Italian scientist, known for his research and inventions from his time to the present, one of the greatest artists and geniuses someone. In addition to his well-known works such as The Vitruvian Man, The Last Supper and Mona Lisa, he also has works about the human body and nature.
Well, the scientist who made a very striking discovery about trees, of this discovery between the trunk and branches of trees. What lay behind the scenes?
In the 1400s and early 1500s, interest in and research on trees and other landscapes in art and in most areas of life was extremely rare.
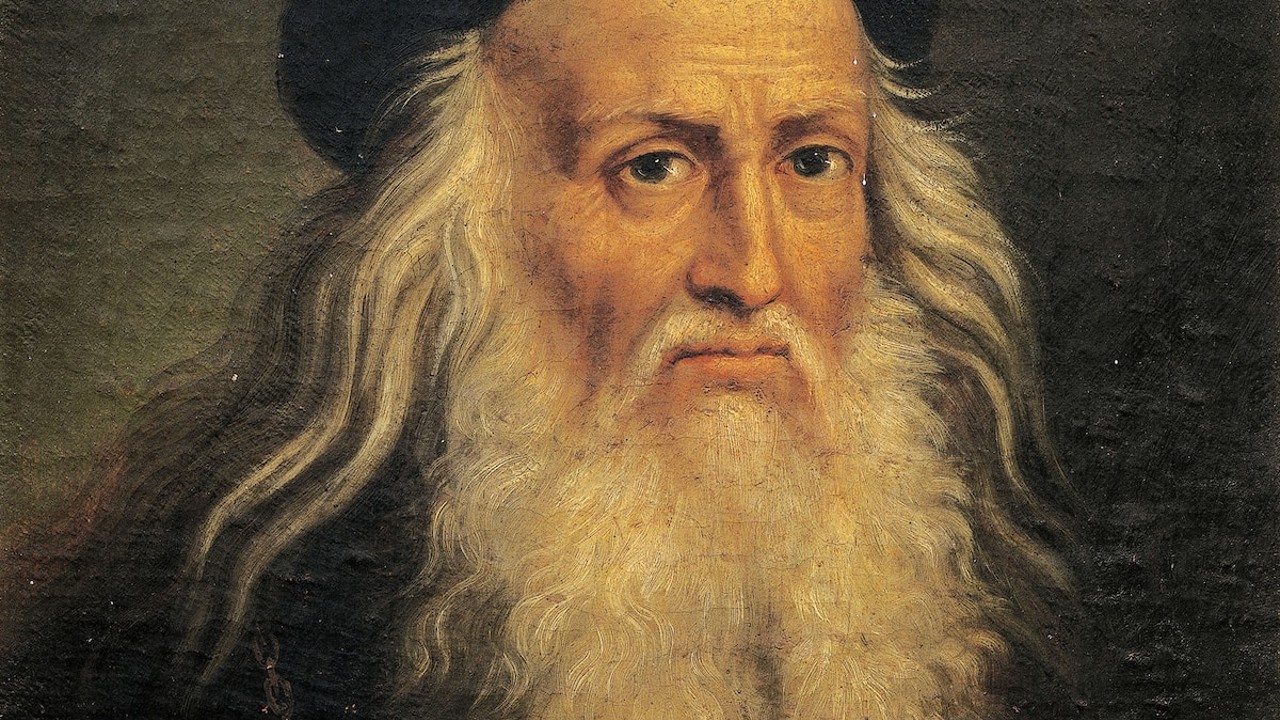

