Scientists discover strange metasurface phenomena
- April 3, 2024
- 0
Dr. from the Electromagnetic Space Institute of Southeast University in Nanjing, China. A new study led by Ruiwen Shao and Professor Junwei Wu investigates the complex dynamics of
Dr. from the Electromagnetic Space Institute of Southeast University in Nanjing, China. A new study led by Ruiwen Shao and Professor Junwei Wu investigates the complex dynamics of
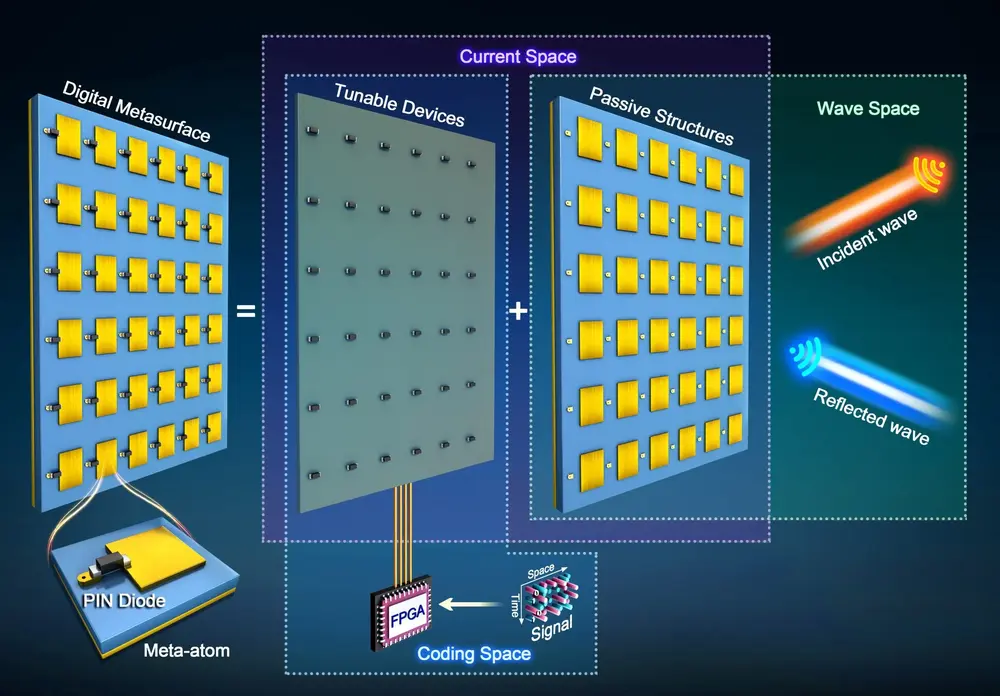
Dr. from the Electromagnetic Space Institute of Southeast University in Nanjing, China. A new study led by Ruiwen Shao and Professor Junwei Wu investigates the complex dynamics of scattered waves on digital metasurfaces. Using the Singular Variance Decomposition (SVD) technique, Dr. Shao discovered a surprising discrepancy: the number of non-zero singular values does not correspond exactly to the number of metaatoms within the metasurface. Instead, it is roughly flat, shedding light on the complex behavior of these electromagnetic structures. “This is a very unusual result that contrasts with the previous method used to model the metasurface,” says Shao.
Ruiwen Shao and Junwei Wu, together with laboratory manager Tiejun Cui, tried to determine what was causing the extreme singular value. The team views the digital coding metasurface as a microwave network consisting of two networks containing passive structures and tunable devices. The composition successfully separates the influence of coding states on scattered waves. “The expression obtained by the cascade microwave network formula still contains a matrix inversion term, so we naturally wonder whether expanding the power series will affect the simplification.” Wu says.
After a series of derivations and approximations, the team found that the scattered wave metasurface of digital coding can be expressed as a second-order polynomial of the coding states, including the constant term, first-order terms, and quadratic terms of the adjacent equations. codes. “The addition of the zero-order term and the quadratic terms doubles the order of the equation, which is consistent with the number of non-zero singular values. These terms can be considered to arise from the mutual coupling of neighboring metaatoms.” Shao says.
