Last August, we shared with you an article dedicated to Intel XeSS, an image resizing technology that starts from a base similar to what we saw in NVIDIA DLSS, and that moves away from the model that AMD used in FSR technology. Ultimately, the goal of these three technologies is the same, reconstruct and rescale an image from a lower resolution to achieve higher resolution with the best possible result, but they differ in the techniques they use to do so.
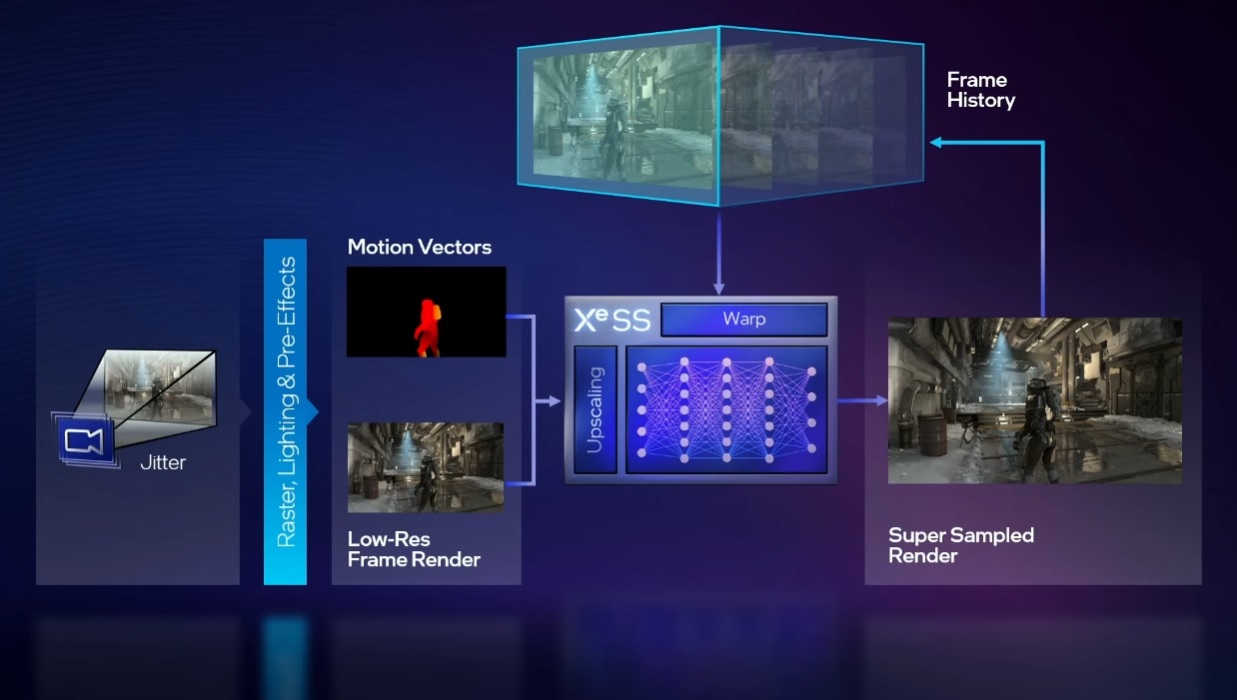
It uses Intel XeSS technology spatial and temporal elements as well as motion vectors and uses artificial intelligence rely on an algorithm to help you achieve the best possible result. This approach is basically the same as that used by NVIDIA with DLSS, while AMD only uses spatial and temporal elements, but does not use AI.
At the time, the chip giant confirmed that Intel XeSS would not require one-on-one in-game training, which will be critical to ease its implementation and drive adoption from the moment it becomes available, and also made it clear that it can be activated via two paths , one through hardware accelerationusing XMX fields and more using software, using DP4a instructions if we have a GPU that supports them.
Intel XeSS tested on video: it will be able to double the performance
We already had a lot of information about Intel XeSS, but the chip giant has just published a new video, where it once again dived into the most important keys of this technology, shared performance results with the Intel Arc A770 and confirmed the complete list with the first games that will be compatible with it. Total, we have 19 titles which we list below:
- Call of Duty: Modern Warfare II.
- Arcadegeddon.
- Ghostwire Tokyo.
- Bloody vampire hunt.
- Releasing the ghosts of the ghostbusters.
- Naraka Bladepoint.
- Great people.
- Gotham Knights.
- Chronicles of DioField.
- Dolmen.
- chivalry II.
- Redoubt II.
- Settlers.
- Death Stranding: Director’s Cut.
- Rift Breaker.
- Hitman III
- DISEASE.
- Shadow of the Tomb Raider.
- Anvil Vault Breakers.


