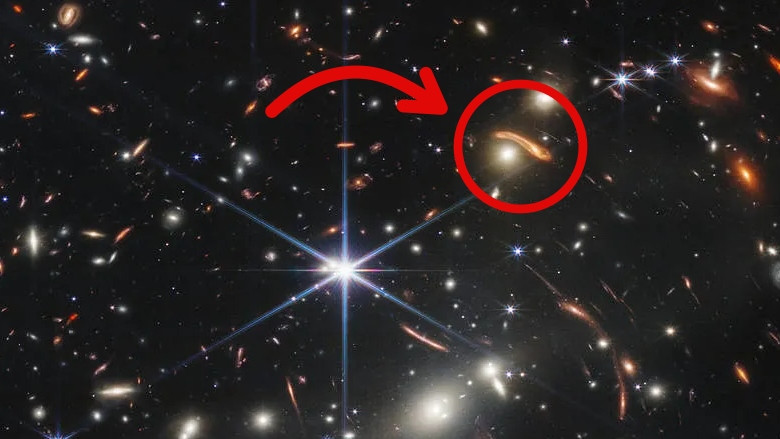
As humanity advances at full speed to explore the unknowns in the depths of space, an important exchange was made last night that will go down in space history. NASA sent it into space after years of delay of the James Webb Space Telescope He shared the first color photo he took with the world.
In that photo of the SMACS 0723 cluster, where many galaxies can be observed simultaneously, there were stars and galaxies in every area the eye could see. This photo, which reminds us of the eternity of the universe and our smallness, is also A phenomenon that has caught the attention of many. He also had: Some of the galaxies seemed skewed, especially in the center of the photo, as if they had entered an invisible gravitational field. So what was the reason for this?
Why do galaxies appear curved?

In the above image, taken by the James Webb Space Telescope, the galaxies in the highlighted area appear skewed,’gravity lensingIt is caused by a condition called ‘. Let’s take a closer look at this situation, which is one of the predictions of Einstein’s general theory of relativity and has been proven many times over with pictures.
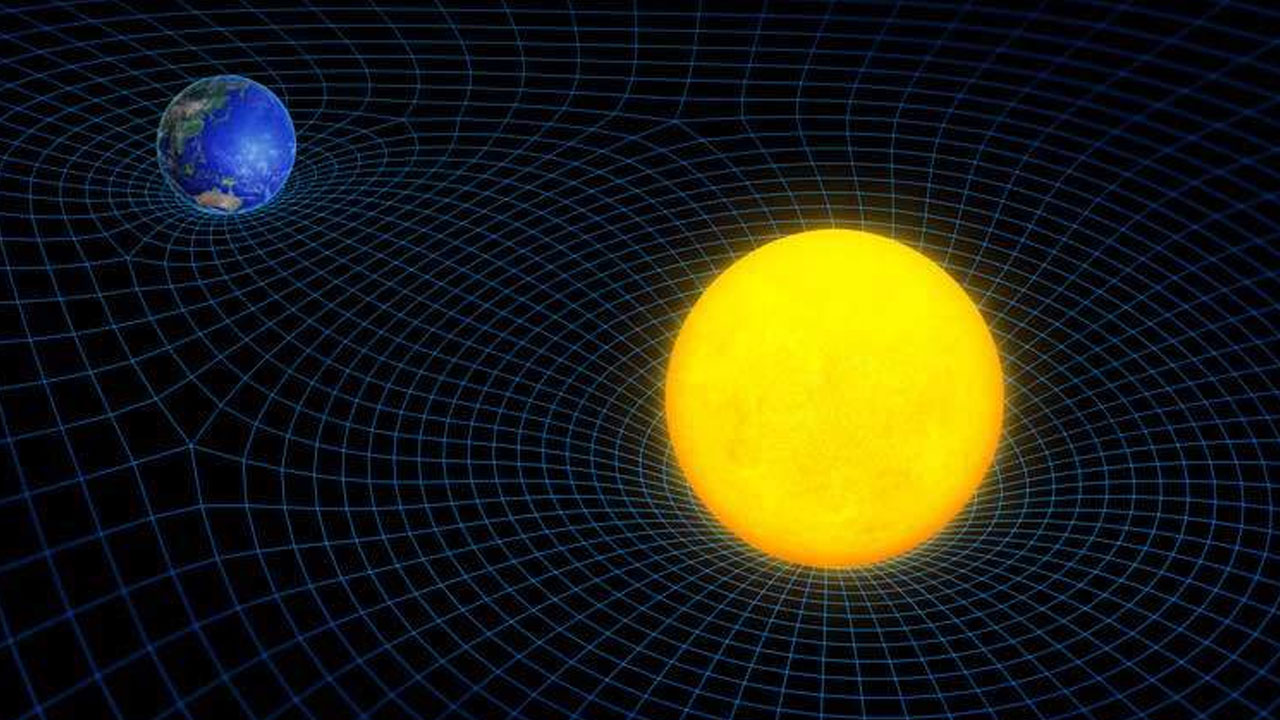
Every object in space has a mass, and this mass of objects can bend space and time around it. This bend allows you to observe all in the image below actual position of the objectaccording to its position reflected in our eye and telescope lenses It could be different† The first evidence of this was provided by Arthur Eddington and Frank Watson Dyson during the solar eclipse of 1919, when they saw that light coming from stars passing very close to the sun was deflected.

