Since 1995, when a planet like Earth was discovered orbiting a Sun-like star, more than 4,000 exoplanet had been discovered. More than half of these discoveries were made thanks to the Kepler Space Telescope, which began work in 2009 to determine if there is another planet with Earth-like living conditions in the Milky Way galaxy.
with conditions similar to planet Earth, habitable Discovering a planet has long been a dream of astronomers. Small, rocky worlds like Earth have been proven to exist in the galaxy, although they don’t have exactly the same features as the recently discovered exoplanets. The bride is the most earthy ever discovered 10 exoplanets What is it, let’s see together.
How is a planet classified as ‘earth’?

First, let’s see what it takes to classify a planet as a habitable world. To put it very simply, a planet that could be considered potentially life-friendly is not only relatively small and rocky, but can also exist in liquid form on the surface of the water orbiting its star. “habitable zone” It should run in the position defined as .
On the other hand, with the further development of existing telescopes with the evolving technology, in addition to these factors, the planet atmospheric compositionIt will be possible to consider other factors such as how active i and its main star are.
Here are 10 potentially life-friendly Earth-like exoplanets
Gliese 667Cc

Discovered with the 3.6-meter telescope at the European Southern Observatory in Chile and just 22 light-years from Earth, according to NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Gliese 667Cc, at least 4.5 times bigger than our planet. This exoplanet, which completes an orbit around its parent star in just 28 days, is believed to be in the habitable zone because this star is a much cooler red dwarf than the Sun.
But of course the warmth of the planet of the red dwarf will overheat It will also likely orbit as close to Earth as possible.
Kepler-22b

Located 600 light-years away, Kepler-22b is the first Kepler planet to be in the habitable zone of its main star. However, it is currently unknown whether the planet, which is about 2.4 times larger than Earth, is rocky, liquid or gaseous.
On the other hand, Kepler-22b, which orbits its star in 290 days, comes pretty close to Earth’s 365-day cycle. Although the exoplanet orbits a G-class star like our sun, this star is smaller and smaller than Earth’s. cold is known.
Kepler-69c

It completes its orbital cycle in 242 days. Kepler-69cThe position of Venus in the solar system is similar to the position of Venus in our system. This exoplanet appears to be in the habitable zone because its parent star is 80 percent brighter than the sun.
But let’s face it, Kepler-69c, located about 2,700 light-years away, is away from Earth. 70 percent ratio is greater. For this reason, scientists currently have no idea about the planet’s component.
Kepler-62f
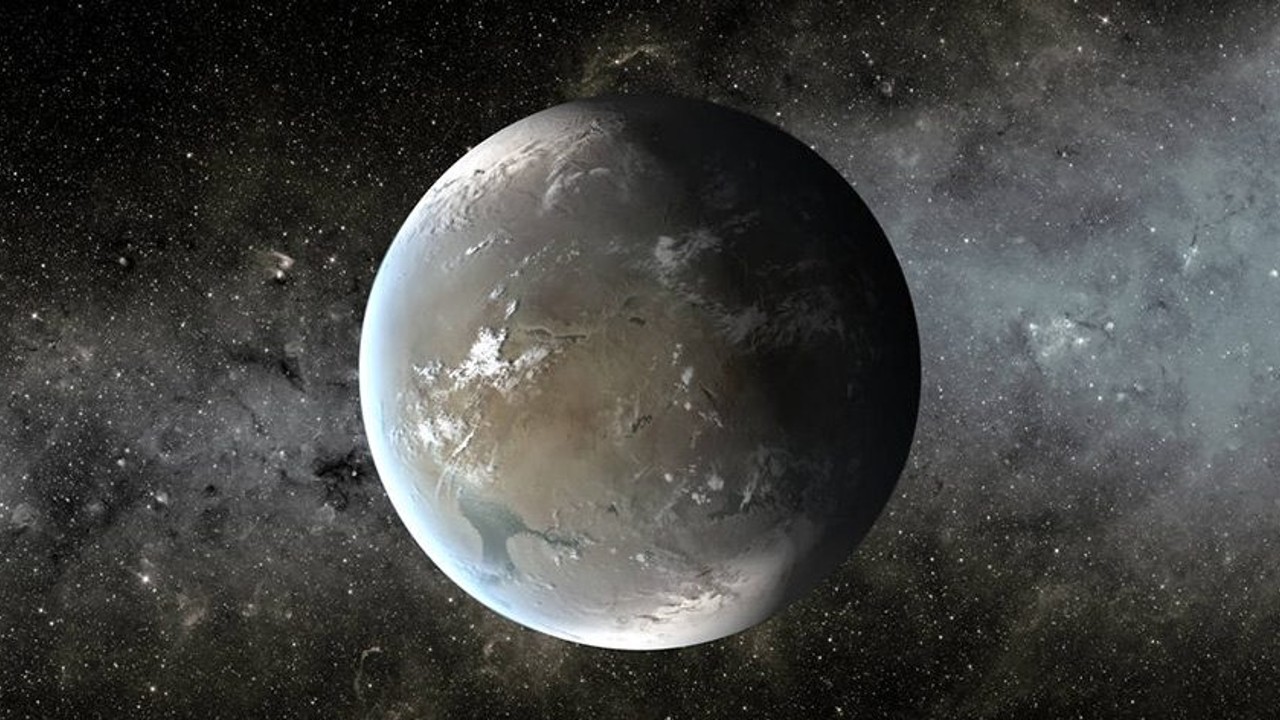

