How the current processor works: three things you should know
- February 17, 2023
- 0
The processor is the brain of any PC and is undoubtedly one of its most important components as it deals with it perform all general tasks starting with
The processor is the brain of any PC and is undoubtedly one of its most important components as it deals with it perform all general tasks starting with

The processor is the brain of any PC and is undoubtedly one of its most important components as it deals with it perform all general tasks starting with a multipurpose approachmeaning that none of the other components that make up a computer could function without it.
When you open a folder, the processor is the one that takes care of it perform the necessary mathematical operations to complete this commandand sends the result that the graphics card needs to show the change on the monitor.
If you start the game, the processor takes care of all the basic tasks necessary for it to read all the logic, instructions and other elements of this and transfer to the graphics card the information it needs to develop its work, thus creating a dependency that explains why the performance of the graphics card can be seriously affected, for example, better or worse, depending on the performance processor.
Over time, processors have retained their basic function, even though important developments have occurred It allowed us to make very important progress which ultimately not only translated into higher performance, but also greatly improved the versatility and efficiency of these chips in handling various workloads.
It’s safe to say that today’s processor basically performs the same as the one from the eighties, but it’s also fair to say that it can handle the workload in a very different way. It’s a very interesting topic that still raises some doubts, which is why we decided to give shape to this guide, in which we will tell you three things you should know about how the current processor works.
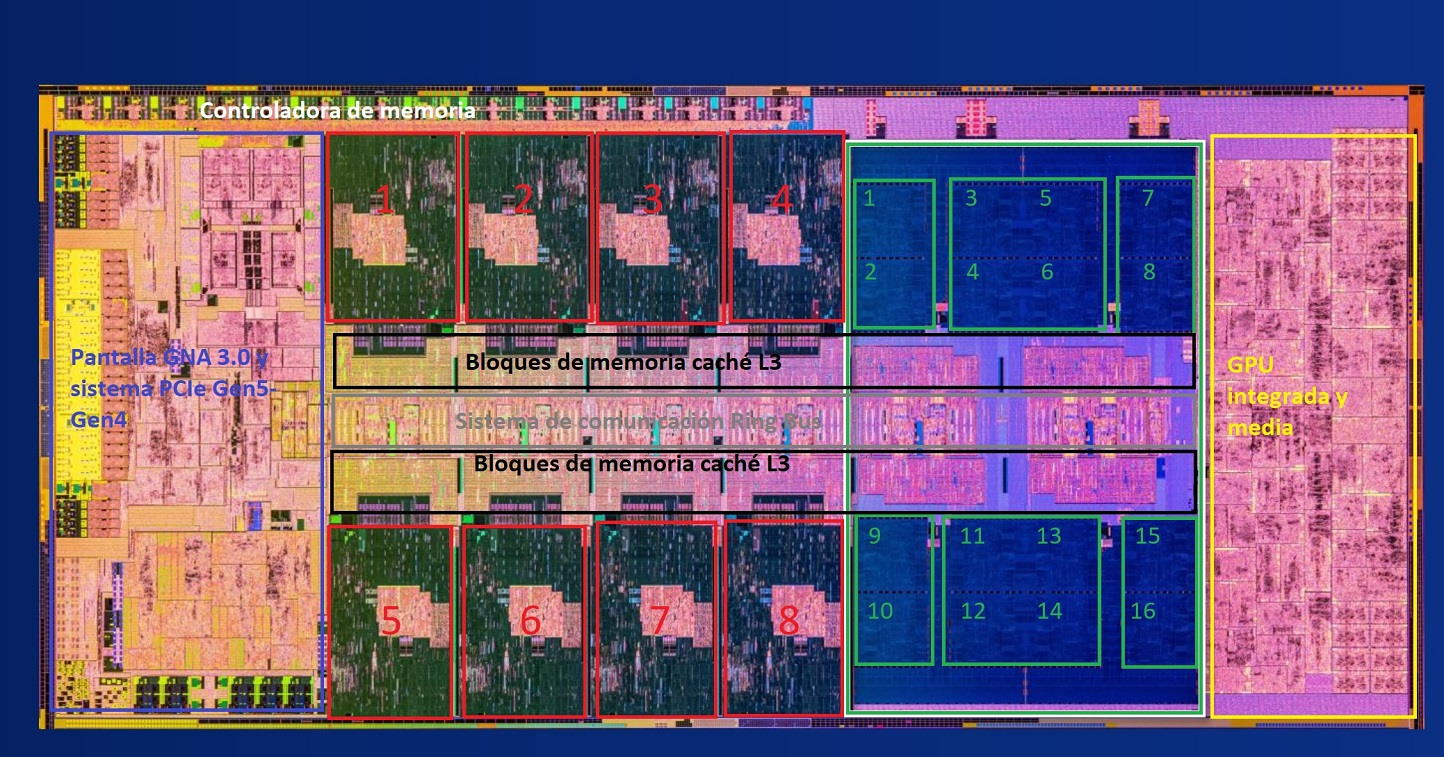

