How cold is space: what processes affect the temperature of the universe?
- July 23, 2022
- 0
What is temperature and does it exist in space? Temperature consists of the speed of movement of particles and the energy they emit as they move. Thus, in
What is temperature and does it exist in space? Temperature consists of the speed of movement of particles and the energy they emit as they move. Thus, in

Temperature consists of the speed of movement of particles and the energy they emit as they move. Thus, in a truly empty space there would be no particles and no radiation, and therefore no temperature.
Of course, space is full of particles that radiate energy as they move, thus producing heat and warmth. So how cold is space, is there really an empty region and is there a place where the temperature drops to absolute zero?
The hottest regions of space are located directly around the stars, where all the conditions for nuclear fusion to begin. There, objects get really hot when the star’s radiation reaches a point in space that has particles in large numbers and densities that can be affected by temperature.
Therefore, the Earth is much hotter than the region between our planet and its star. The heat comes from particles in our atmosphere that vibrate with solar energy and then collide with each other, dissipating that energy.

Galaxy cluster RXJ1347 is one of the hottest places in the universe / NASA photo
However, proximity to a star is not always a guarantee of temperature. For example, Mercury is the closest planet to our Sun. It is incredibly hot during the day and very cold at night. Its temperature drops to -178 degrees Celsius.
The temperature of Uranus drops to -224⁰C, making it even cooler than Neptune, the furthest from the Sun. By the way, Neptune is still very cold – its temperature reaches -214⁰C.
This is the result of a collision with an Earth-size object early in planet formation, causing for example to orbit Uranus with an extreme inclination that prevents it from trapping the Sun’s internal heat.
Far from the stars, the particles are so spread out (they are less dense) that heat transfer via anything but radiation is impossible, meaning the temperature drops dramatically. This area is called interstellar space.
Mechanisms of heating the interstellar medium
The cooling mechanisms of the interstellar medium
The coldest and densest clouds of molecular gas in the interstellar medium can have temperatures as low as -263 ⁰C, while less dense clouds can have temperatures as low as -173 ⁰C.
The universe is so vast and filled with so many objects that some are incredibly hot and some are incredibly cold. Therefore, space cannot have a uniform temperature.
At the same time, there is something permeating our entire universe with a temperature equal to one hundred thousandth. In fact, the difference is so small that the difference between the hot spot and the cold spot is only 0.0000018 K.
We’re talking about the cosmic microwave background (CMF), better known as Relic radiation. It has a uniform temperature of 2.7 K (-270⁰C). Since 0 K is absolute zero, this temperature is only 2,725 degrees above absolute zero.
residual radiation It is the remnant of an event that occurred just 400,000 years after the phenomenon known as the Big Bang. Although for proper understanding it should be called the Great Scatter. This is the moment when, after electrons combine with protons to form hydrogen atoms, the universe ceases to be opaque, the electrons stop the endless scattering of light and allow the photons to move freely.
