Disk partitions are the names for the sections into which a computer’s storage units can be divided. To understand each other, this event consists of “chop” an SSD or hard drive into different “logical disk” partitions to better organize them.
Although creating these partitions is optional and most users don’t use them, it should be said that this is a method ideal for managing your computer’s internal memory and among its advantages we can mention improvements in the maintenance of units, their organization, data security and even performance, in addition, it allows advanced functions such as the installation of multiple operating systems.
Types of disk partitions and systems
Each operating system treats these partitions differently and according to their type, since there are several of them. The main partitions are the system installation partition and the user data partition, but you’ll also be able to see other partitions that are typically dedicated to tasks like data caching, temporary virtual memory, system recovery, or hosting and UEFI management. firmware information.
When we buy a new computer with a pre-installed operating system, it is common for all disk space is taken. Some manufacturers add small partitions for system recovery and also create their own others, but generally only one is available for user management.
If we buy internal storage units from a vendor, such as modern SSDs, the situation is different, because they are usually supplied “empty” so that the user can create the ones he needs and choose the number of partitions to use. Once created and ready with what we know as formattingpartitions are recognized and managed by the operating system independently and each has its own file system.
You can prepare SSD or hard disk partitions in advance on any computer or directly during the installation of the operating system, since all the usual ones (Windows, Linux or macOS) allow you to manage partitions in the same installation process of the systems. . It will always depend on the capacity and number of units your team has, but generally we recommend going from there create at least two partitionsone for hosting the operating system and the other for your own data.
Focus on Windows, if you want to manage partitions on a disk that is already working, you can view them in “My Computer”, in file explorer, or directly through disk manager, where they can be created. , change or delete partitions that are managed by the system, which we will walk through below as a tutorial. There you will also – if possible – see additional drive letters for optical discs, network locations or external and/or removable storage media whose drives are created when we insert them into the computer.

Why are disk partitions so useful?
These sections are completely unknown to the general public and are used only by administrators or intermediate users. However, there are good reasons to use them, such as the ones we’re about to point out:
Install multiple operating systems
Most operating systems must be installed on their own primary partitions. In this scenario, it is mandatory to have multiple separate partitions. You can also create third partitions to share files between them if they use different file systems. In this guide you have an example of using partitions for systems where we have seen the installation of Windows 11 and Ubuntu 21 on the same computer.
Protect your data in case of system failure
If the operating system fails for some reason (drivers, applications or viruses), and this is very likely in Windows, you can be left without access to the disk or restore it. Having at least two partitions, one for system and one for data, ensures that your personal files will not be affected by a system failure. Likewise, if we need to reinstall the operating system from scratch, we will only need to format its partition and keep the other partitions we created for our backups and personal files safe.
improved performance
Large hard drives (10, 12, 15 or even 20 Tbytes) offer huge storage capacity, but they force read heads to travel further. Thanks to this, dividing the disk into several partitions ensures less delay when moving data and better performance. It’s not high and doesn’t affect SSDs that otherwise work without moving parts in the same way, but when it comes to performance, it all adds up.

better maintenance
Multiple partitions facilitate storage drive maintenance, error checking, drive optimization, and drive defragmentation (hard drives only). Several smaller sections also speed up file searches
Greater simplicity in organization
Having multiple partitions makes personal organization easier. An example usage in a typical storage drive in Windows would consist of a C: partition for system; D: for installing applications and games and E: for backup copies, documents, photos, music or video. The possibilities, depending on the capacity of each drive, are almost unlimited and improve organization compared to a single partition.
How disk partitions are managed
All operating systems offer their own native partition management tools, and third-party developers offer more advanced commercial applications. In Windows, it is managed via “Control Panel-Administrative Tools-Computer Management-Disk Management”. You can also access it using the Run Tool (Windows Keys + R) with the command «diskmgmt.msc” and in another more direct way, by right-clicking on the Start button and clicking on disk management:

