Yesterday was a big day, AMD introduced the RDNA3 architecture and Radeon RX 7900 XT and Radeon RX 7900 XTX, two graphics cards that will be the most powerful models of the new generation of the Sunnyvale giant for the general consumer market. We already had enough information about them, we actually made a compilation with the most reliable Radeon RX 7000 data and finally most of the rumors we had on the table came true.
The Radeon RX 7900 XT and Radeon RX 7900 XTX use a chiplet-like architecture, but the GPU maintains a monolithic core design. It is important to distinguish because RDNA3 does not use two linked GPUsbut it integrates the GPU on a single chip and it is connected to six chips that contain only L3 cachealso known as infinite cache.

In the picture we can clearly see the design, The GPU is located in the central package, which is the largest, and the L3 cache is distributed in six smaller packages that surround it. With this design, AMD has freed up a significant amount of space at the silicon level in the GPU, and without having to give up that infinite cache. Imagine the complexity it would add to the GPU design and the space it would take up if all that cache was integrated with the GPU on a single chip, and thus in a single package.
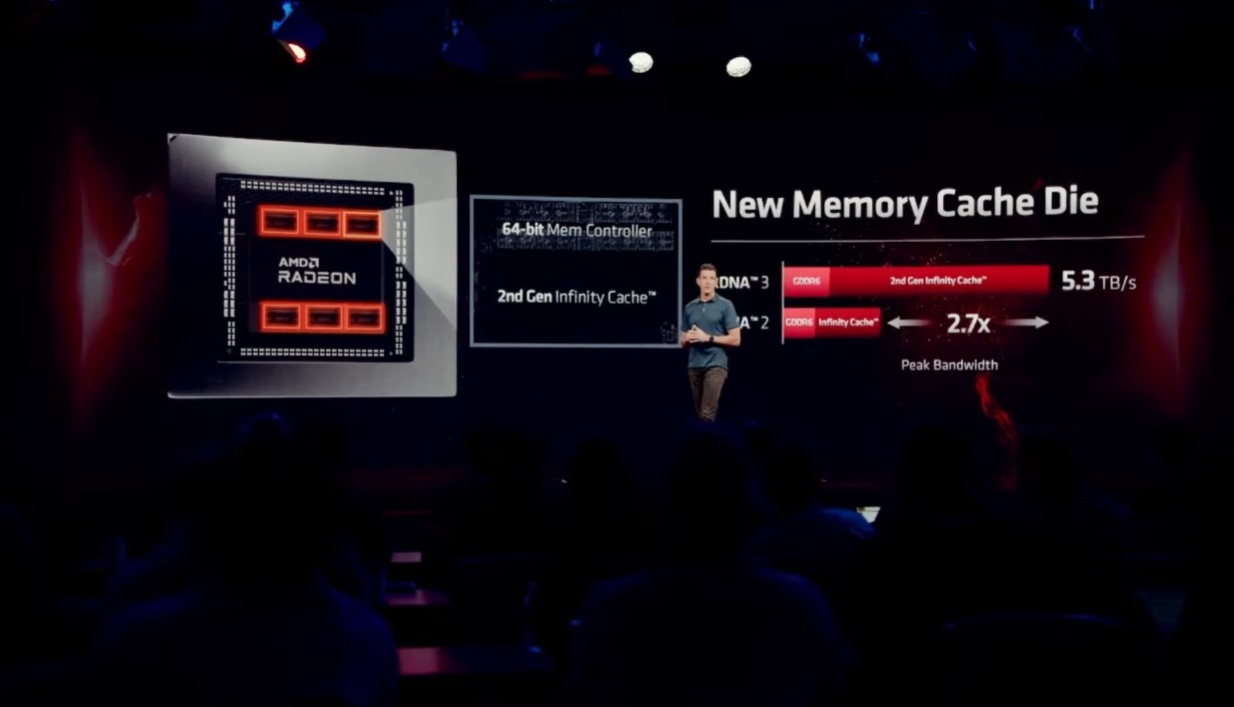
As we have already told you in the previous information, the GPU block is known as GCD, or “Graphics Core Die”and cache blocks are marked as “MCD” or “multi-cache die”. The GPU is manufactured in a node 5nmand each GCD uses a node 6 nm. GPU Navi 31 has total 12,288 shadersand each MCD adds 16MB of infinite cache and also integrates a 64-bit memory controller. Since we have six GCD units, we find 96 MB L3 in total and with a 384-bit bus. The bandwidth of the infinite cache has a peak 5.3 TB/s.

