Mars may ‘bubble’: planet found may have magma beneath its surface
- October 29, 2022
- 0
The more we learn about Mars, the stronger the theory that the red planet was once a habitable place and has become what it is after a catastrophe.
The more we learn about Mars, the stronger the theory that the red planet was once a habitable place and has become what it is after a catastrophe.
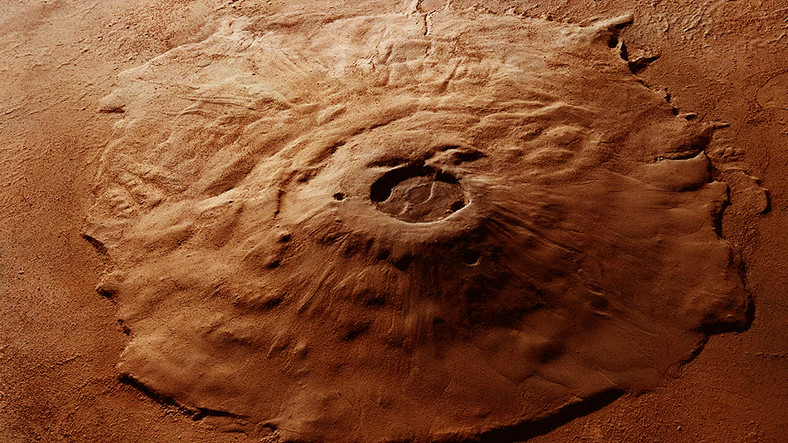
The more we learn about Mars, the stronger the theory that the red planet was once a habitable place and has become what it is after a catastrophe. Because many studies have been conducted so far that the planet may have been quite mindful of our world in the past.
Another important news about Mars was the “active volcanic structure” claims, which were reinforced by the recently obtained data. A new study has bolstered these claims, showing that magma is present beneath the surface of Mars. Besides, this magma isn’t dried or anything, active and vibrant. Let’s look at the details.

In light of data obtained from NASA’s InSight exploration vehicle, scientists at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH Zurich), Earthquakes on Mars examined. Examining the earthquakes showed that most of the widely distributed surface faults found on Mars were not seismically active, and that seismicity was largely due to a single tectonic structure.
This structure, called Cerberus Fossae, is actually a series of semi-parallel fissures formed by crustal fractures in the Cerberus region of the red planet. The team, which also examined the region’s low-frequency seismic activity data, Potentially hot, liquid magma at a depth of 30-50 km and that there may be active volcanic activity.
In addition, according to the information from the images and data around the same region, this region may be the region where the last active volcanic eruption on Mars occurred. The research team found that the dark dust found in the region is the remnant of volcanic activity and that these remnants are about It can be dated to 50,000 years ago. there is.
The most striking result of the study was the following statement from the team members:What we see are the last remnants of this once active volcanic area, whether magma is now moving east. on the way to the next blast site possible.“So maybe in the future we’ll see a big volcanic eruption on Mars, who knows…
Source: Web Tekno
Alice Smith is a seasoned journalist and writer for Div Bracket. She has a keen sense of what’s important and is always on top of the latest trends. Alice provides in-depth coverage of the most talked-about news stories, delivering insightful and thought-provoking articles that keep her readers informed and engaged.