according to NASA Kepler-62fIt orbits a star that is about 40 percent larger than Earth and much cooler than our sun. But its 267-day orbit makes Kepler-62f a member of the habitable zone class. Kepler-62, the star of this exoplanet, which orbits much closer to its red dwarf star than Earth does to the sun, produces much less light.
The size of Kepler-62f, which is about 1200 light-years from Earth, is potentially: have oceans characterizes it as a rocky planet.
Kepler-186f
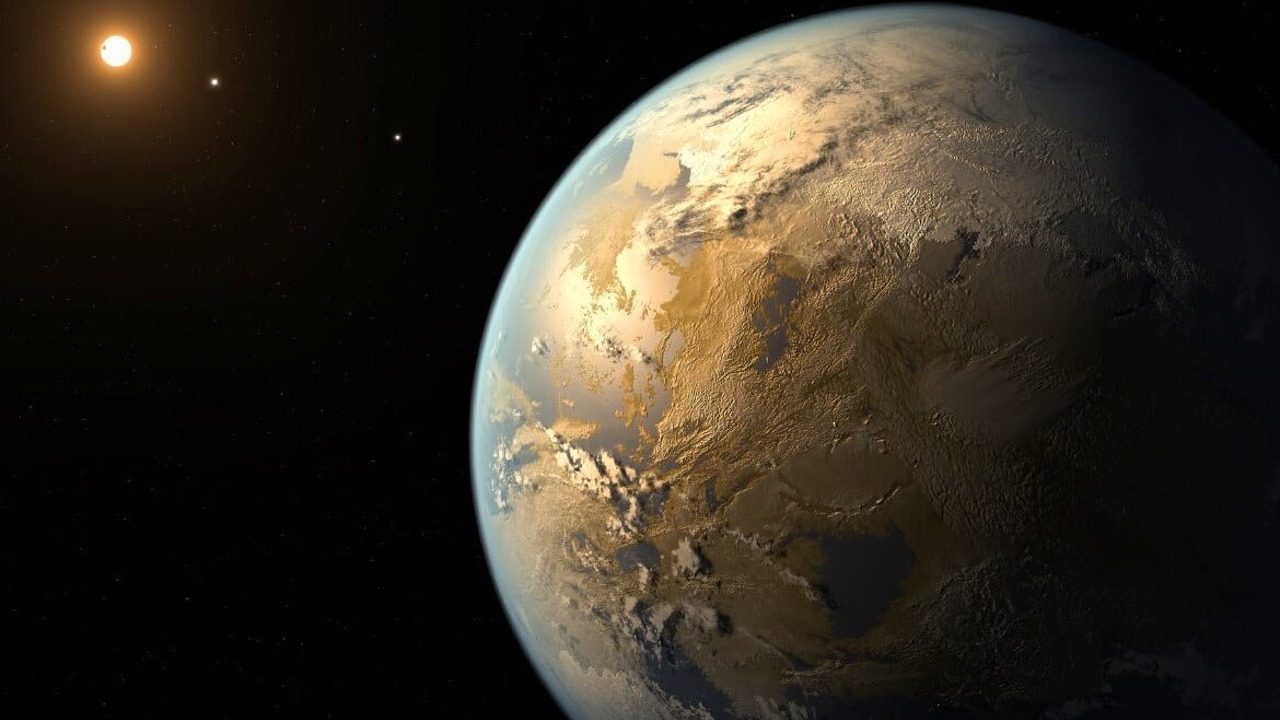

