ESA (European Space Agency) has designed, in collaboration with the University of Bologna and ETH Zürich, a new RISC-V CPU capable of agglutinating a total of 432 coresthanks to a chiplet-like approach which, as many of our readers know, reduces the wafer-level complexity of this CPU as well as the manufacturing cost.
This CPU, known as Occamy, impresses with the high number of cores and performance that it is able to achieve 0.76 TFLOPs in FP64, 1.5 TFLOPs in FP32, 3.07 TFLOPs in FP16 and 6.1 TFLOPs in FP8. Internally, Occamy consists of two computing blocks, each with up to 216 cores, interconnected by a silicon matrix that facilitates the passage of microscopic, high-density connections.
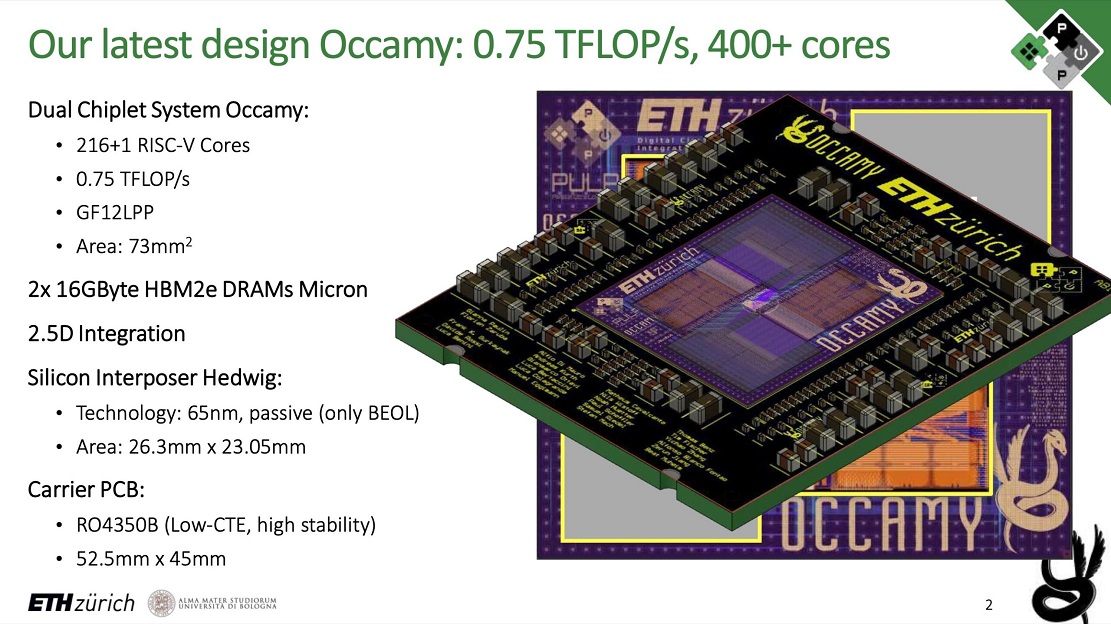
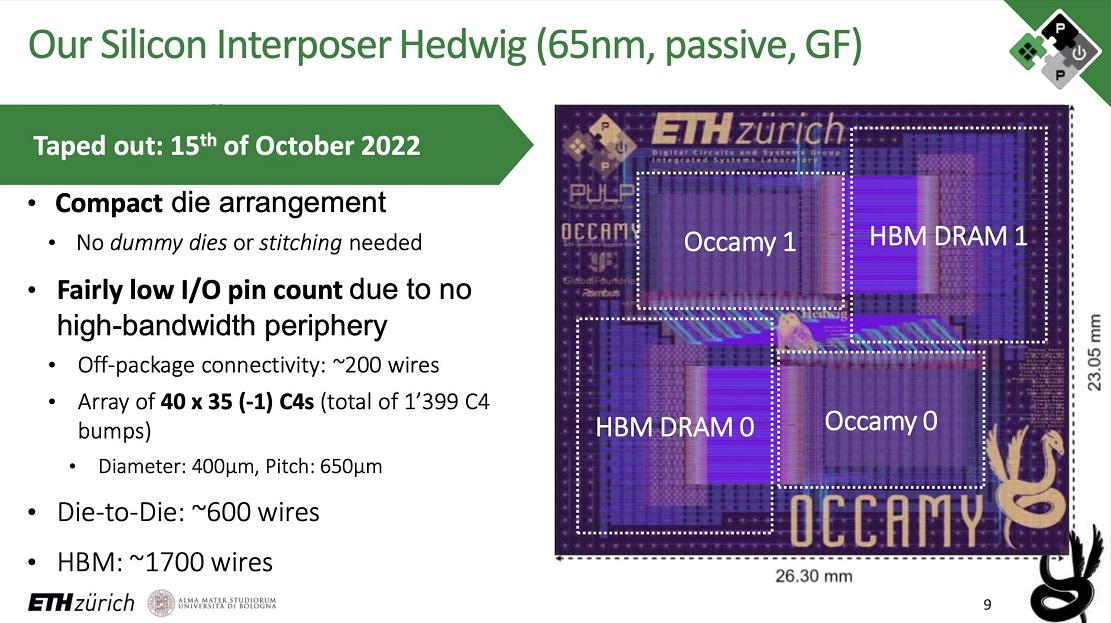
We continue to review the components of this impressive RISC-V CPU and find two 16GB blocks of 2.5D HBM2e integrated memory, it contains 64-bit floating-point units for matrix calculations and adds a total of one billion transistors in an area of just 72 mm square. Each package has consumption of 10 watts at a frequency of 1000 MHz.
Occamy also has a 32-bit RISC-V control chip which handles important tasks such as mapping data and routing information to the corresponding cores. The CPU was built on GlobalFoundry’s 12nm node, known as the GF12LPP, and the die, which acts as the interconnect system, is built on a 65nm node.
This processor will be used by ESA to create more efficient high-performance computing solutions, which will deal with work in space with workloads and processes associated with artificial intelligence, as well as other challenging tasks. In general, this is a very flexible processor that can be easily integrated into rugged computing modules that are ready to withstand the extreme conditions of space.
With Occamy, ESA has made important progress because this processor allows it to reduce its dependence on other companies such as ARM, it can be easily integrated into very durable modules and replicate at low cost. I remind you that this is not the first time that the RISC-V architecture has been chosen for a trip to space, already a few months ago we saw that NASA decided on it for future missions to Mars.















