Google Deepmind delivers AI audio for video
- June 18, 2024
- 0
Researchers at Google Deepmind have developed a technology that uses video pixels and text prompts to generate sound for videos. Video generation models are evolving rapidly, but many
Researchers at Google Deepmind have developed a technology that uses video pixels and text prompts to generate sound for videos. Video generation models are evolving rapidly, but many


Researchers at Google Deepmind have developed a technology that uses video pixels and text prompts to generate sound for videos.
Video generation models are evolving rapidly, but many current systems only produce silent video. The next step is to create audio tapes for these videos. New video-to-audio (V2A) technology enables synchronized audiovisual production. V2A combines video pixels with text prompts to create rich sound atmospheres that match the images.
V2A can be linked to video generation models such as Veo (also from Google Deepmind) to create dramatic soundtracks, realistic sound effects or dialogues to match the videos. The technology can also create audiotapes for traditional images such as archival footage and silent films, opening up new creative possibilities.
Users can create an unlimited number of audio bands for each video. A “positive prompt” allows the creation of desired sounds, while a “negative prompt” helps avoid unwanted sounds. This flexibility gives users more control over the audio output and allows them to quickly experiment and choose the best sound adjustment.
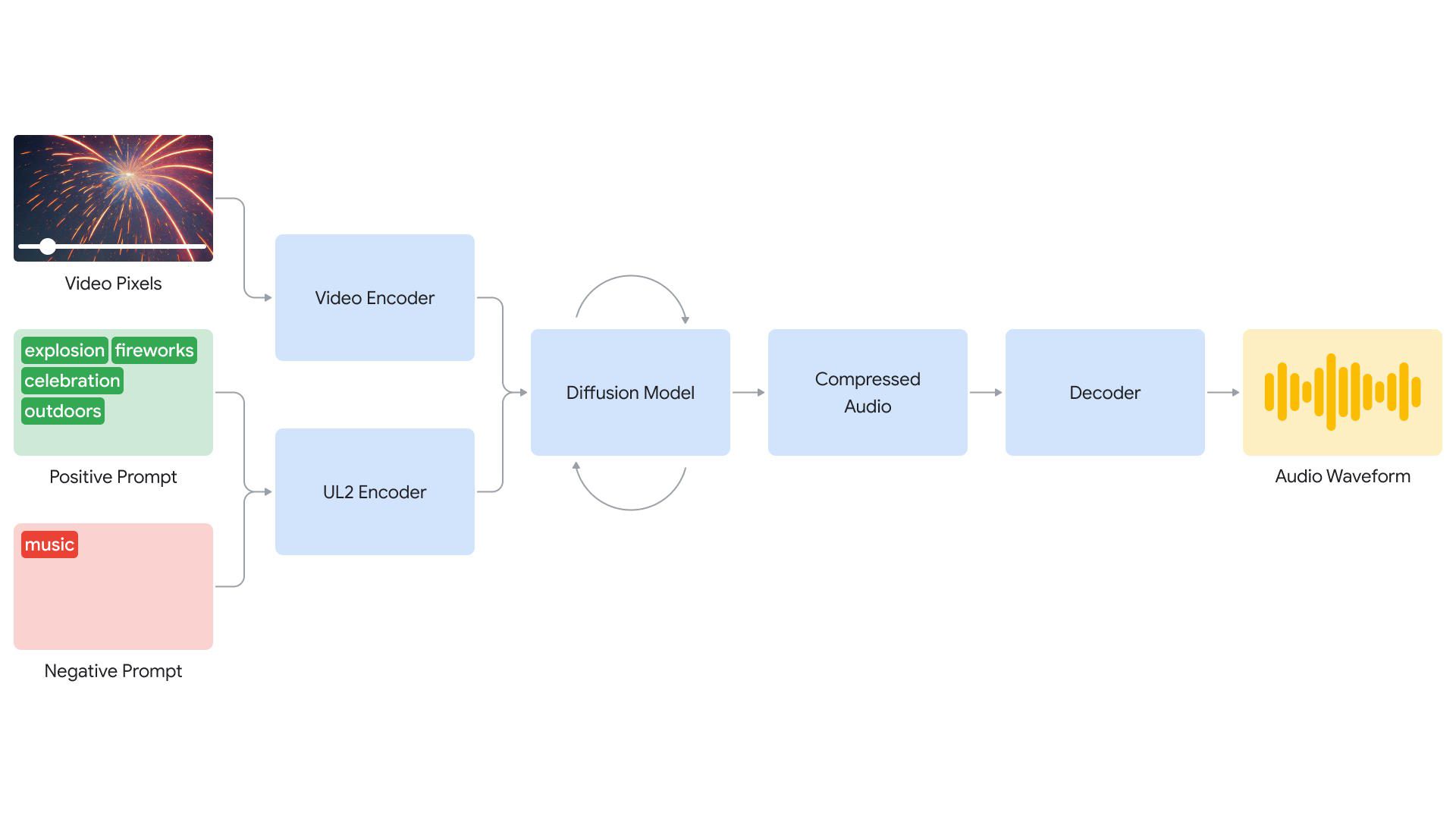
Deepmind’s V2A system begins by encoding video frames into a compressed representation. The model iteratively refines sound from random noise. This process is guided by the visual input and natural language prompts to produce synchronized and realistic audio that closely matches the prompt. The audio output is then decoded, converted to an audio waveform, and combined with the video data.
To produce higher quality audio and control specific sounds, more information has been added to the training process. This includes AI-generated annotations with detailed sound descriptions and transcriptions of spoken dialogue. Through training on video, audio, and additional annotations, the technology learns to associate specific audio events with different visual scenes while also responding to the information in the annotations or transcripts.
V2A technology is different because it understands raw pixels and adding a text prompt is optional. In addition, the system does not require manual matching of the generated sound with the video, which greatly simplifies the process.
There are still limitations that need to be addressed. The quality of the audio output depends on the quality of the video input. Artifacts or distortions in the video can cause a noticeable degradation of the audio quality. Lip movement synchronization is also improved for videos with speech. V2A attempts to generate speech from the transcriptions and synchronize it with the lip movements of the characters. However, the coupled video generation model may not be tuned to transcriptions, which may result in unnatural lip movements.
V2A is not yet publicly available today. You can find several video demos here.
Source: IT Daily
As an experienced journalist and author, Mary has been reporting on the latest news and trends for over 5 years. With a passion for uncovering the stories behind the headlines, Mary has earned a reputation as a trusted voice in the world of journalism. Her writing style is insightful, engaging and thought-provoking, as she takes a deep dive into the most pressing issues of our time.