Kepler-186fIt is located about 500 light-years from Earth. Kepler-186f, which is up to 10 percent larger than Earth; It appears to be in its star’s habitable zone, although it is slightly out of the way.
Since the main star is a red dwarf, Kepler-186f cannot be said to be a true twin of Earth. Moreover, this exoplanet is the only energy source that the earth receives from the sun. a third he gets his star.
Kepler-442b
Discovered in 2015 at 1,194 light-years away, it is 33 percent larger than Earth, according to NASA. Kepler-442bcompletes its star’s orbit every 112 days.
A study published in 2021 suggests that this exoplanet must maintain a large biosphere. enough light He claims he can. According to researchers who have analyzed the possibility that different planets photosynthesize, Kepler-442b receives enough radiation from its star.
Kepler-452b
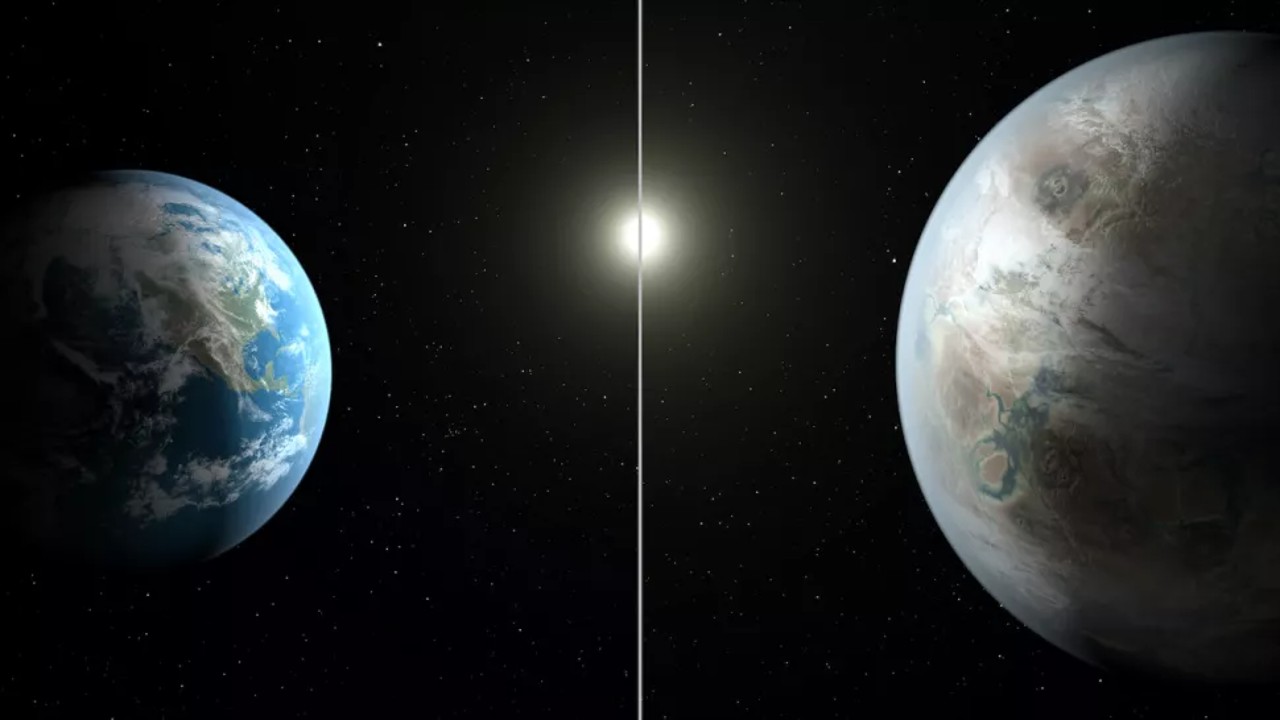

