How close does a supernova explode to Earth?
- December 27, 2022
- 0
one of the most glorious events in our universe, supernova explosions have caught the attention of almost everyone interested in space. These massive explosions are powerful enough to
one of the most glorious events in our universe, supernova explosions have caught the attention of almost everyone interested in space. These massive explosions are powerful enough to

one of the most glorious events in our universe, supernova explosions have caught the attention of almost everyone interested in space. These massive explosions are powerful enough to destroy everything around them. Given that there are countless stars around us, I’ve always thought about what it would be like for us humans to make such a finale.
First of all, there are two ways a star can become a supernova. The first of these is ours SunThey are stars that have a much greater mass than ours and a much shorter lifespan than other stars. Along with these, white dwarfs in the binary star system can also create supernovae.

For Earth to avoid the harmful effects of a supernova, according to NASA required distance 50 light years. Of course there are some negative effects that will affect Earth at distances over 50 light years, but it seems unlikely that we will survive a nearby supernova explosion at this distance.
For example around the world If a supernova occurs 25 light-years away, our planet will lose all of its atmosphere. and life as we know it disappears. Let’s reassure you on this point: there are no stars near Earth that could cause such an explosion.
Since the Milky Way galaxy contains between 200 and 400 billion stars, you might think that supernovae are very rare explosions. However, if we consider the entire universe, on average It is thought that 30 supernova explosions occur every second. This shows us how big the universe is.
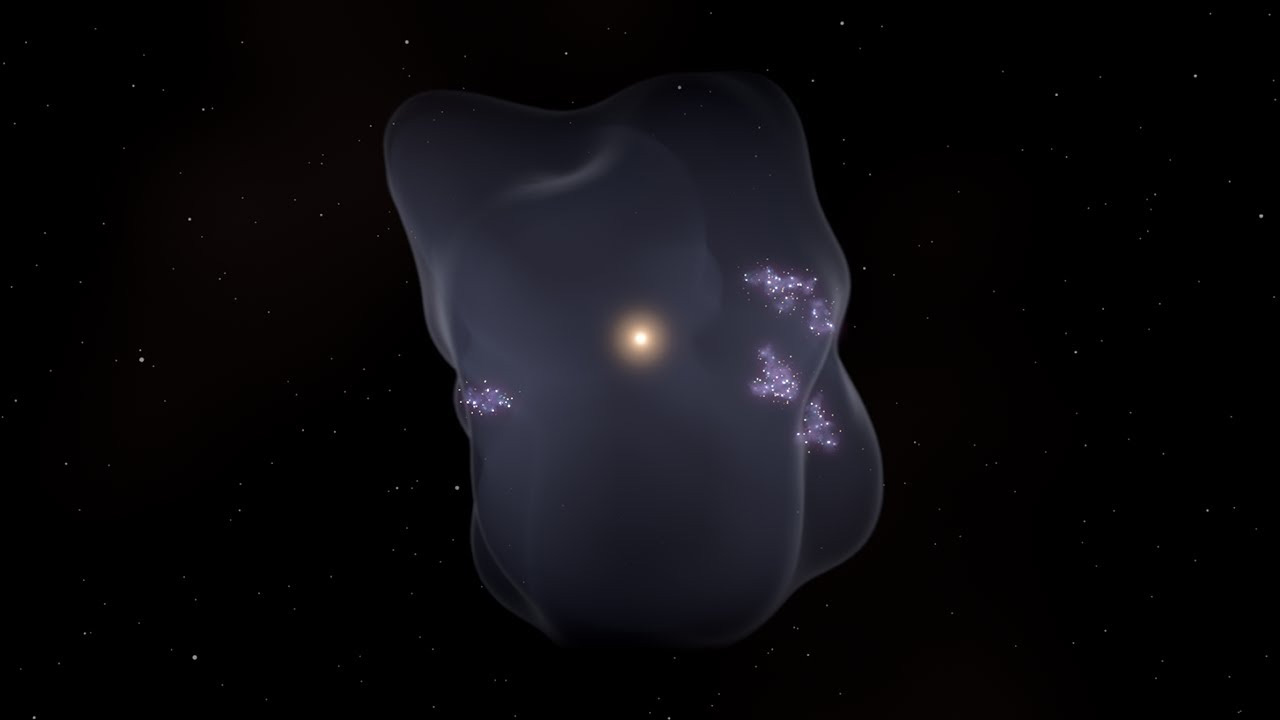
The Local Bubble, an area about 30 light-years across, contains the solar system, to peanuts a special field. This area is believed to have been formed as a result of a supernova explosion as recent as 10 million years ago.
In fact, there are high-energy gases from the supernova around this bubble that protect us by cleaning many things around us. If there is another supernova explosion near us, these gases could come to Earth with the effect of the explosion and increase the amount of high-energy radiation.
Although this explosion was far from us, the consequences were felt. Because of this explosion, which took place 6.5 times further from the danger zone Some iron from the star’s core has reached our planet. We can still see traces of this eruption on the ocean floor.
No supernova in known human history is known to explode within 50 light-years. in 1987 Supernova 1987A A supernova was observed. However, this explosion occurred at a distance of about 168,000 light years from our planet.
Calcium in our teeth, oxygen we constantly need to live, iron in our blood and more. The elements that make up us and everything around us are actually produced in the stars (Anything except hydrogen). Massive stars that go into supernovae, in particular, form heavier elements such as lead, gold and uranium towards the end of their lives, apart from relatively lighter elements such as oxygen.
Then a huge one In the explosion, all these ready-made elements are scattered in the interstellar medium. The elements on our earth, from the gold ring on our finger to carbon, one of the basic building blocks of life, were also produced in a star.

It is reassuring to all humanity that there is no expectation of a supernova explosion that will harm the Earth in the near future. However, it would be really nice to see a supernova explosion with our own eyes. It is unclear exactly when it will explode, but it is expected to become a supernova in the near future. betelgeuse The star is constantly observed. Betelgeuse, which is 642 light-years away, will not harm Earth when it explodes. Of course, the visual feast it creates will be beautiful.
Sources: ESO Supernova, EarthSky, Business Insider
Source: Web Tekno
Ashley Johnson is a science writer for “Div Bracket”. With a background in the natural sciences and a passion for exploring the mysteries of the universe, she provides in-depth coverage of the latest scientific developments.