Antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which are very likely to infect humans, especially in the hospital setting, can cause serious problems in people with low immunity. Among these bacteriaStaphylococcus aureus”, can cause vital diseases such as pneumonia and sepsis in human skin.
Fighting these bacteria with antibiotics is another threat for the future, as the resistance of the bacteria continues to increase. But the scientific world is against this problem. to develop a solution maybe succeeded.
Some bacteria can be controlled without antibiotics:
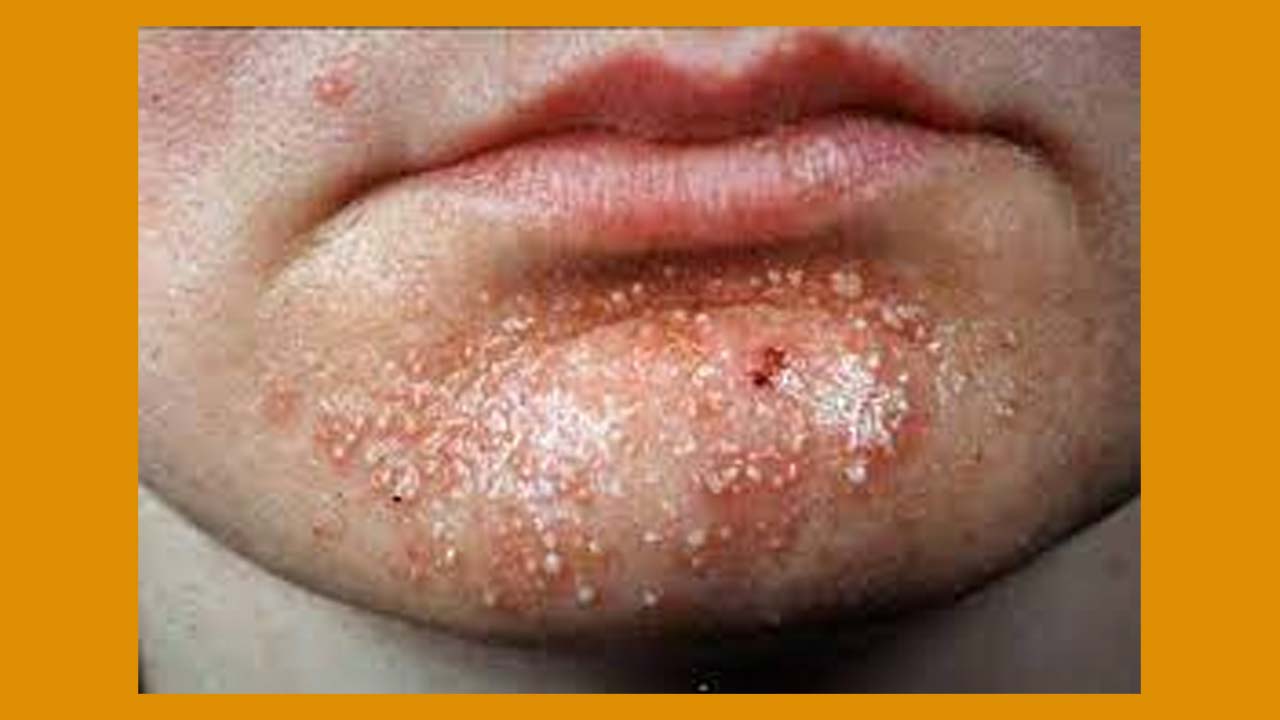
Sensitive image
- Skin infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Scientists at the University of Copenhagen artificially infect bacteria in a laboratory setting and produce enzymes that fight them.. The artificial version of the endolysin enzyme, normally produced by the bacteriophage in our body, has been successfully used against staphylococcus aureus.
The artificial enzyme, called XZ.700, succeeded in blocking its tumor-promoting effects. In this way, the bacteria in the skin samples in the laboratory environment was destroyed and the action of the bacteria that could cause cancer was also disabled.
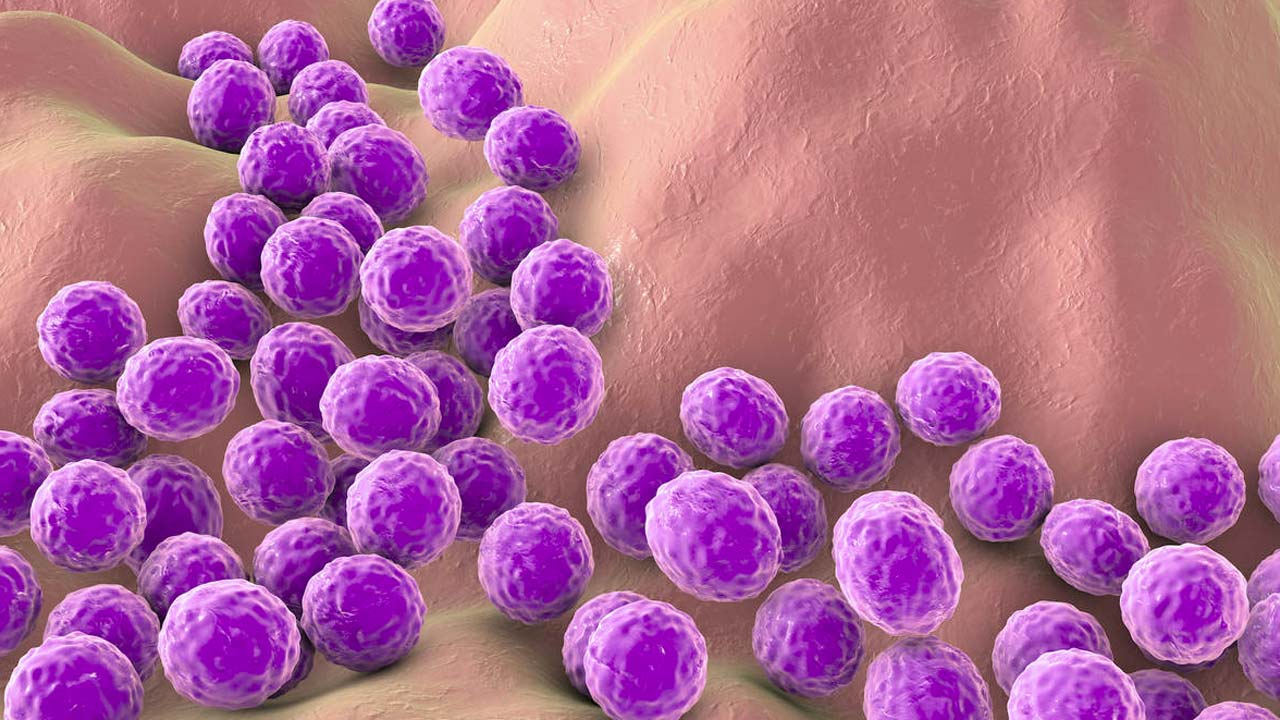
The bacteria destroyed by the enzyme were not actually antibiotic-resistant bacteria. But the success of this bacterium raised great hopes. Scientists use the enzyme in the next step. resistant to antibiotics It also aims to eradicate the methicillin-resistant staphylococcus (MRSA) aureus strain.
On the other hand, there are some missing points in success. Experiments and established conditions in the lab environment may not be enough to produce the same effect against infections and cancer in the real world. Therefore, to see the effect of the artificial endolysin enzyme, more research will be needed.
The scientists shared their research results in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Affordable exchange campaign for those who want to renew their Apple computer