This world, whose discovery was announced in 2015, is the first planet in size close to Earth to orbit a star the size of the Sun, according to NASA. 60 percent larger than Earth and 10 percent larger than the Sun with its main star Kepler-452b† It is very similar to our sun and is in the habitable zone.
According to the data obtained, Kepler-452b, which is 1.6 times the size of Earth, is just as likely to be rocky. Kepler-452b’s orbit around its star, located 1,400 light-years away, is only distant from Earth. more than 20 days It takes 385 days to complete.
Kepler-1649c: Like Earth’s Fraternal Twins
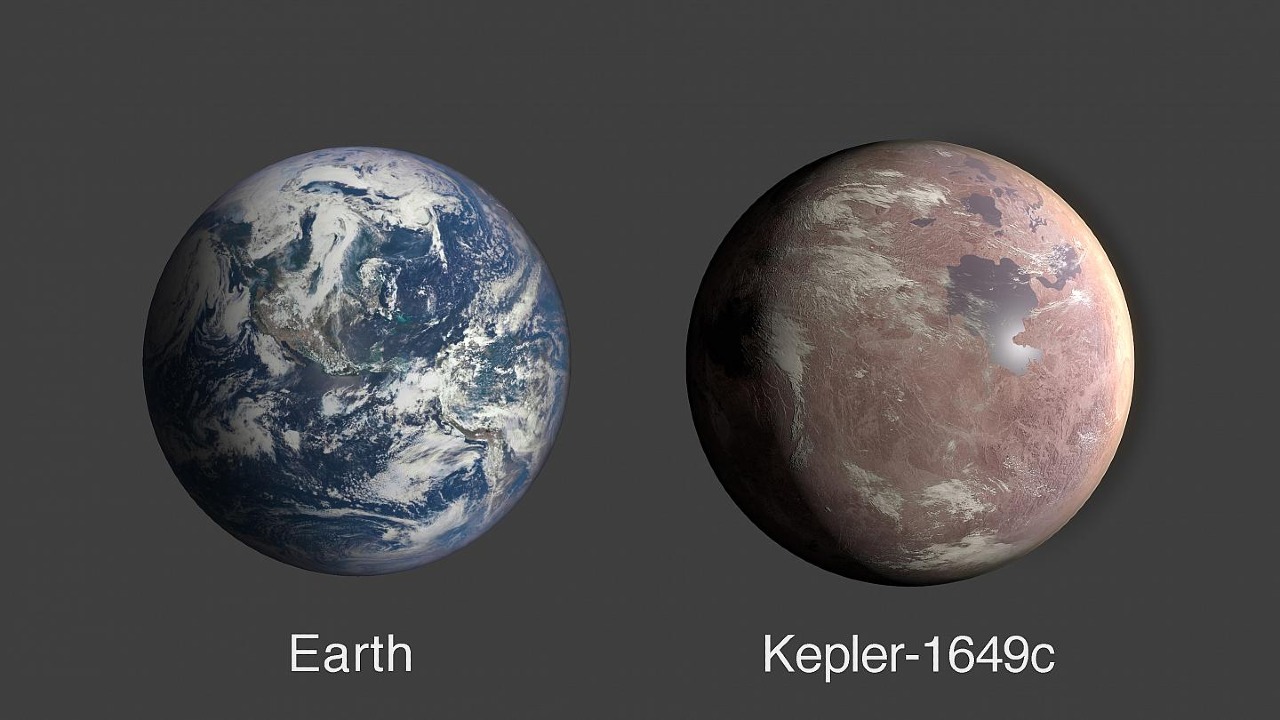