According to the general theory of relativity, light also follows these curves that occur in space-time. Therefore, when light goes around a massive object, it is bent due to the bending of space-time by the effect of that object. The journey of light through warped space, to humanity The chance to observe celestial bodies that are hidden behind other objects and that are very far away. can give. An example of this situation can be explained with the following image:

In addition, this situation can lead to the appearance of other structures behind the massive structures more than once. For example, in the image below, a quasar, which is actually behind a giant galaxy, is due to the diffraction of the light it emits. It can appear as separate celestial bodies in four different places.
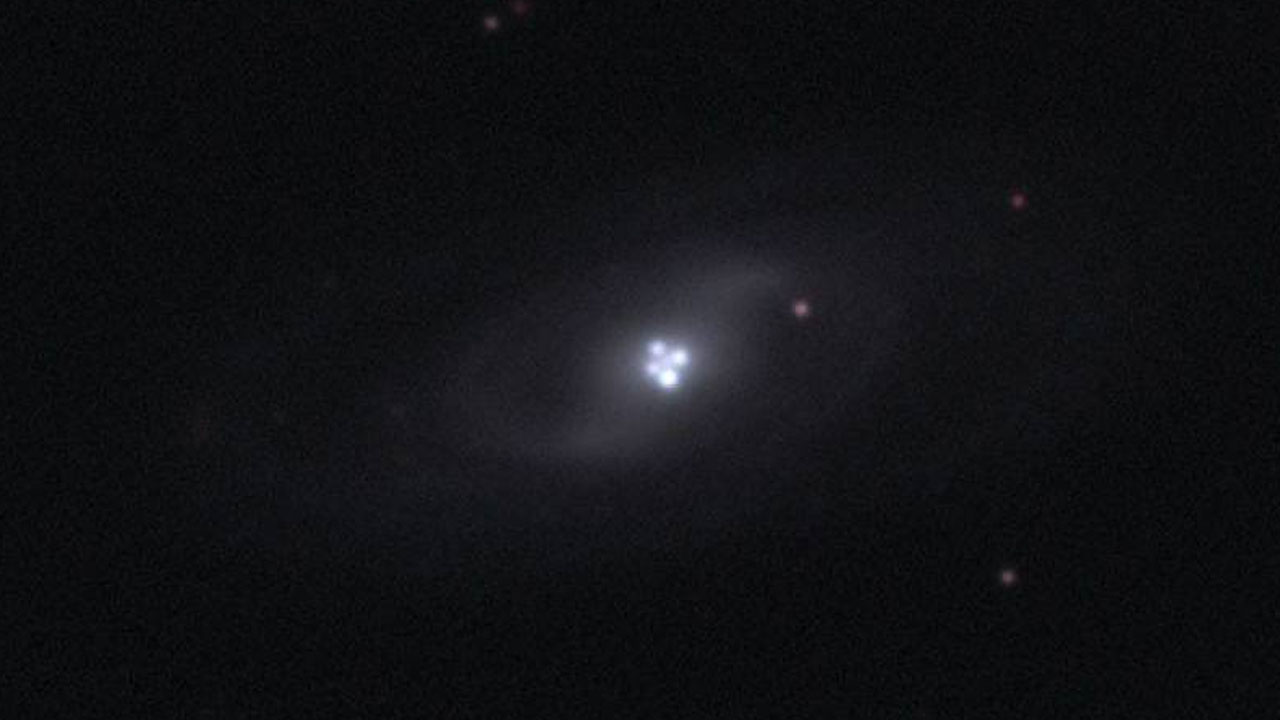

Therefore, the new image, which is the clearest image of the distant universe ever captured, clearly shows the effect of gravitational lensing. Some galaxies that we wouldn’t be able to see without this effect have the potential to be some of the oldest galaxies. Of course, these galaxies billions of years ago We also have to consider what we see.