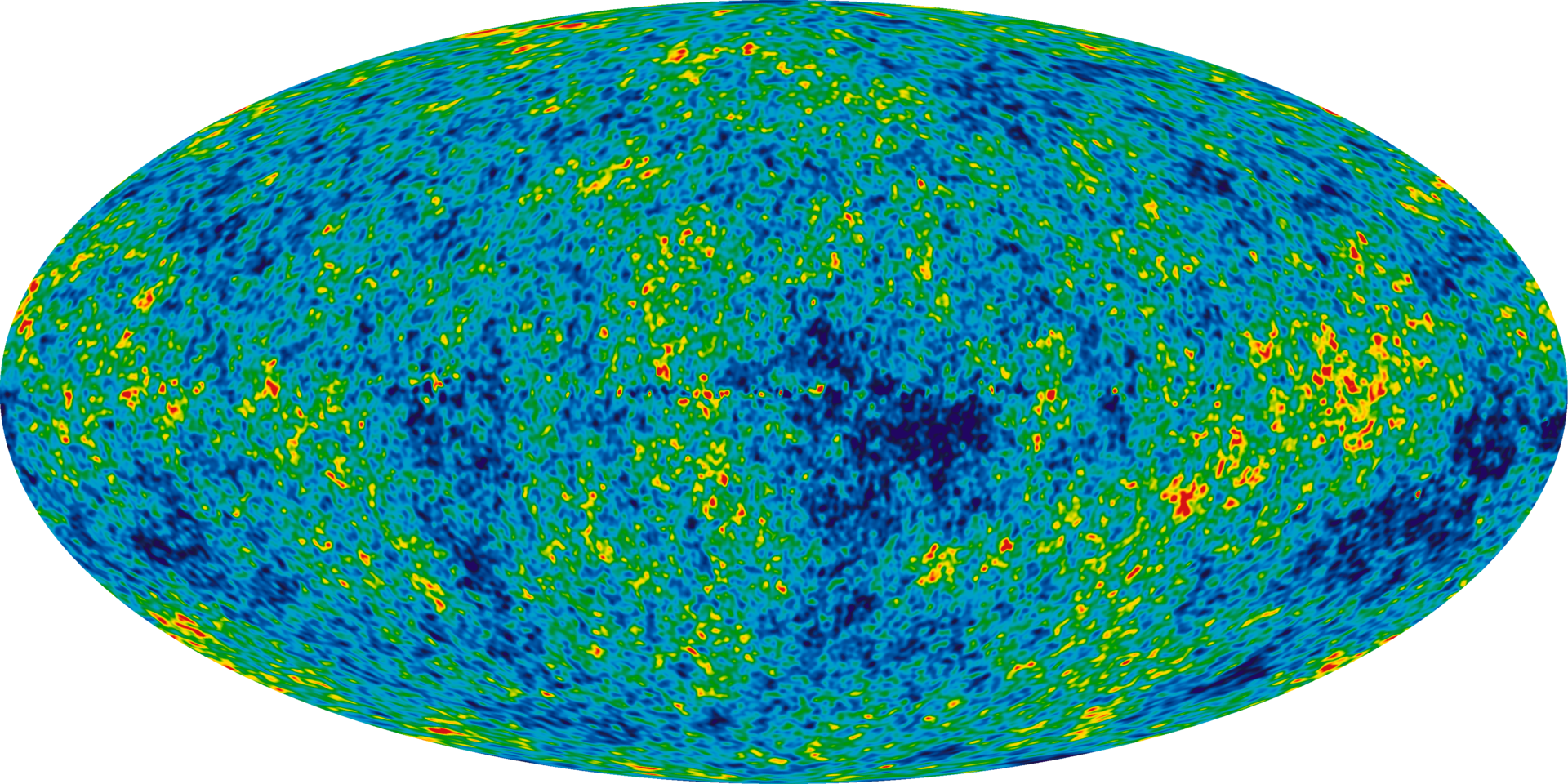
Relic radiation map recorded over 9 years by the WMAP telescope / Photo NASA
Thus, this “frozen” fossil remnant in the universe is the final point at which matter and photons align in terms of temperature.
The photons that make up the residual radiation were not always very cold and took about 13.8 billion years to reach us. The expansion of the universe has redshifted these photons to lower energy levels.
The residual radiation appeared when the universe was much denser and hotter than it is now. Its initial temperature is estimated to be around 2726⁰C. As the universe continues to expand, this means that space is colder than ever and the temperature continues to drop.
If an astronaut were left to drift through space alone, the effects of the near-emptiness of space could not freeze the astronauts as is often portrayed in science fiction.
There are three methods of heat transfer:
Since there is no matter in empty space, conduction and convection cannot occur, and heat transfer takes place only slowly through radiation processes. This means that heat is not transferred quickly in space.
Because freezing requires heat transfer, an irradiated astronaut—who only loses heat through radiative processes—will die much sooner than he would freeze to death from decompression due to a lack of atmosphere.
Source: 24 Tv
I’m Maurice Knox, a professional news writer with a focus on science. I work for Div Bracket. My articles cover everything from the latest scientific breakthroughs to advances in technology and medicine. I have a passion for understanding the world around us and helping people stay informed about important developments in science and beyond.