Earthy Dimensions Kepler-1649c, located in the habitable zone around its star. Located 300 light-years away and only 1.06 times larger than Earth, this exoplanet receives 75 percent of the light Earth receives from its star’s sun.
Proxima Centauri
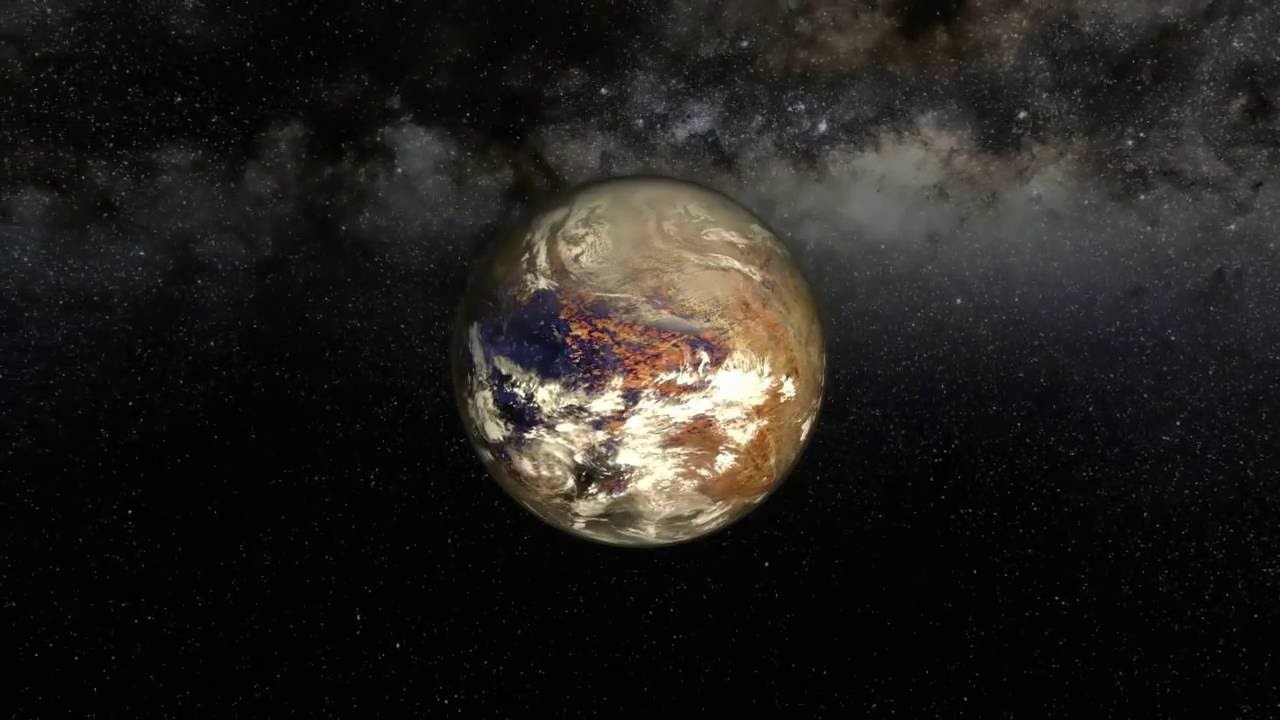

