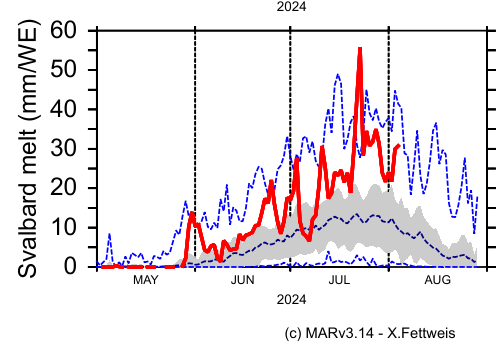
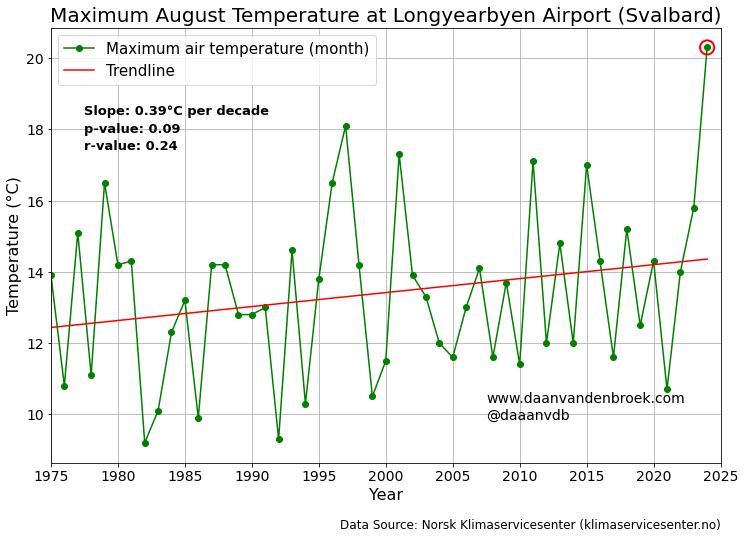
In the summer of 2024, the ice sheets of Svalbard, a large polar archipelago in the Arctic Ocean, experienced extreme melting caused by extremely high air temperatures.
In late July and early August 2024, the temperature in the Svalbard Archipelago was around four degrees Celsius, which was above average for this part of the world.
Climatologists from the Xavier Fettweiss University in Liège reported that on July 23, 2024, Svalbard glaciers broke the daily surface melt record.
The rapid melting of ice continued in August. In Longyearbyen, the administrative center of the Norwegian province of Svalbard (the Svalbard archipelago), the temperature reached 20.3 degrees Celsius on 11 August, the highest August temperature on record.