The Spaceborne Computer-2 from Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) has launched towards the International Space Station (ISS) on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. This new computing model seeks to expand high-performance computing and processing capabilities in space, including artificial intelligence and machine learning tasks, allowing scientists housed at the station to conduct new experiments with better tools.
Once the HPE Spaceborne Computer-2 is installed on the International Space Station, Researchers will use it to support innovation and save research time. Traditionally, data collected in space was sent to Earth for processing. However, with a supercomputer on board, the data can be evaluated in near real time in low Earth orbit, making it possible to reduce the size of the download by up to 30,000 times and only transmit the data output to Earth.
The HPE Spaceborne Computer-2 will be used for a federated learning experiment that will independently train machine learning models and inference engines originally created in the cloud. This experiment will involve the collaboration of cloud service providers to contribute to the machine learning models used on Earth and keep the AI inference engine updated in space.
HPE Spaceborne Computer-2: technical specifications
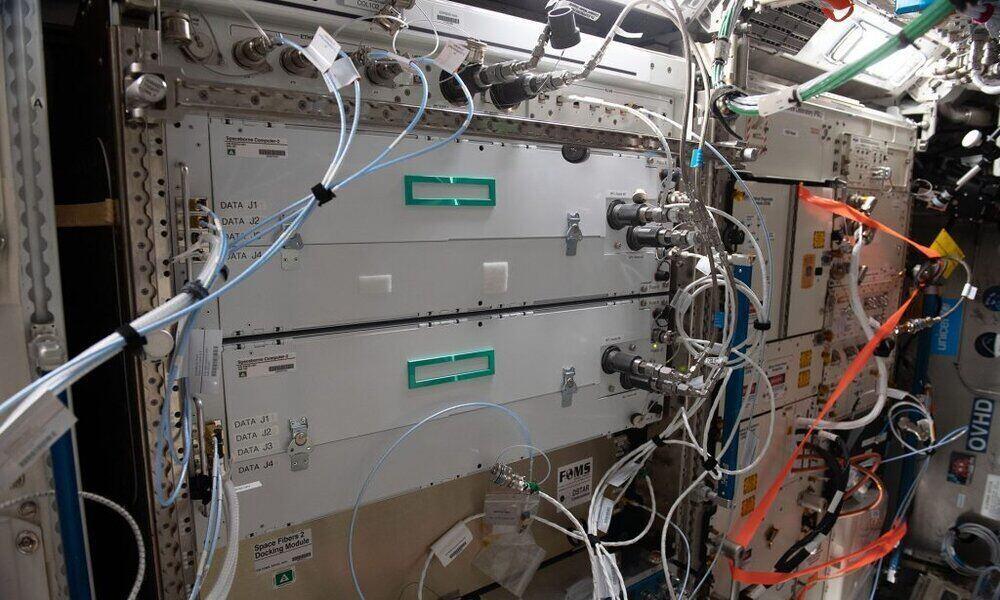

The system, which is based on commercial servers (COTS), has been updated with more than 130 TB of KIOXIA flash storage, including four 940GB KIOXIA RM Series Value SAS drives, eight 1TB XG Series NVMe drives and four 30.72TB PM6 Enterprise SAS SSDs. This represents the largest storage capacity ever sent to the ISS in a single mission. This increase in storage will allow you to run new applications and conduct research with larger datasets.
In addition, the HPE Spaceborne Computer-2 offers a an updated operating system, NASA spaceflight support software, and a new security system. Once on the ISS, the status and conditions of these technologies will be monitored daily to evaluate their performance in the harsh space environment and once again successfully complete their mission as in the past.