Located just 4 light-years from Earth Proxima Centauri, stands out as the closest known exoplanet to Earth. The exoplanet’s mass, discovered in 2016, is 1.27 times that of Earth.
On the other hand, although it is in its star’s habitable zone, this exoplanet is extreme ultraviolet radiationis exposed to. The reason for this is that the planet is very close to its star and completes its orbit in 11.2 days.
TRAPPIST-1st
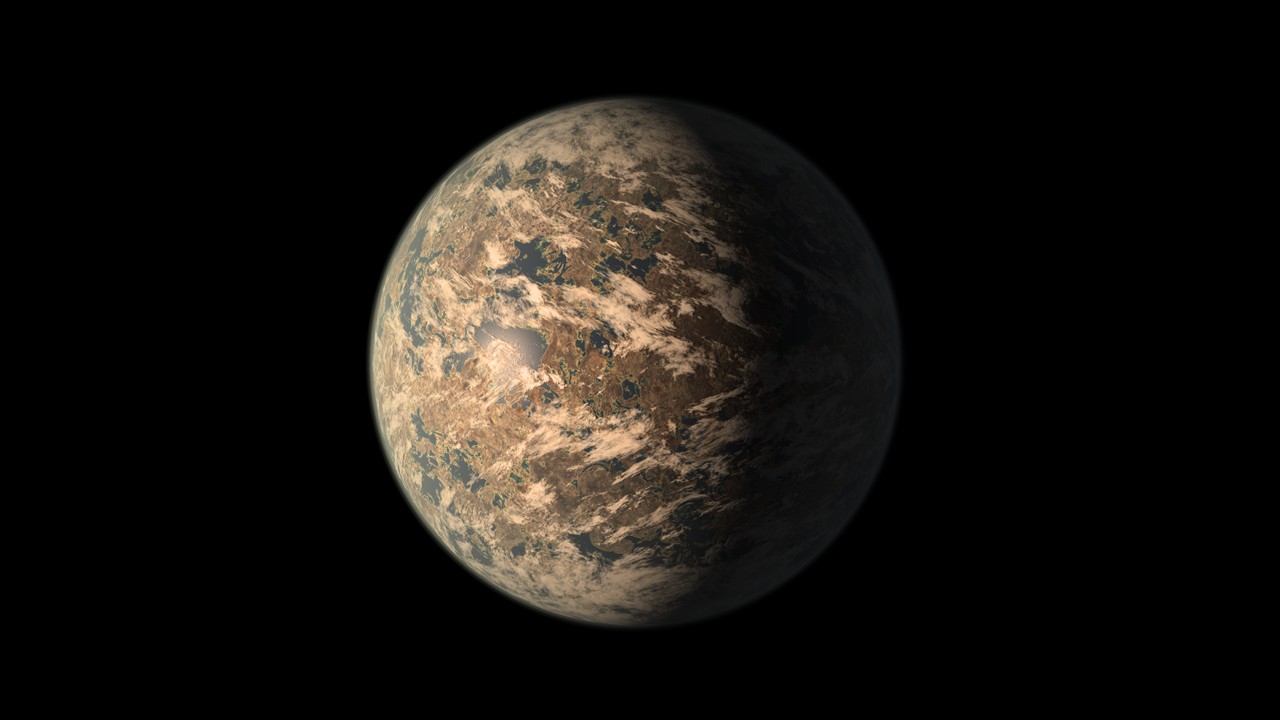

The planets orbiting the star TRAPPIST-1 are the most Earth-sized planets ever discovered in the habitable zone of a single star. However from seven worlds It is very likely that the water has evaporated on most of the planets in this planetary system.
Some planets in the system may also contain more water than Earth’s oceans, according to a 2018 study. TRAPPIST-1st The chance of life on Earth is estimated to be quite high.




















![Smart introduces Smurf or Smurf new electric SUV concept [Video] Smart introduces Smurf or Smurf new electric SUV concept [Video]](https://cdn.webtekno.com/media/cache/content_detail_v2/article/122510/smart-konsept-ete-kemige-burunmus-hali-gosterdi-1649416228.jpg)