Radeon RX 7900 improves performance, efficiency and specialization
We have already seen that RDNA3 represents, precisely because of its design that externalizes the L3 cache, an important development compared to RDNA2, but the changes brought about by this architecture go much further and deserve an in-depth analysis. AMD has done it double the number of shaders per computing unit, which means we went from 64 shaders to 128 shaders. In this way, the Radeon RX 7900 XTX, which has 96 CUs, adds a total of 12,288 shaders. If the number of 64 shaders per CU was kept, it would only have 6,144 shaders.

The jump from 7nm to 5nm node in the GPU is another of the most important innovations. Using a more advanced node allows for better efficiency and transistor density, and also frees up space at the silicon level by reducing transistor size. That space that AMD freed up at the silicon levelthanks to the 5nm node and L3 cache outsourcing, was optimally usedas the Sunnyvale giant has confirmed that the Radeon RX 7900 XT and XTX integrate:
- The second generation of beam-tracing accelerator cores.
- Artificial Intelligence Acceleration Units.

So the Radeon RX 7900 XT and XTX are the first mainstream graphics cards from AMD to include specialized AI coresa component that we can consider equivalent to NVIDIA Tensor Cores and Intel XMX Arrays.
We can infer that from what AMD showed at the launch of both graphics cards the RDNA3 compute unit consists of 128 shaders, two AI accelerators and a ray tracing accelerator. The number of texturing units per CU should be 4.

New ray tracing accelerators in theory improve performance by 50% over the previous generationwhich means that the Radeon RX 7000 has made an important generational leap in this regard compared to the Radeon RX 6000. The performance data shared by AMD allows us to compare the GeForce RTX 4090 and the GeForce RTX 3090 Ti, and here are the results:
- In Cyberpunk 2077 With 4K resolution, maximum quality and ultra ray tracing, the Radeon RX 7900 XTX, with FSR enabled in performance mode, achieves 62 frames per second. If AMD used performance mode, this result lags behind 67 frames per second you get a GeForce RTX 3090 Ti with DLSS 2 in performance mode and it’s a long shot 139 frames per second which the GeForce RTX 4090 achieves with ray tracing in insane and DLSS 3 in performance mode.
- In Dying Light 2 With 4K resolution, maximum quality and ultra ray tracing, the Radeon RX 7900 XTX achieves 72 frames per second. Given the huge improvement that FSR indicates, we assume it was configured in performance mode. With the same settings and DLSS 2 in performance mode, the GeForce RTX 3090 Ti achieves 77 frames per second on average and the GeForce RTX 4090 achieves 130 frames per second.
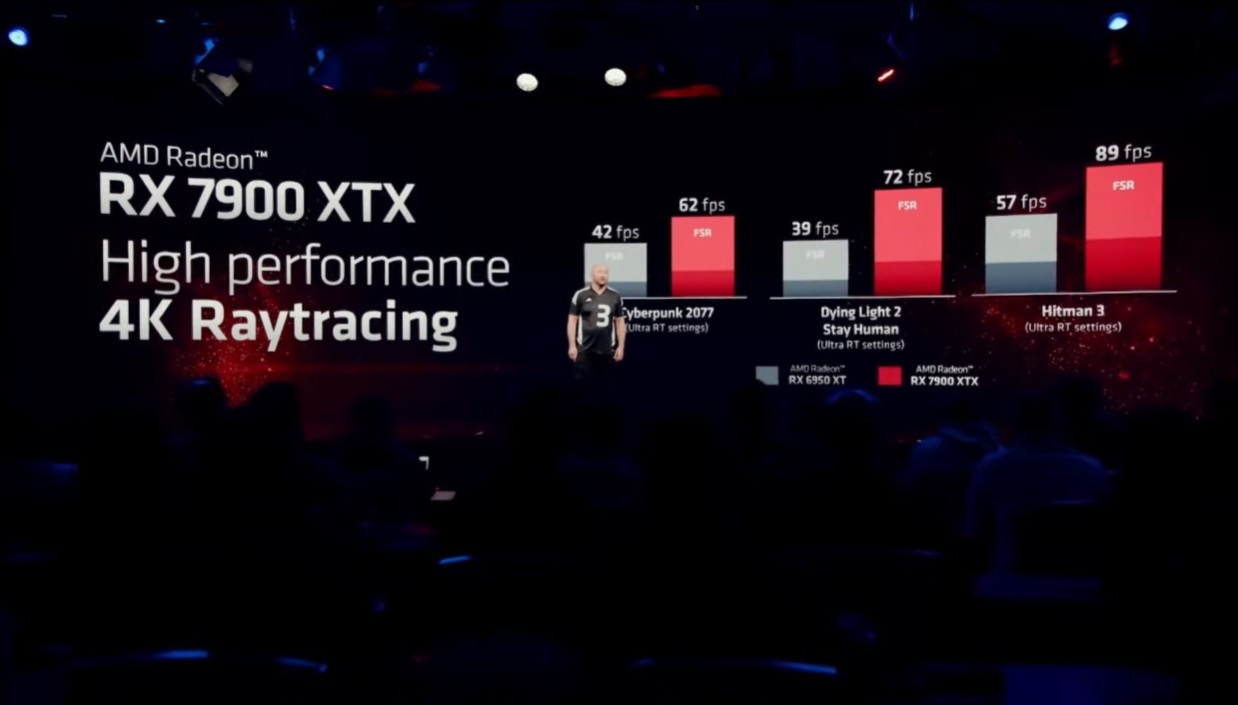
I wanted to do this comparison to give you a more realistic idea of what we can expect from the Radeon RX 7900 XT and XTX in ray tracing, and yes, it’s clear that Although we have an important generational improvement, the RDNA3 architecture is still not at that level of NVIDIA’s most advanced when it comes to ray tracing. This was exactly one of the things the Radeon RX 7000 needed to directly compete with the GeForce RTX 40 and improve its ray tracing performance.
In terms of raw performance, AMD has confirmed that the Radeon RX 7900 XTX will peak at 61 TFLOPs. Architecture of RDNA3 improved efficiency by 54%and will be able to perform two instructions per clock cycle in the shaders. Another interesting detail is that AMD differentiated shader and frontend frequencies, which will operate at slightly different levels to “improve efficiency,” in the company’s words.