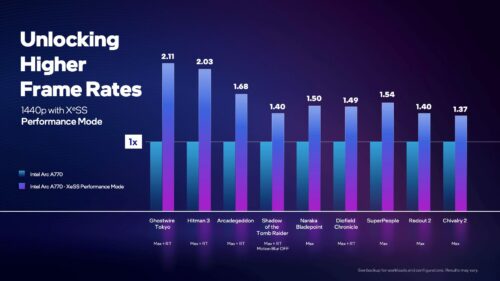
As we can see, there are quite a few type A degrees, and some of them are quite demanding on the hardware level. For example, Ghostwire Tokyo supports ray tracing, a very demanding technology that significantly reduces the frame rate per second. Thanks to Intel XeSS, this will be possible compensate for the loss of performance when ray tracing is activated.
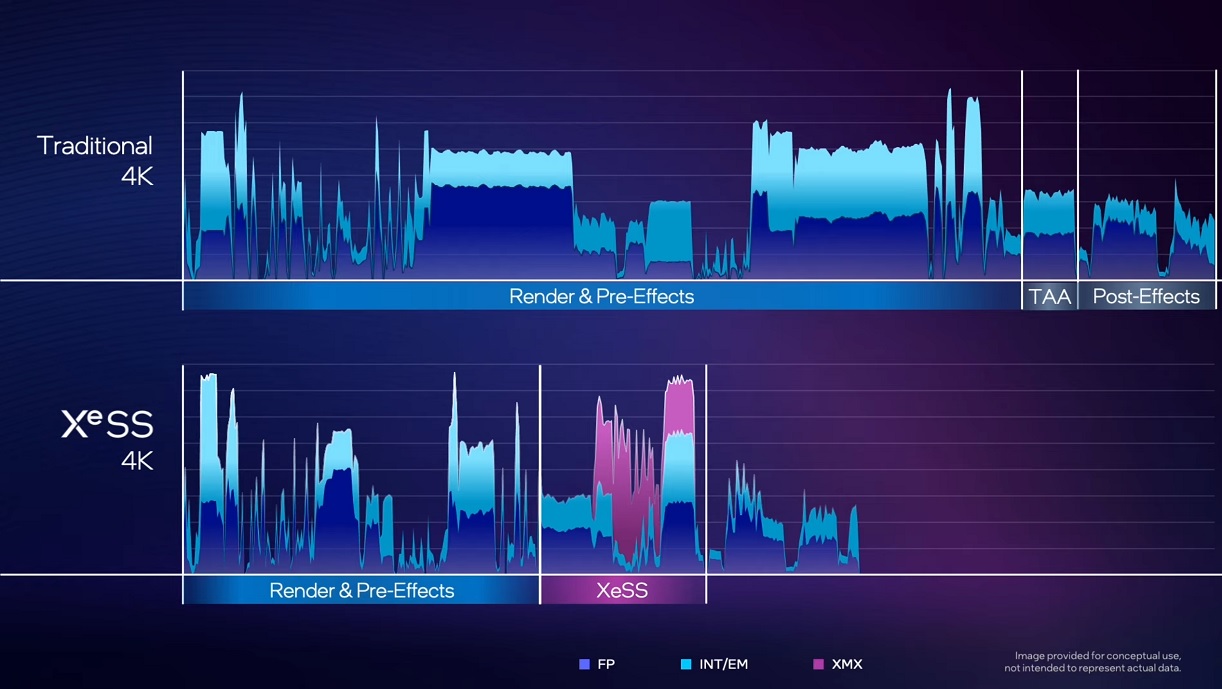
The technical explanation offered by Intel in this video is very interesting and starts from these two keys that we gave you, the XMX matrix and the DP4a instructions. To improve performance, Intel decided to parallelize operations more. Instead of starting by multiplying two registers and stacking them in another register, they do what they do divide a 32-bit register into 8-bit parts that are multiplied and addedwhich allows the power to be multiplied by four under DP4a.
impression? Wait until you see what the XMX field can do. This hardware unit specialized in artificial intelligence can work eight accumulations in parallel and not with just one, which Intel says makes it possible multiply the result by 16.