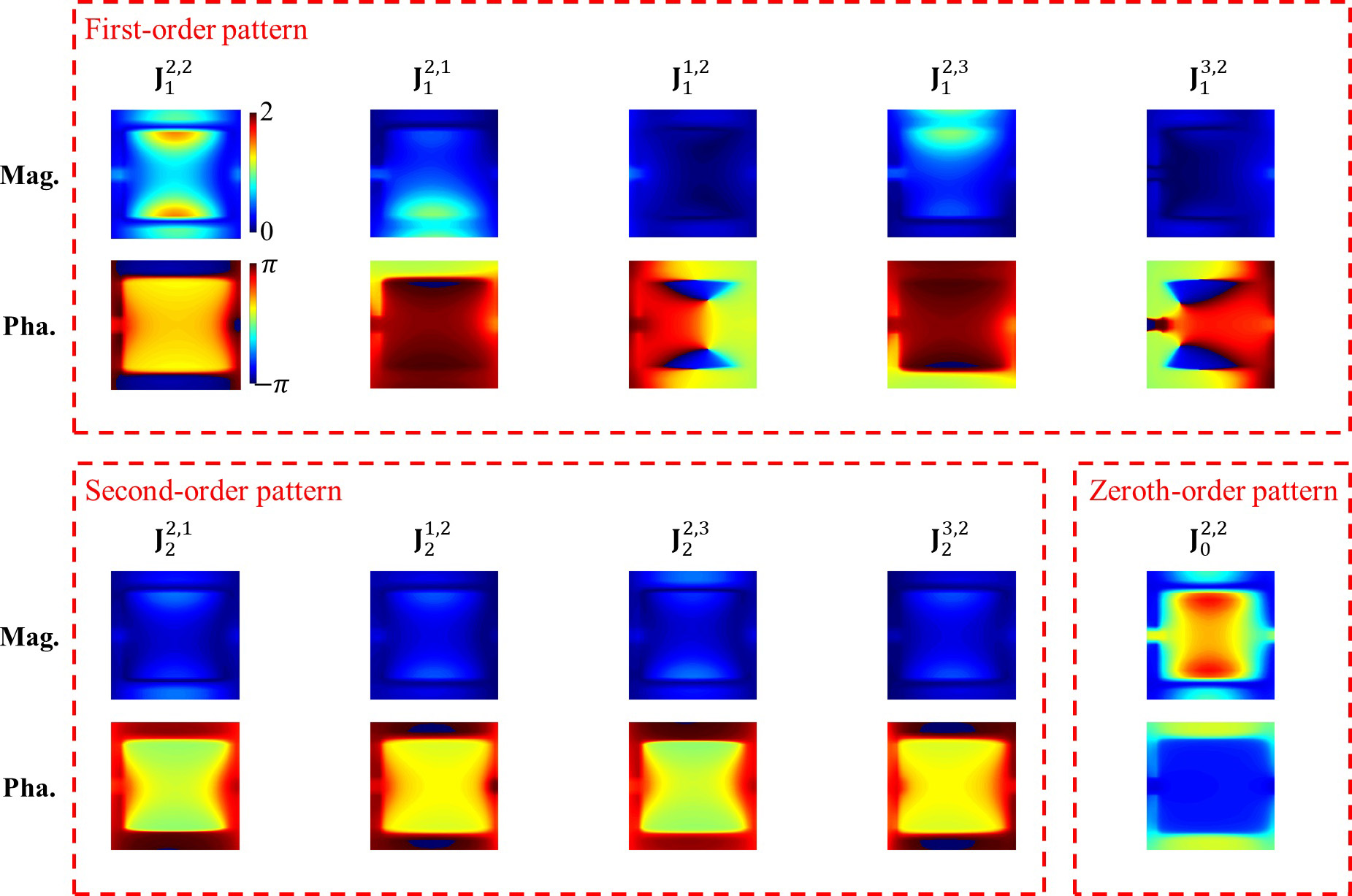
The researchers derived these existing models using full-wave simulations. Based on the patterns, they accurately predict the scattered electromagnetic waves of the metasurface in any coding situation. “A high-fidelity semi-analytical expression is a powerful tool for the theoretical study of the statistical properties of metasurfaces. With the help of a macroscopic model, the interconnection of elements is transformed into the current covariance. Thus, we find that the probability distribution of the current in the metasurface is a set of dependent normal distributions. The differential distribution of dependent distributed currents “We compare their entropy with independent and identical ones, and the difference between them indicates the loss of information when converting digital signals into electromagnetic waves.” Wu says.
How to evaluate the ability of a metasurface to transmit information is an urgent problem that needs to be solved when implementing metasurface communication systems. In this study, researchers proposed a new method to measure information loss resulting from mutual communication. According to common knowledge, as the period of an element decreases, information loss increases.
Source: Port Altele
As an experienced journalist and author, Mary has been reporting on the latest news and trends for over 5 years. With a passion for uncovering the stories behind the headlines, Mary has earned a reputation as a trusted voice in the world of journalism. Her writing style is insightful, engaging and thought-provoking, as she takes a deep dive into the most pressing issues of our time.