Here you will access an interface similar to the one in the picture. Its options range from creating additional partitions (if we have enough space); reduce the size of each to make this possible; format them; change the drive letter and path or format it for a complete cleanup.
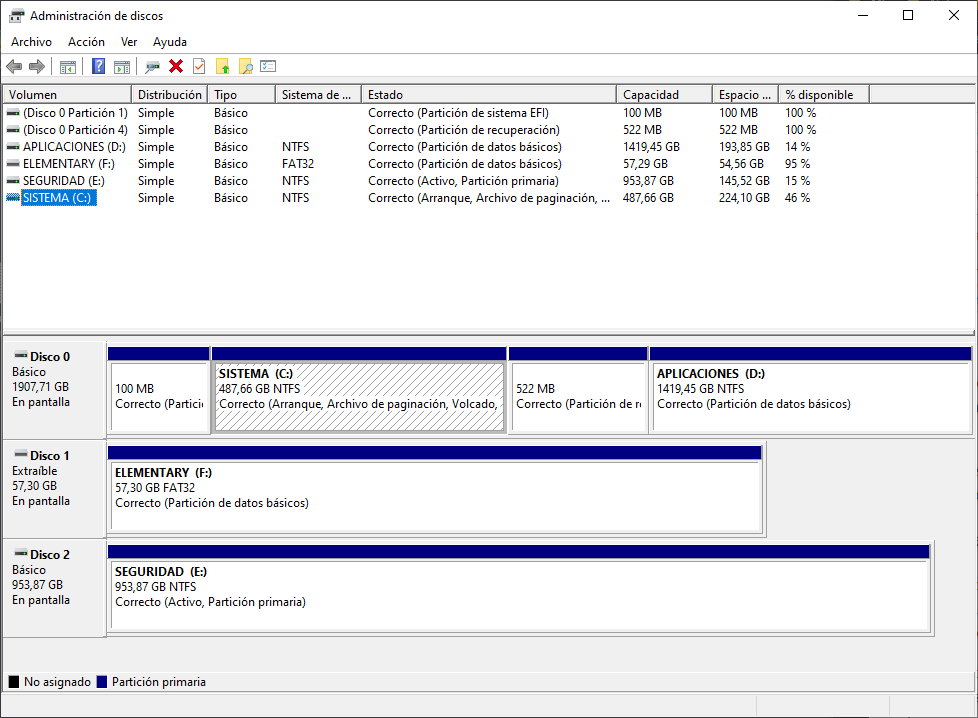
Some usage examples:
create partitions
If you have free space on your storage drives, you can use it to create one or more new partitions. Unallocated space is highlighted and labeled “Unallocated” or “Free Space”. The fastest and easiest way to create a partition using all or only a portion of the available free space is to right-click or long-press that unallocated space and click “New Simple Volume”.
delete partitions
In the same way, you can delete partitions that you do not use and free up disk space to create new ones or add this space to an existing one. Make sure you save the files you need beforehand as they will all be deleted. As in the previous cases, right-click on the partition and select “Delete Volume”. There are partitions that you won’t be able to remove from this tool, such as the partition reserved for the EFI system or the “C:” partition that keeps the operating system running.
Resize partitions
You can also shrink or extend partitions if there is free (unpartitioned) space immediately before or after the partition you are trying to modify. To reduce (or increase) the size of a partition, right-click on it and select “Expand Volume” or “Shrink Volume”. This tool allows you to shrink a partition to the maximum amount of space that you are not currently using. After the process completes, you will have enough free disk space that you can use to create more partitions.

format partitions
If you have just created a partition on one of your drives, the wizard will offer you the option to format it. However, you can also format a partition that is already created and located on the drive. Formatting a partition means that all data on it will be deleted, so be sure to back up any files you want to save before proceeding. To format an existing partition, right-click on it and select “format” from the context menu. You will be able to choose a file system or “volume name”, the name of this partition that you will see when accessing it from a file browser, for example.
Change unit letters or labels
The tool can also change partition drive letters, which you can see in file explorer, for example. You can do this both for convenience and in case of a conflict between partitions occupied by different partitions, except for the partition installed by the system “C:”, which cannot be changed by this tool. In the same way, you can change the “volume name” or what is the same, the name of the partition. Useful for making them easier to see and manage when you have a lot of them. As with the previous functions, to modify these parameters, right-click on the partition and follow the wizard.

As you’ve seen, using partitions is relatively simple once you know how they work. They are very useful for storage unit maintenance, data security and especially for file organization on our personal computer. The internal tools included in the operating systems are sufficient for most uses, and if you need more, you can resort to third-party software that is more complete and specialized.



