Radeon RX 7900 XT and XTX support Simultaneous encoding and decoding according to the AV1 standardand are also compliant with standards DisplayPort 2.1 and HDMI 2.1awhich means that we can play with them in 4K resolution with a refresh rate of up to 480 Hz, or in 8K with a refresh rate of up to 165 Hz.
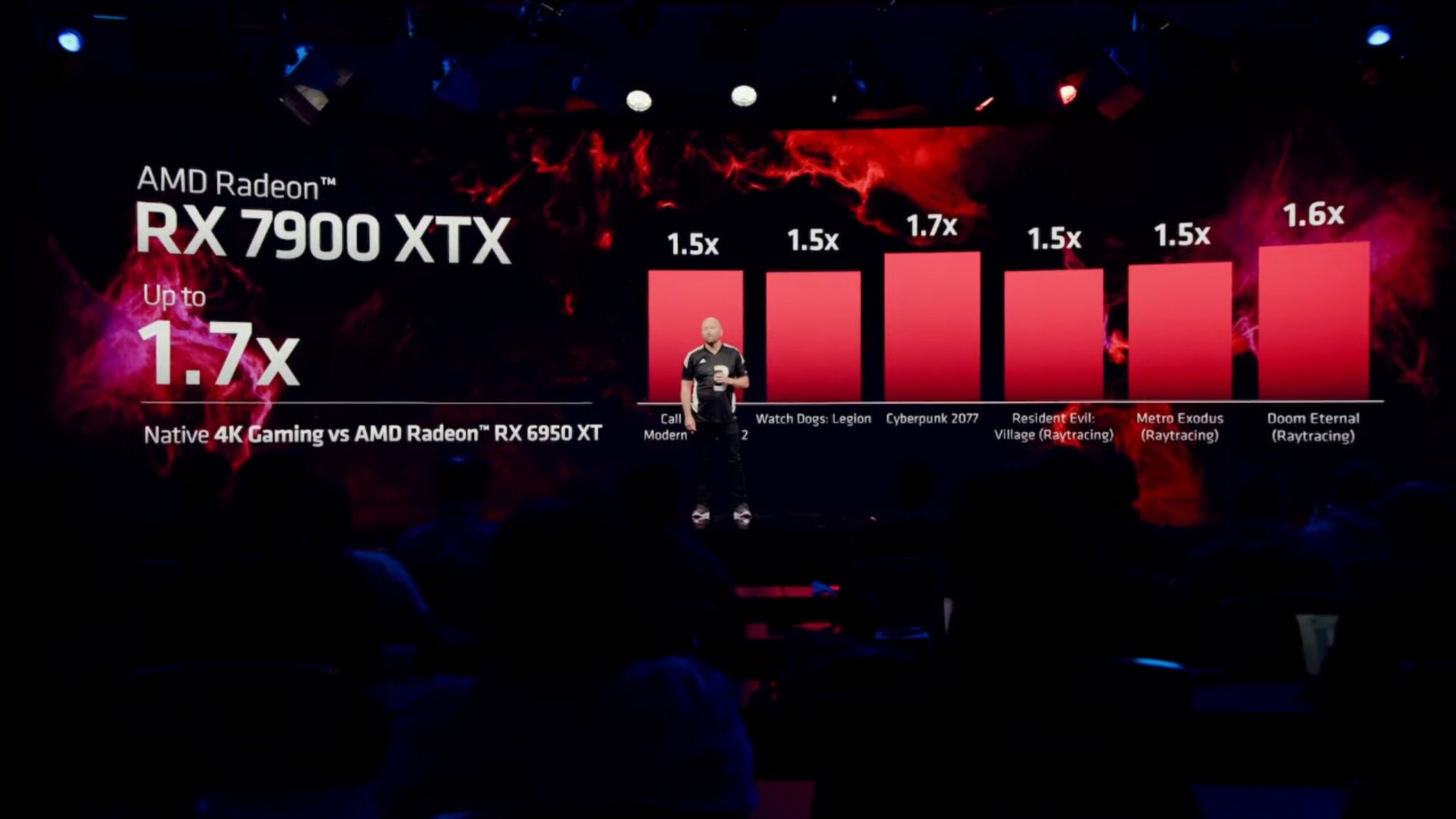
AMD also took the opportunity to compare the performance of the Radeon RX 7900 XTX against the Radeon RX 6950 XT and it was clear what we can expect 50% to 70% improvement, depending on the game used, with 4K resolution. In the attached graph, we can see the captions used in the comparison.

