Hubble recorded the birth of a star similar to the Sun
- May 19, 2024
- 0
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured a spectacular image of three stars in the Reflection Nebula, including the variable star HP Tau. These young T Tauri stars, which have
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured a spectacular image of three stars in the Reflection Nebula, including the variable star HP Tau. These young T Tauri stars, which have
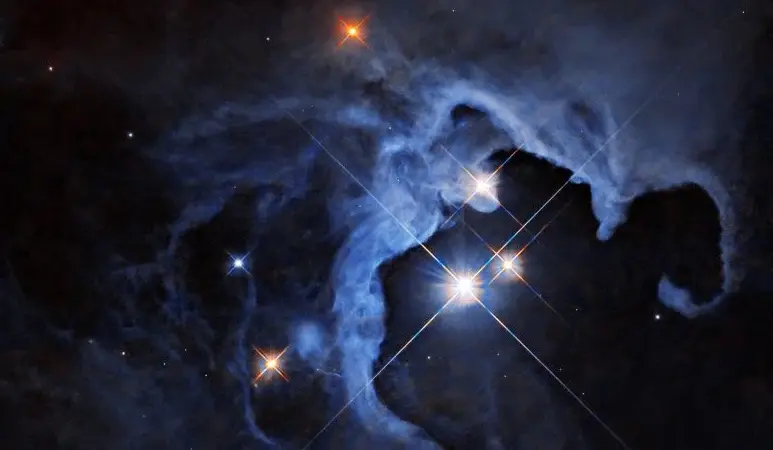

NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured a spectacular image of three stars in the Reflection Nebula, including the variable star HP Tau. These young T Tauri stars, which have not yet undergone nuclear fusion, are still shrouded in remnants of the dust and gas clouds from which they formed; this highlights the early stages of star formation and planetary disk development.
In this new image taken by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, a striking trio of stars erupt from the hollow void of the Reflection Nebula, looking like a glittering space geode. This triple star system consists of the variable stars HP Tau, HP Tau G2 and HP Tau G3. HP Tau is known as a T Tauri star, a type of young variable star that has not yet begun nuclear fusion but has begun to evolve into a hydrogen-fueled star similar to our Sun.
T Taurus stars are generally less than 10 million years old. By comparison, our Sun is about 4.6 billion years old. They are often found still shrouded in the dust and gas clouds from which they formed.
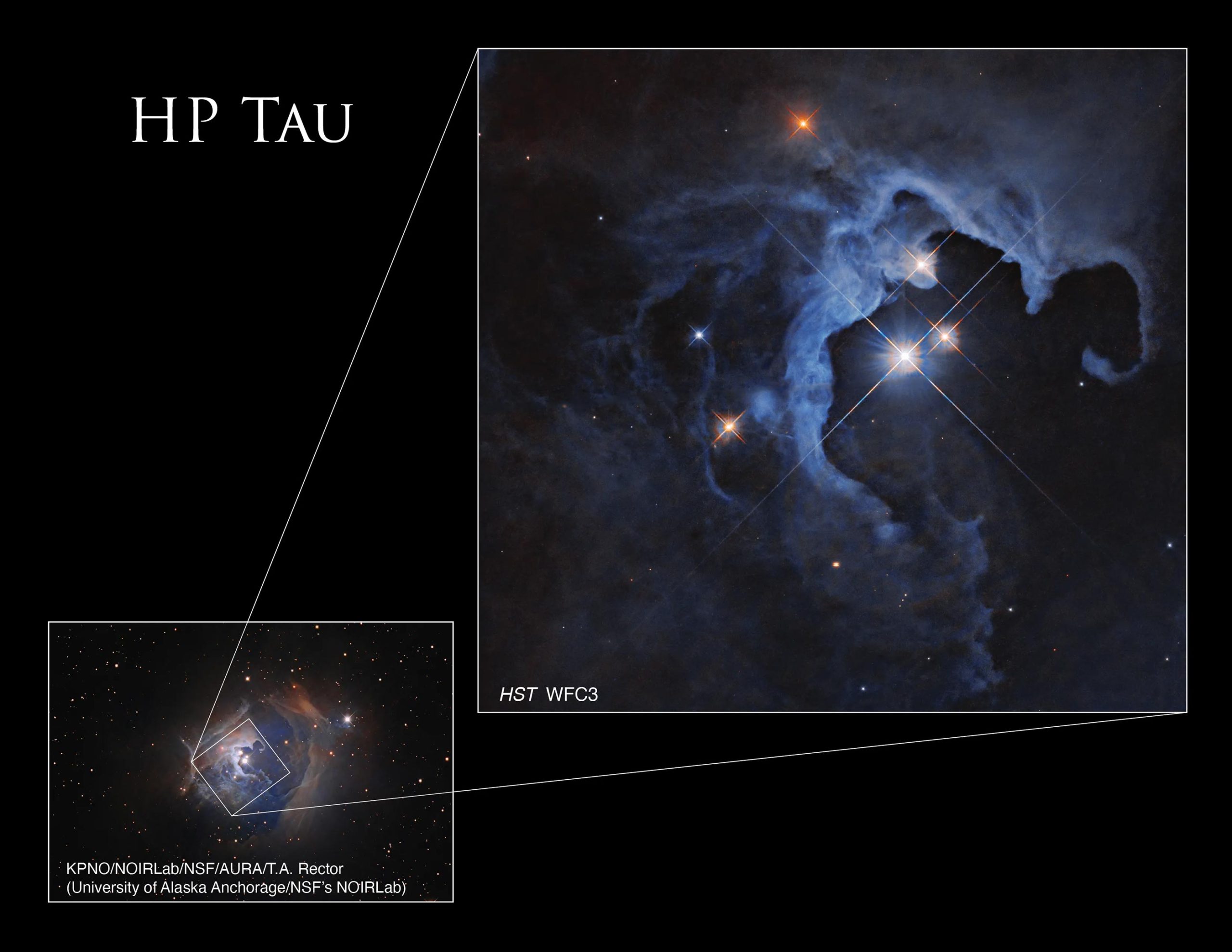
Like all variable stars, HP Tau’s brightness varies over time. T Taurus stars are known to have both periodic and random fluctuations in their brightness. Random changes can result from the chaotic nature of the developing young star, such as instabilities in the dust and gas accretion disk around the star, consumption of material from this disk falling onto the star, and flares on the star’s surface. Periodic changes can be caused by giant sunspots that move in and out of view.
The cloud of gas and dust twisting around the stars shines with reflected light. Reflection nebulae themselves do not emit visible light, but they shine when light from nearby stars reflects off gas and dust, such as fog illuminated by car headlights.
HP Tau is located approximately 550 light-years away in the constellation Taurus. Hubble studied HP Tau as part of a study of protoplanetary disks, disks of material around stars that develop into planets over millions of years.
Source: Port Altele
As an experienced journalist and author, Mary has been reporting on the latest news and trends for over 5 years. With a passion for uncovering the stories behind the headlines, Mary has earned a reputation as a trusted voice in the world of journalism. Her writing style is insightful, engaging and thought-provoking, as she takes a deep dive into the most pressing issues of our time.