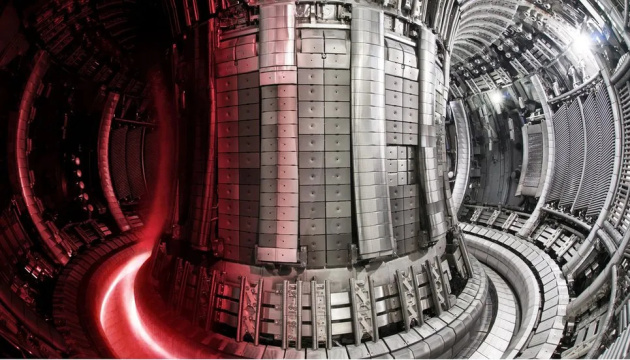
British scientists at the JET laboratory have set a new world record for energy production from nuclear fusion, where stars obtain their energy.
According to Ukrinform, this situation was reported by the BBC.
The result was obtained in the latest experiment after more than 40 years of thermonuclear fusion research.
In five seconds of the experiment, 69 megajoules of energy (11 megawatts of power) were produced.
Nuclear fusion is the process that powers the Sun and other stars. It works by heating small particles and forcing them to combine into heavier particles, releasing energy. Additionally, nuclear fusion could potentially produce large amounts of clean energy.
If successfully scaled to commercial level, it could produce infinite amounts of clean, carbon-free energy. Unlike wind and solar energy, it will not depend on weather conditions.
However, Dr., a researcher in the field of nuclear fusion at the University of Manchester. As Aneka Khan explains, it’s not that simple: “For atoms to fuse on Earth, we need temperatures ten times higher than on the Sun; about 100 million degrees Celsius, and we need a high enough atomic density and a long enough time to fuse.” “
However, scientists said that this experiment deepened the understanding of fusion physics.
The European Joint Fusion Reactor (JET) was built at Culham in Oxford in the late 1970s and until late last year was the most advanced experimental fusion reactor in the world. In December, all experiments on this were stopped. Although the reactor was located in Great Britain, it was mainly funded by the EU’s Euratom nuclear research program and operated by the UK Atomic Energy Agency. Scientists from Great Britain, Europe, Switzerland and Ukraine worked on it for forty years.
British scientists have doubled their previous record for creating and sustaining thermonuclear fusion, as reported by Ukrinform.
Photo: UK ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY / EUROFUSION