by Leonardo da Vinci his interest in tree anatomy It was extraordinary for its time. This da Vinci discovery made the scientific qualities and relationships in paintings seem much more dimensional and realistic.
Researchers believe that Leonardo’s rule is for today’s scientists. good start agreed.
More than 500 years ago, Leonardo da Vinci, a master of Renaissance art and science, made a very interesting observation about trees.
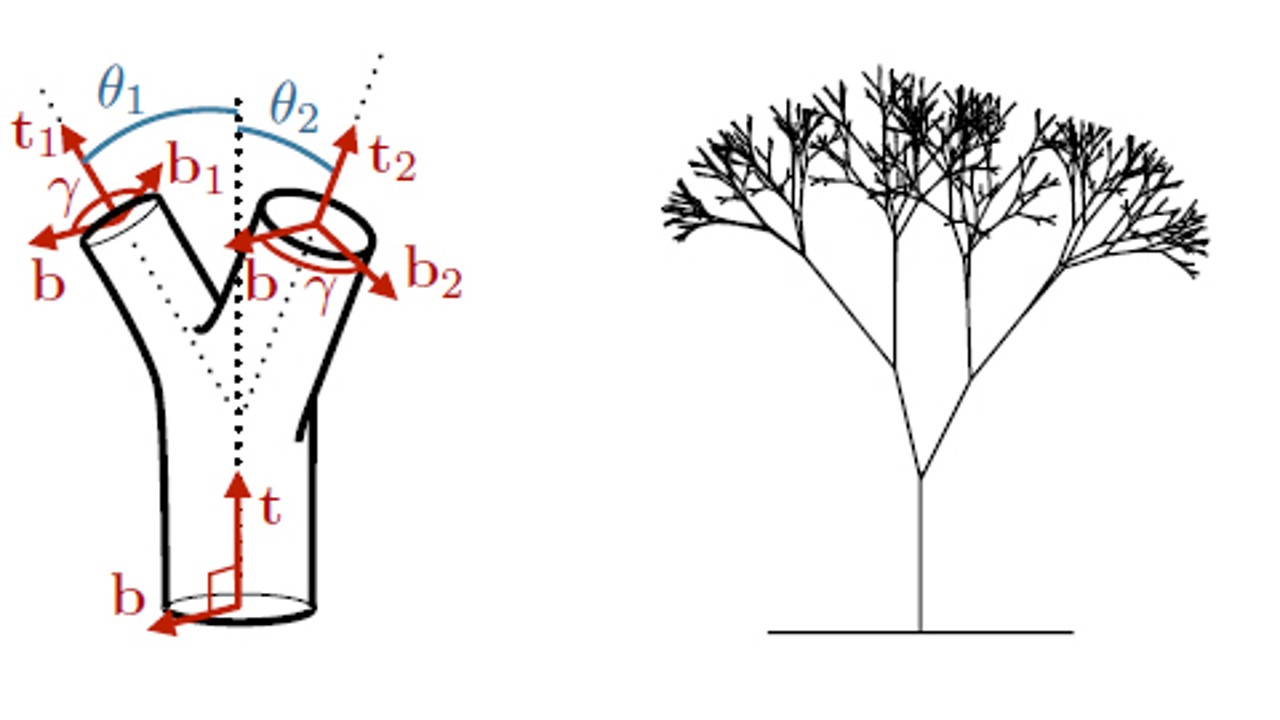
The famous scientist stated that trees show a universal growth pattern and a relationship between the tree trunk and the size of its branches realized it was.
Da Vinci, trying to express this discovery in a detailed way in his notebook, expressed his work with the sentence “If all the branches of a tree are brought together at any stage of its height, its thickness is equal to the thickness of the trunk.”

In other words, assuming the branches of the tree are brought together and tied to the end of the trunk, a columnar image was on the rise.
According to a recently published study on Leonardo’s discovery, this is because it is used to protect itself from the damaging effects of wind. a self-developed characteristic of the tree it was.
Physicist Christophe Eloy, who designs complex branch patterns in a computer environment, investigated how the rule proposed by Leonardo came about.

A program in which it repeatedly adds smaller copies of large branches to create a virtual tree. with fractal tree skeleton Eloy, who started his experiment, made sure that even the lightest trees have strong trunks that can withstand the wind.
model tree testing in a virtual wind tunnel After calculating the wind force that could break the branches, the researcher also worked on how thick the branches should be.
At the end of this test, the thickness calculated for each section from the smallest branch to the trunk, In accordance with Leonardo’s rule he saw it.
Discussions on the topic were basically divided into two categories, “Hydrological and Structural” theory.

hydrological theorywhile arguing that the characteristic shape of trees evolved for the purpose of reaching the water from their roots to their branches; Supported by Eloy structural theorysuggested that the shape of the trees evolved to achieve the goal of survival.
To measure Leonardo’s experiment, physicist Grigoriev and his colleagues took pictures of trees of different species and analyzed these branches.
Verify that real-world models match hypotheses Although Grigoriev and his team have not yet studied evergreen trees, they found that this rule applies to all deciduous trees, as the researchers examined.
In addition to oak, chestnut and birch trees, the famous physicist continued his research. maple, lime and apple trees added, he found that the same general structure was confirmed.
- Sources: Inside Science, Medium, Science News