Parker solar probe detects solar wind source
- June 14, 2023
- 0
The solar wind is the flow of charged particles or plasma From the Sun – it spreads to all the bodies of the Solar System and forms a
The solar wind is the flow of charged particles or plasma From the Sun – it spreads to all the bodies of the Solar System and forms a
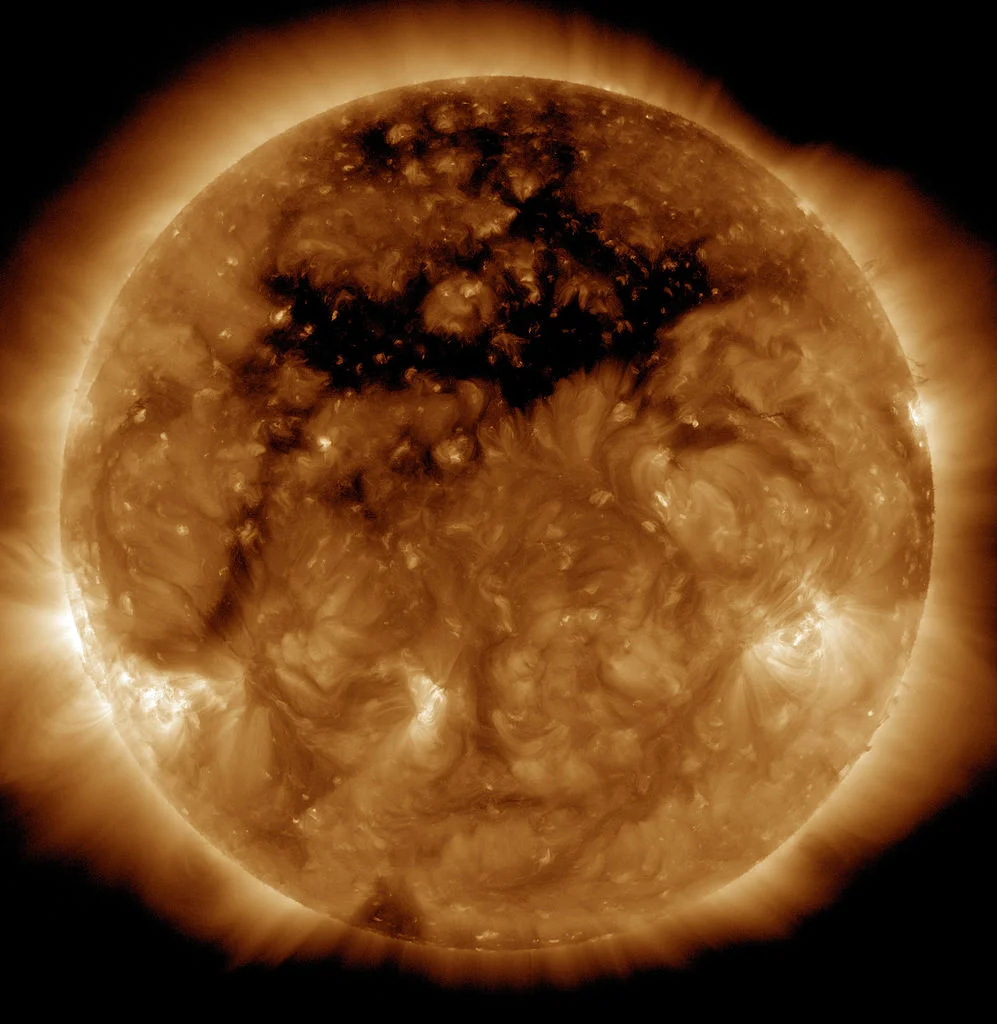
The solar wind is the flow of charged particles or plasma From the Sun – it spreads to all the bodies of the Solar System and forms a great bubble with the center of the Sun in the dark vacuum of space. It is important to life on Earth, but it also causes geomagnetic storms that cause power outages, auroras and other terrestrial disturbances. The mechanism of the solar wind is still not fully understood, so a research team led by Stuart Bale (University of California, Berkeley) set out to solve this problem.
Published team Nature was based on data collected by NASA’s Parker Solar Probe. Since its launch in 2018, Parker has orbited the Sun in a series of gradually narrowing orbits, bringing it closer to the Sun’s surface than any previous man-made object.
Parker even plunged into the atmosphere of the Sun, or crownPassing 5.3 million miles from the visible surface of the Sun, or photospherecovered with boiling “bubbles” called granulesas well as larger scale molds called super granules.
Parker was used to answer what accelerates the plasma and accompanying magnetic fields ejected from the photosphere to the corona. This solar wind It spreads at different speeds, fast and slow. While both wind speeds are related to magnetism in the Sun’s atmosphere, each has its own source. There is broad consensus that the fast solar wind originates. coronal holesRegions where the Sun’s magnetic field lines are effectively “open” and extend into interplanetary space before returning.
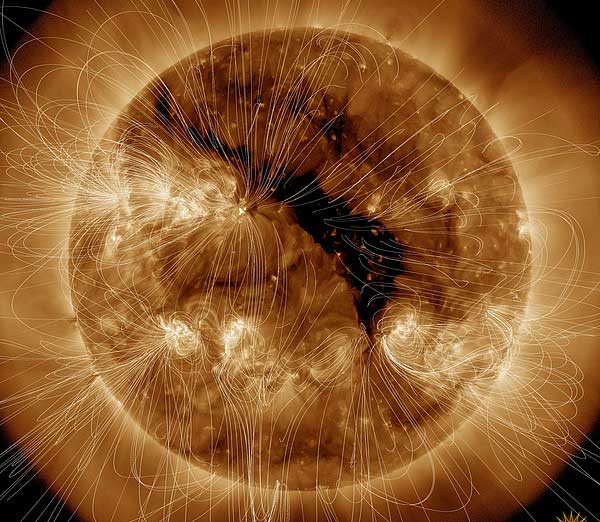
But what’s going on in these open spaces to drive the solar wind? There are two competing theories. known as magnetic waves. Alfvén waves passing through the plasma or magnetic reconnection . Both processes are known to take place on the Sun.
The researchers analyzed a series of measurements Parker made on his 10th birthday in November 2021. winter solstice , when it passes near the Sun. The probe measured the density and energy of the solar wind plasma, as well as the intensity of its magnetic field. The team combined this data with surface magnetic field measurements from the Solar Dynamics Observatory, a separate research fellow launched in 2010.
During the collision, the team found Parker’s microstreams — short jet bursts of high-speed solar wind. Using computer simulations, the team determined that these microstreams are likely driven by reconnection.
According to the reconnection hypothesis, plasma is accelerated from the surface of the Sun by magnetic reconnection inside the coronal holes, especially in the regions between the supergranules. Read more
Source: Port Altele
As an experienced journalist and author, Mary has been reporting on the latest news and trends for over 5 years. With a passion for uncovering the stories behind the headlines, Mary has earned a reputation as a trusted voice in the world of journalism. Her writing style is insightful, engaging and thought-provoking, as she takes a deep dive into the most pressing issues of our time.