One of the biggest leaps that occurred in the processor industry was the development of multi-core chips. This marked the end of the GHz race and ushered in the era of multithreading.although in this sense it should be noted that Intel overtook multi-core processors with its HyperThreading technology, which allowed the core to work with a single process and a single thread.
The AMD Athlon X2 and Pentium D processors were the first to implement dual-core configurations, and today we find processors configured with up to 24 cores and 32 threads in the mainstream consumer market. When we talk about cores, we mean physical units to handle the processwhile threads refer to the combined total number of processes and threads that the processor can handle.
A multi-core processor has a certain number of cores, but not all of its cores are created equal. This reality gives rise to what we know as favorite kernels, which are the ones that are slightly better than othersand that they can offer excellent performance. These cores are usually the ones that achieve higher operating speeds without stability issues, and their proper use is key for the processor to develop its full potential.
For all of the above, it is necessary that the operating system is capable of this identify these popular coresand that they prefer to distribute different workloads because if they don’t, they will waste the most important resource that the CPU has. Proper use of popular cores can make a significant difference in performance especially in tasks that are executed in two or four threads.
Another very interesting evolution that occurred in the world of processors was their dynamic adaptation to each workload, in the broadest sense of the word. Take the Intel Core i9-13900K as an example, which is a processor that has two different core blocks, one with high performance and the other with high efficiency.
High-efficiency cores are designed to offer good performance with low power consumption, while high-performance cores offer maximum performance but higher power consumption. Well, the first one they are used in specific workloads that do not require as much powerand also in those that remained in backroundwhile high-performance cores are used for demanding tasks that require a high level of performance and that run in the foreground.
It is also important to note that not all jobs need the same number of cores and threadsand that they are not distributed in the same way. So, for example, a basic task that could only be assigned to two cores, while running a game, the most normal thing is to parallelize all processor cores, but if we have a processor with eight or more cores, it will really only saturate two or four cores and leave the rest with a charge level below 30%.
What I explained to you earlier leads us to the concept of active cores, which ultimately determine the actual CPU load. The processor can work at 10% of its capacity, at 50% or at 100% depending on how we use the device, because ultimately It is designed to adapt to every task we perform.
The same happens with the operating frequencies, which will be higher or lower depending on the difficulty of each task, and will also depend on the load, processor temperature and consumption. Most current processors they have a base working speed and a maximum working speedwhich is the one they can achieve when turbo mode starts.
However, the maximum frequency depends on the number of active cores and threads. When we only have one or two active cores, this is when the maximum speed peak is experienced, if the operating temperatures and power supply allow, and this maximum peak decreases when the cores and threads of the processor become saturated, that is, as its use increases until it stabilizes at a certain level. So when you see that a processor can run at a maximum of 5.7 GHz, for example, be sure that this speed is only possible with one active core, or in certain cases with two active cores.

We have already seen that a processor has a number of favorite cores, which are the ones that offer the best performance, and also that is able to adapt to each specific task depending on the number of cores you need and fine-tuning the operating speed to maximize performance whenever possible.
All of this has a significant impact on the two main keys of any processor, consumption and working temperatures. It’s very easy to understand, a processor that only works at 10% or 15% load will have much lower power consumption and operating temperature than one that works at 80% or 100% load.
For this reason, you should not trust the base consumptions that Intel and AMD state in their processors, because the actual values will end up being much higher and the cooling solutions we will need will also have to be higher. strong. Let’s take a concrete example and return to the Core i9-13900K, a processor that according to Intel has a TDP of 125 watts, but in its PL2 mode, i.e. in more realistic use and with the turbo mode activated, it shoots up to 251 watts.
As we can see, the difference is huge, which means that the operating temperatures and cooling needs will also be much higher. In my tests, the specified processor achieved peak 98 degrees with a load of 100%, while in games with a load that usually did not exceed 30%, it registered an average of 73 degrees. If we talk about consumption, we have a similar story, as the Intel Core i9-13900K consumes 165 watts in games, 52 watts in Cinebench R23 working in one thread and reaches 309 watts in the multi-threaded test.
These huge variations are the result of what I told you, how the processor adapts in real time to each workload to offer the maximum possible performance. I used Intel as an example, but the same goes for AMD. The Ryzen 9 7950X has average consumption on a Windows 11 desktop 34 watts, a number that increments by one Average gaming power of 122 wattsand which is shot at 225 watts in the Cinebench R23 multi-threaded test. Temperatures also oscillate with increasing consumption, from the 68 degrees it registers in games to the 95 degrees it reaches under full load.

From everything we have told you at this point, you must be clear that the power value that is important for a processor is not PL1 and neither is the base TDP, but the maximum value when turbo mode comes into play, which is typically identified as PL2 in the case of Intel or PPT in the case of AMD. The difference between one and the other can be double or maybe more, and this can play into your hands if you have a very limited power supply or a very tight cooling system.
If you are in doubt about the maximum CPU consumption ask and be well informed before buying, because if you don’t, you could end up with a nasty surprise. I speak from the knowledge of the matter, because I have encountered more than one case where they asked me for help with a new PC that had stability problems, and in the end it turned out that the power supply was not enough for that configuration, because they did not expect high CPU consumption.
As a reference and to give you a rough idea as a starting point, in general, if we are going to build a high-end processor, it is advisable to supplement it with a power supply. 100 watts more than the recommended minimum value for your graphics card.
For example, if we plan to buy a GeForce RTX 4080 and complement it with a Core i9-13900K, the ideal would not be a 750 watt power supply, but an 800 watt onebecause the real consumption of the device will be around 710 watts under load, but it will record higher peaks and could increase if we have connected peripherals, network cards or RGB LED lighting systems.
Continuing the previous example, if we replace the Intel Core i9-13900K with the Ryzen 5 7600X consumption would be reduced to approx. 610 watts, and in this case we would be fine with a 750 watt supply, in fact we could fit a 700 watt supply without a problem. The difference in consumption that we achieved just by changing the processor is very large, as we can see.
Source: Muy Computer
Donald Salinas is an experienced automobile journalist and writer for Div Bracket. He brings his readers the latest news and developments from the world of automobiles, offering a unique and knowledgeable perspective on the latest trends and innovations in the automotive industry.