Radeon RX 7900 XT and XTX specs, price and release date
Both graphics cards will be available from December 13, and they will be very similarly priced, confirming that the performance differences between the two will be quite small. The Radeon RX 7900 XT will cost $899 and the Radeon RX 7900 XTX will cost $999. Please note that in both cases these are prices without taxes and that in Spain after currency conversion and taxes are applied would correspond to 1,110 euros and 1,213 euros.
Radeon RX 7900 XT specifications

- Navi 31 graphics core with MCD (Multi-chiplet Die) design in a 5nm node for the GPU block and a 6nm node for the cache block.
- 10,752 shaders.
- 336 texturing units.
- 192 raster units.
- 2GHz-2.4GHz GPU, normal and turbo mode.
- 52 TFLOPs of performance in FP32.
- 84 computing units.
- 84 second generation ray tracing acceleration units.
- 168 units for AI acceleration.
- 320-bit bus.
- 20 GB GDDR6 20 GHz memory with 800 GB/s bandwidth.
- 80 MB infinite cache.
- PCIe Gen5 interface.
- 300W TBP, requires two 8-pin power connectors.
Radeon RX 7900 XT specifications

- Navi 31 graphics core with MCD (Multi-chiplet Die) design in a 5nm node for the GPU block and a 6nm node for the cache block.
- 12,288 shaders.
- 384 texturing units.
- 192 raster units.
- GPU at 2.3 GHz-2.5 GHz, normal and turbo mode.
- 61 TFLOPs of performance in the FP32.
- 96 computing units.
- 96 second generation ray tracing acceleration units.
- 192 units for AI acceleration.
- 384-bit bus.
- 24 GB GDDR6 20 GHz memory with 960 GB/s bandwidth.
- 96 MB of infinite cache with 5.3 TB/s bandwidth.
- PCIe Gen5 interface.
- 355W TBP, requires two 8-pin power connectors.
























