Engineers managed to insert an electronic chip into the goat’s brain without opening the skull. To do this, they used an endovascular device inserted through a vein and began accurately reading the animal’s brain signals after it had moved to the desired area of the motor cortex.
According to the developers, the new approach is much safer than open neurosurgery, which carries the risk of infection and tissue damage. The major advantage of this technique is that no invasive surgery is required to obtain electrical signals in the open brain. In addition, the entire operation can be completed in less than two hours, according to scientists.
This approach is an entirely new way of capturing the brain’s electrical signals. This solution could be a breakthrough technology,
– said Professor Duan Feng, who headed the project.
He also noted that this experiment is the first of its kind for the Chinese scientific community.
how was the operation
In the research, Feng and colleagues placed a stent in a vein and routed it through the veins to the motor cortex of the animal’s brain. The chip itself was delivered to the right place via the stent. With the sensor in the correct position, he attached the electrodes to the vessel walls and began recording strong and clear electrical signals from the goat’s brain. The operation was carried out with the help of a high-precision robot. The collected data was transferred to a remote computer.

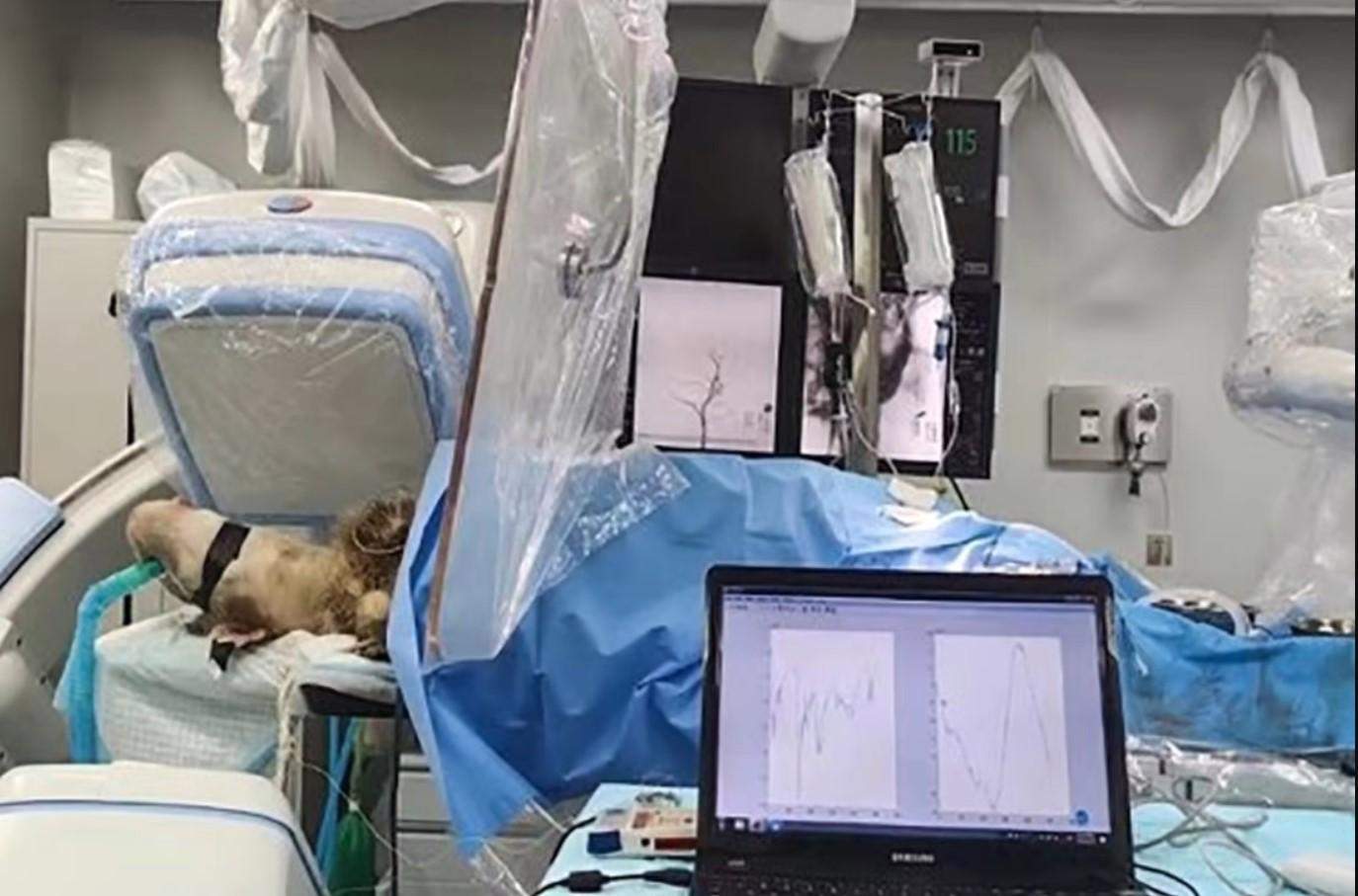
Scientists non-invasively used goat chip / Photo Nankai University
According to the head of the project, conventional implants are destructive compared to the described technology and are far from the practical application of the system. By using endovascular devices instead, scientists and doctors will be able to guarantee the safety of surgery and brain integrity for their patients, Feng is sure.
Development of neuroimplants
It is worth noting that brain implants are nothing new and groundbreaking. Today, these devices help thousands of people around the world suffering from diseases that cannot be treated with other methods. In particular, we are talking about Parkinson’s disease, stroke and other diseases of the brain and nervous system.
With the development of technologies, promising projects began to appear more and more often – in addition to pharmaceutical and biochemical companies, large IT companies participated in work on neuroimplants.
One company you may have heard of is Neuralink, founded by Elon Musk. The company is working on wireless microchips that work on the basis of artificial intelligence. The peculiarity of Neuralink is that the neuroimplant will be implanted in the human brain with the help of a special robot that does it on its own, very precisely and absolutely safely, as Musk claims.
However, the invasive technique, however automated, poses significant risks of infection and brain tissue destruction. The same Neuralink had to put eight experimental monkeys to sleep because of its failed experiments. But most of the tests at the American company were successful, so next year Neuralink plans to move on to experiments with the participation of people.















