New research shows that twisted carbon nanotubes can store high energy densities into power sensors or other technologies. Researchers found that spun carbon nanotubes can store three times more energy per unit mass than lithium-ion batteries, making them ideal for lightweight and safe energy storage applications such as medical implants.
Groundbreaking research into energy storage
A global team of scientists, including two researchers from the Center for Advanced Sensor Technologies (CAST) at the University of Maryland in Baltimore County (UMBC), has demonstrated that twisted carbon nanotubes can store three times more energy per unit mass than the current state. – state-of-the-art lithium-ion nanotubes. This breakthrough positions carbon nanotubes as a promising solution for energy storage in lightweight, compact and safe devices such as medical implants and sensors. The findings were recently published Nature Nanotechnology .
The study was a joint effort from four institutions, led by Shigenori Utsumi of Suwa University of Science in Chino, Japan, Katsumi Kaneko of Shinshu University in Nagano, Japan, and Sanjiv Kumar Ujjain of CAST. Kumar Ujjain started the project at Shinshu University and continued his studies after joining UMBC in 2022. Preeti Ahuja, also from CAST, played an important role in the research phase of the material.
Innovative properties of carbon nanotubes
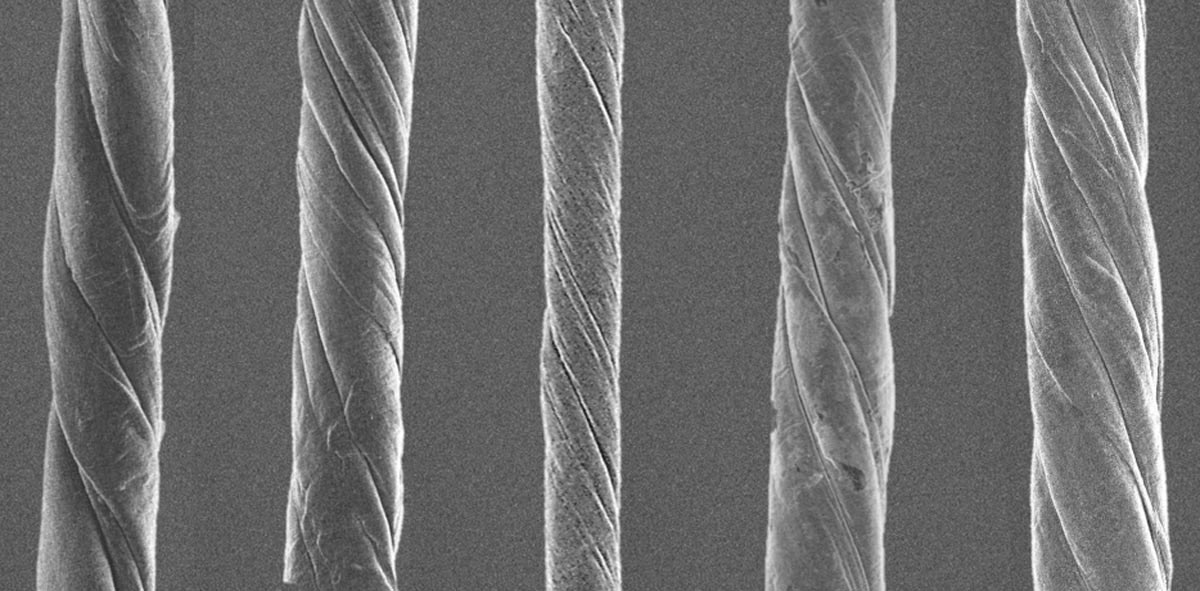
Researchers studied single-walled carbon nanotubes that look like straws, made of pure carbon sheets just 1 atom thick. Carbon nanotubes are lightweight, relatively easy to make, and about 100 times stronger than steel. Their surprising properties have led scientists to explore their potential use in a wide variety of futuristic technologies, including space elevators.
To investigate the energy storage potential of carbon nanotubes, UMBC researchers and colleagues fabricated carbon nanotube “ropes” from commercially available nanotube bundles. After stretching and twisting the tubes into a single thread, the researchers coated them with various substances designed to increase the strength and flexibility of the ropes.
Also read – Scientists solve quantum mystery that could change electronics forever
Impressive energy storage capabilities
The team tested how much energy the ropes could store by bending them and measuring the energy released when they unwound. They found that the most efficient ropes could store 15,000 times more energy per unit mass than steel springs and nearly three times more energy than lithium-ion batteries. The stored energy remains stable and usable at temperatures between -76 and +212°F (-60 and +100°C). The materials from which carbon nanotube ropes are made are also safer for the human body than those used in batteries.
“Humans have long had energy stored in mechanical coil springs to power devices such as watches and toys,” says Kumar Ujjain. “This research shows that twisted carbon nanotubes have great potential for storing mechanical energy, and we are excited to share this news with the world.” He says the CAST team began using bent carbon nanotubes as the power source for the prototype sensor they were developing.
Read PortalTele on GOOGLE NEWS