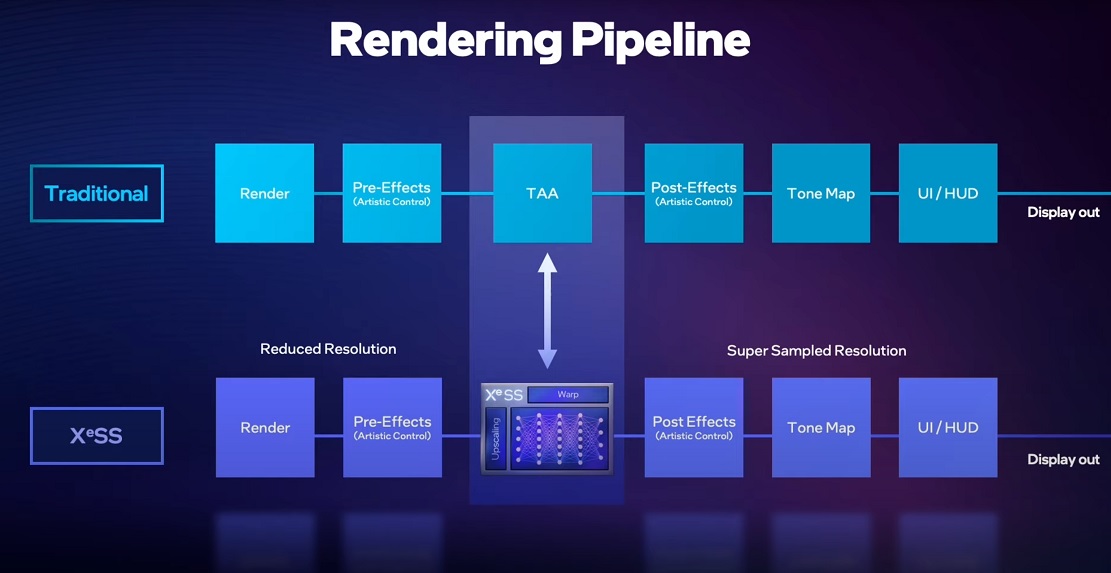
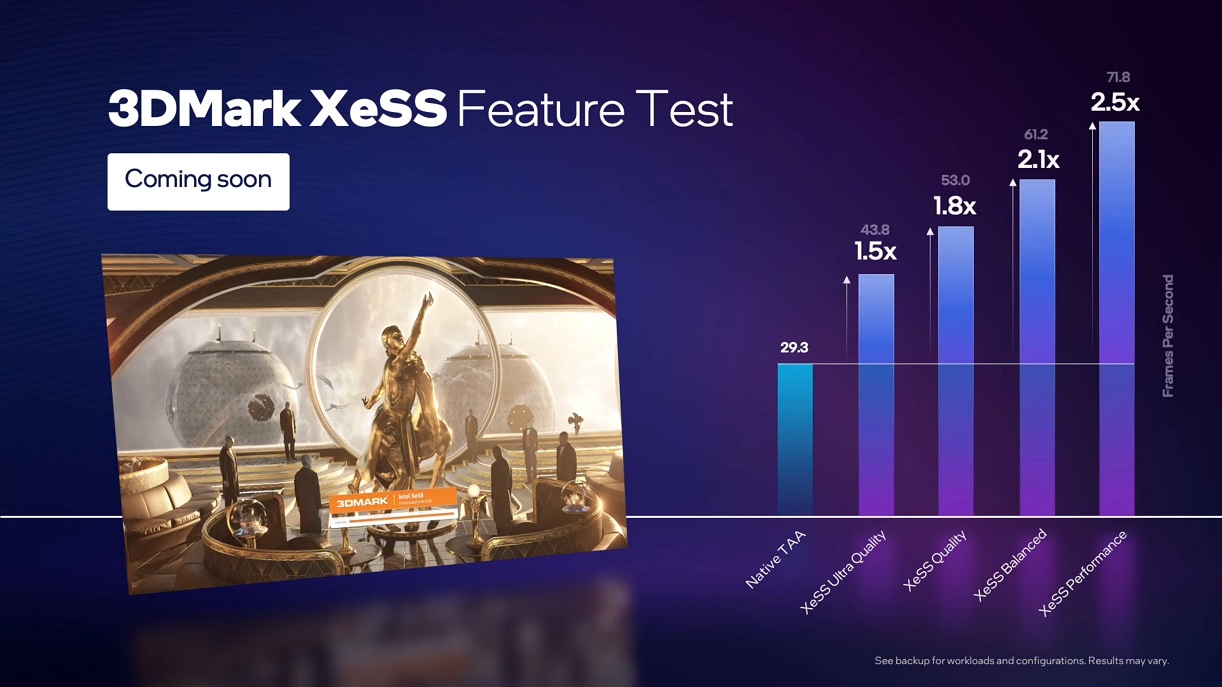
Intel XeSS technology starts from a lower resolution to render an image, which it reconstructs and scales to a higher resolution. This reduces the required rendering time to generate a high-resolution image that allows a higher frame rate per second and significantly reduces resource consumption. In terms of performance, the impact it has is so great that it can double the performance, as we can see in the attached graphics and video.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frlXry38tYeah