Humanity is trying to resolve the things it has seen or even seen since the day it came into being, but which it feels exist. As they began to understand what we see and the big things we see, namely space, some scientists and philosophers focused on the little things we can’t see. As we explained in detail in our article here, these little things were atoms and first thoughts about atoms It started in the 5th century BC.
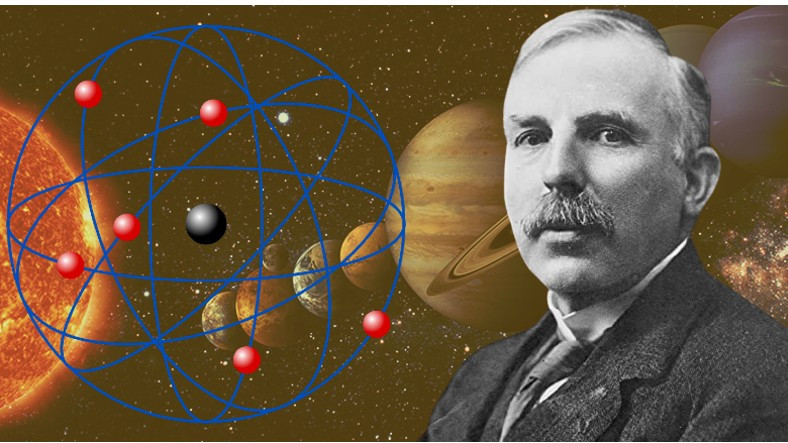
Over thousands of years, many different scientists and philosophers have developed their own models of the atom. Although it has flaws, the Rutherford atomic model is undoubtedly the most interesting. Because this model is very similar to the solar system, including our Earth. Bride What is the Rutherford model of the atom? Let’s take a closer look at its features and shortcomings.
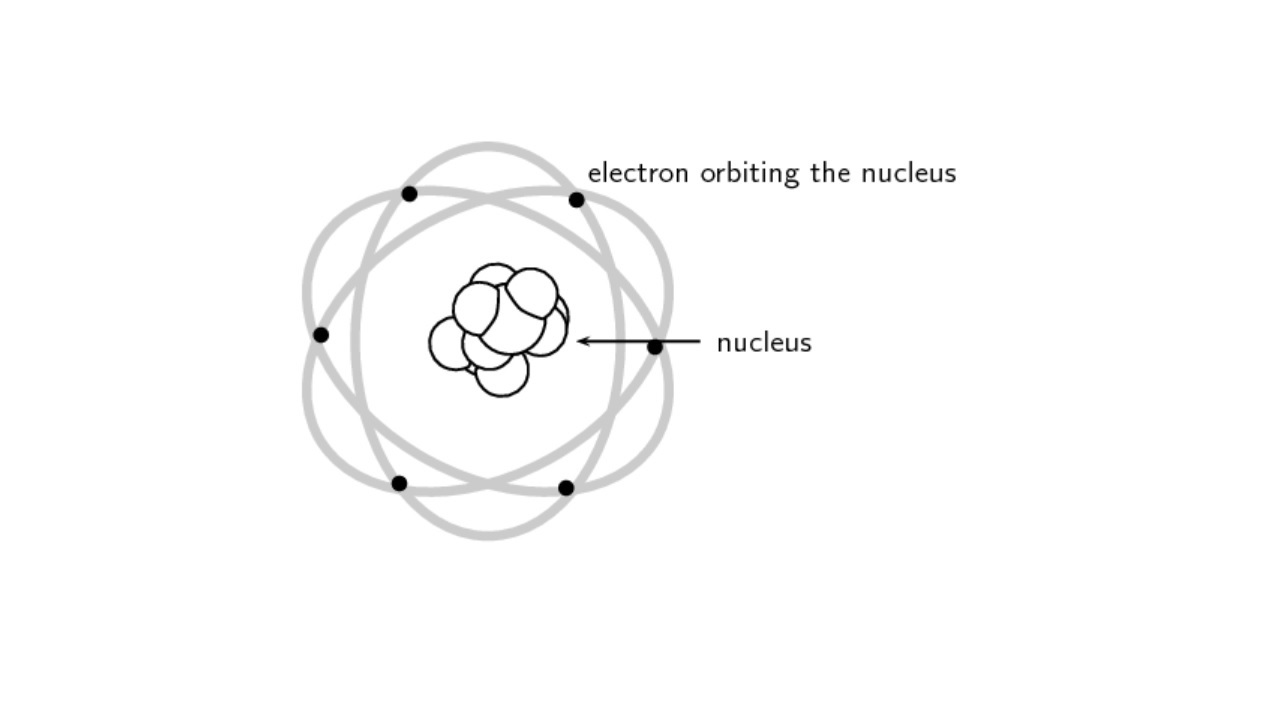
What is the Rutherford model of the atom?
