For most children “What will you be when you grow up?” The answer we got when we asked “Astronaut”friendly. This profession, which offers the opportunity to explore the depths of space, has undoubtedly graced the dreams of many of us as children. But you will appreciate that astronaut is also of the world The hardest It is one of his professions. So much so that this profession often demands that you put your work above your private life and give a lot of yourself.
However, the challenges of astronauts are not limited to this. Being in a different environment than the Earth’s atmosphere to which you have been accustomed for a long time, of course, has some consequences for your body. Even months after astronauts return to Earth, a new study shows: clear changes in their brains is one of these results.
For the first time, major changes are taking place in the brains of astronauts in space
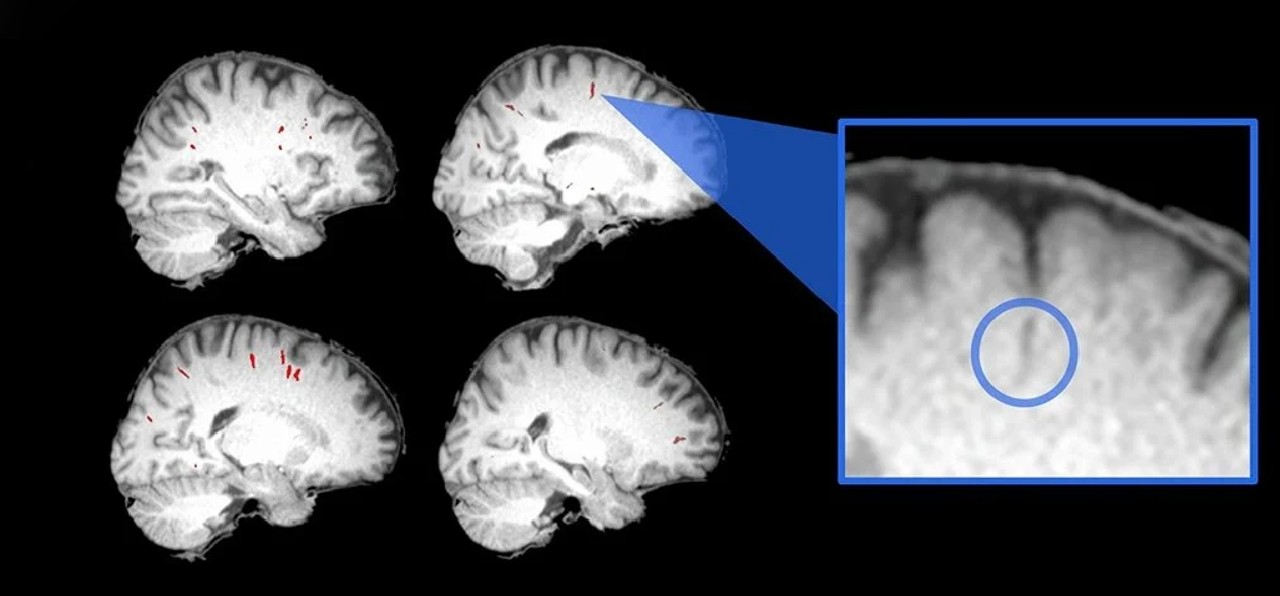
Astronauts are among the missions, according to the latest assessments of the warping effect of microgravity on our biology, focusing on the areas around the blood vessels that run through our brains. to worrying changes exposed.
Researchers from across the US compared a series of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the brains of 15 astronauts before they went to the International Space Station and six months after their return. spaces in brain tissue thought to facilitate fluid balance perivascular spaces team using algorithms to carefully evaluate their size; time spent in orbit, at least cerebral vascular pathways of new astronauts was found to have a profound effect on
Brain scans of senior astronauts show no major changes

On the other hand, the dimensions of the perivascular spaces of the studied experienced astronauts differed from each other in two scans taken before the mission and four scans after it. not very different popped up. Neurologist Juan Piantino of Oregon Health and Science University says experienced astronauts are kind of ‘homeostasis’ that the body has undergone changes to adapt to environmental differences. balance He explains by saying that he may have reached his status.
Given what we already know about how the brain degrades in the absence of constant gravity, these findings may not be too surprising. Previous studies of brain tissue and fluid volumes have shown that their recovery after space travel slow is; even a year of some changes or longer time appeared to continue.
Astronauts’ brains in space are adapting to a new kind of ‘normal’

Currently, astronauts very rarely make more than a few trips to space in their lifetime and usually stay in space for about six months at a time. However, with developments in space science in recent years, the space industry has become more and more become more commercial This means that this situation may change. At this point, it’s clear that repeated journeys are harmful, and the changes that occur in astronauts’ brains during the first trip to space will leave them wondering. to a new kind of ‘normal’ It is very important to understand whether it adapts or not.
Even with enlarged perivascular spaces, it is not yet clear whether this change poses a significant health risk. Unknown† It is too early to say whether microgravity has any effect on cerebrospinal fluid circulation, or whether changes in the shape of the duct networks are significant. And it looks like it will remain a mystery until researchers have many more examples of senior astronauts.
But hypothetically speaking, if these channels in the brain don’t work efficiently, there could be a buildup of destructive materials in the brain, potentially leading to that of a person, in this case astronauts. neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease can contribute to its development.
















