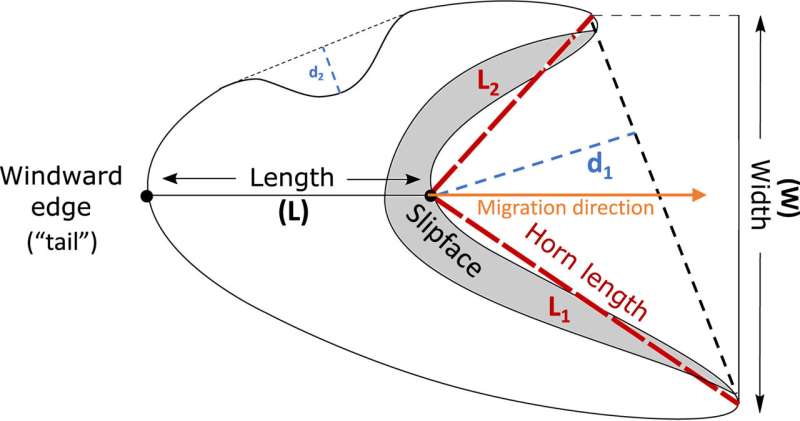
To map dune fields, a machine learning component was trained to automatically identify the shape of dunes. From these images, scientists determined the orientation of the steep side of the dunes (the slide) and the orientation of the tips protruding from the edges (called horns). If the horns are asymmetrical (one longer than the other), this indicates the interaction of many wind directions.
The research team found a clear pattern of dune migration due to summer northward atmospheric circulation in the mid-latitudes and cyclonic (counterclockwise movement around the center of low pressure) near the North Pole. The latter also separates into a smaller component that experiences the opposite anticyclonic wind direction; The authors attribute this specifically to the influence of winds moving across the polar ice cap.
Dr. Rubanenko and colleagues found that at latitudes above 45° N, dune migration patterns are predominantly eastward, consistent with cyclonic polar vortex circulation, while at latitudes below -45° N, they are southward. Local wind regimes are most influential in areas where topographic features are 10–50 km horizontally, but have little impact when landmarks exceed the 100 km scale, being instead influenced by larger planetary wind systems.
One of the limitations of the machine learning project is that it does not fully account for the complexity of wind patterns that vary between day and night and across seasons, and instead focuses on long-term patterns. Difficulty is also experienced in areas with significant topographic changes, such as the large impact craters of Valles Marineris, Hellas and Argyre, where dunes spread over a larger area.
These craters act as sand traps, providing enough material to form dune fields that form closer to the center of the crater basin as they go deeper. Migration inside craters may be caused by strong winds blowing from the slopes.

Although further improvements in machine learning technology are needed, previous research in testing tracks real-world data and matches anecdotal evidence on the direction of windblown dust and sand during dust storms.
As on Earth, planetary-scale circulation patterns show a general trend of movement from the poles towards Mars’ equator, with a disturbance in the mid-latitudes. Understanding atmospheric circulation patterns on Mars is crucial to supporting human missions to the planet and future habitability prospects. Source
Source: Port Altele
As an experienced journalist and author, Mary has been reporting on the latest news and trends for over 5 years. With a passion for uncovering the stories behind the headlines, Mary has earned a reputation as a trusted voice in the world of journalism. Her writing style is insightful, engaging and thought-provoking, as she takes a deep dive into the most pressing issues of our time.