Rutherford’s model of the atom, 1911 New Zealander – British experimental physicist It is a physical model of the atom put forward by Ernest Rutherford. Rutherford, winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1908, revealed this physical model of the atom as a result of his research into the results of his experiments.
During the same period as Ernest Rutherford, many scientists worked on the atom and presented various atomic models. Rutherford’s model of the atom It has quite a few shortcomings like similar models. however, it must be admitted that Rutherford’s atomic model laid the foundation for Bohr’s atomic model and modern atomic theory.
How did the Rutherford model of the atom come about?

Ernest Rutherford, who one day has been working on the atom for years He decided to do another experiment. In this experiment, Rutherford would send particles to a layer and observe their movements. The layer that would be used in this experiment would be gold and the particles would be positively charged.
When the day of the experiment came, Rutherford said… prepared a gold layer with a film on the back. He sent +2 positively charged alpha particles, represented as He+2, to this layer. As the rays hit the plate, Ernest Rutherford studied the path they took and the effects of the impact. The data he obtained as a result of the research was interesting and the Rutherford atomic model emerged.
Features of the Rutherford Atomic Model:
Ernest Rutherford calculated the diameter of the atom as a result of his experiment. managed to calculate with a margin that would be considered very small compared to that period. It was only one that deviated from the 22,000 positively charged alpha particles sent into the gold layer. Deviation is considered normal because we are talking about the early years of the 20th century.
Ernest Rutherford, based on his observations, claimed that the atom is just like the solar system. Accordingly, the nucleus of the atom was positively charged with protons and negative electrons. like planets orbiting the sun they revolved around this core. Rutherford accordingly came to some findings;
- Since most of the rays sent to the gold layer pass directly through, there are large holes in the atom.
- The positive charges in the atom are concentrated in the nucleus because a small portion of the rays are refracted and reflected.
- Since the largest charge is in the nucleus, the atomic mass is also concentrated in the nucleus.
- There are as many negative particles as there are positive particles in any atom.
- Positive particles are concentrated in the nucleus while electrons revolve around the nucleus.
- Since electrons are not collected at one point, they occupy a large portion of the atomic volume.
Shortcomings of the Rutherford model of the atom:
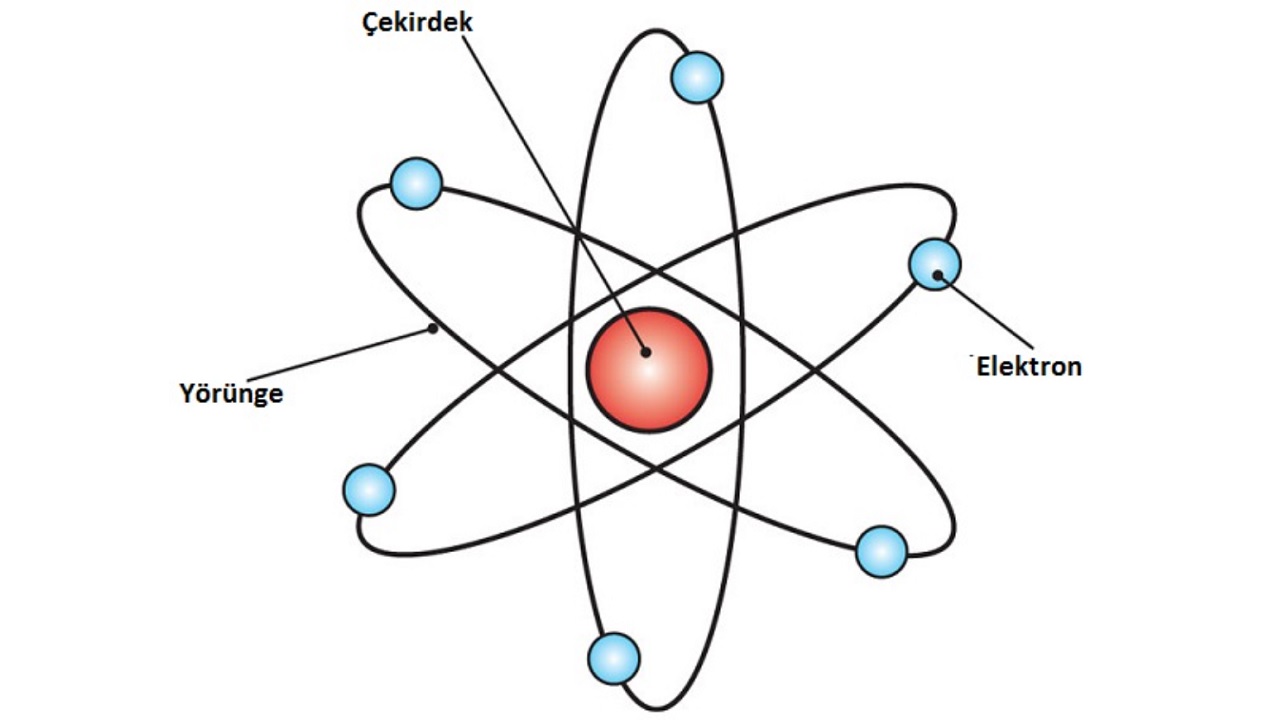
Rutherford’s model of the atom was a very successful physical model for the time. In fact, it inspired many models, but unfortunately it is one of the important building blocks of the atom. did not contain the neutron. Same way Nor could he properly explain the movements of electrons. Simply put, the solar system is also valid in an atom.
The Bohr model of the atom, inspired by the Rutherford atom model:
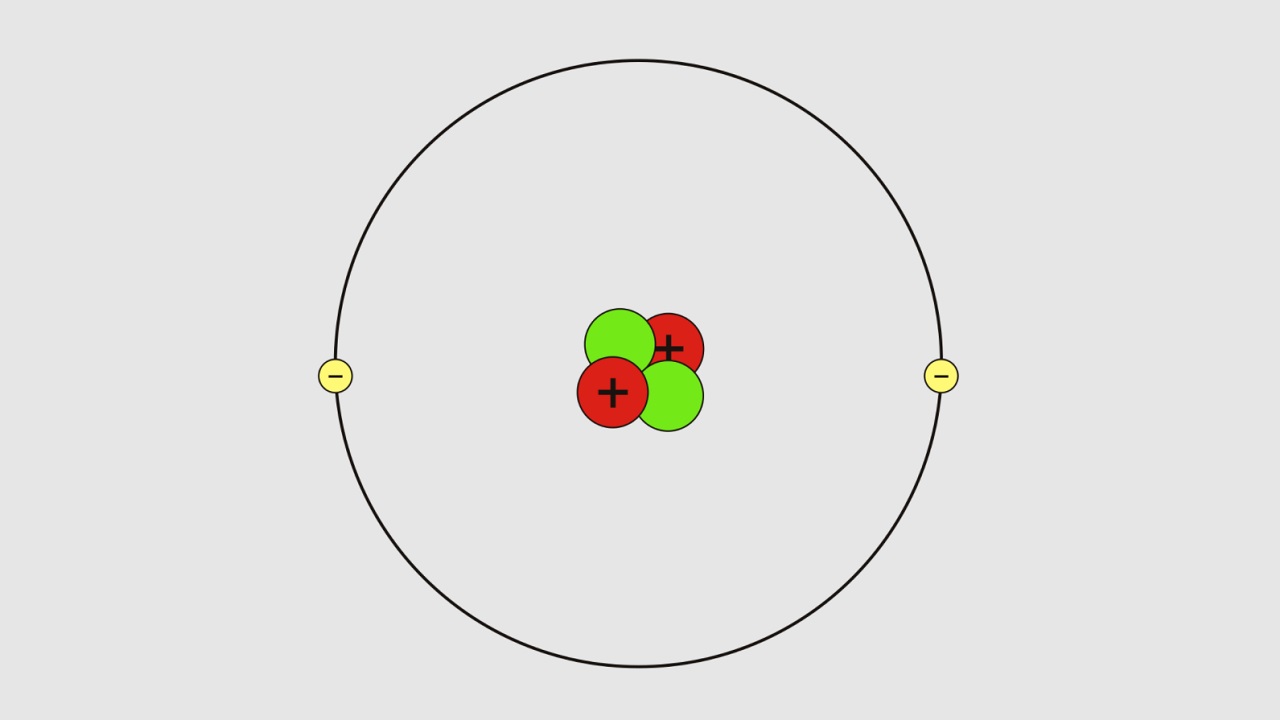
Bohr atomic model, Rutherford atomic model in the same year 1911; Danish physicist who would win the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922 Introduced by Niels Henrik David Bohr. Unlike the Rutherford model of the atom and the theories that preceded it, Bohr studied and explained the movement of electrons in the atom. According to Bohr’s atomic model;
- The steady state of electrons moving at a certain distance from the nucleus has a constant energy.
- The steady movement of electrons draws a circular orbit.
- The electron in a stable state does not emit radiation.
- An electron falling from a high energy level to a low energy level emits an amount of light equal to the varying level difference.
The shortcomings of the Bohr atomic model are as follows;
- He only approached the atom from the framework of classical physics.
- It can only explain atoms with one electron.
- He ignored the duality of waves and particles.
- According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, the definition of orbital that electrons claim to form is incorrect.
- There is no mention of the neutron.
- It is insufficient to explain the bond between atoms and molecules.
While it’s easy to criticize when you look at it today, it was considered quite successful for its period. What is Rutherford’s atomic model, what are its features and what are its shortcomings? We answered frequently asked questions such as: Let us respectfully commemorate all the scientists who have shaped today’s scientific world with their work, albeit incompletely.